Kerberos unconstrained delegation
10 minute read
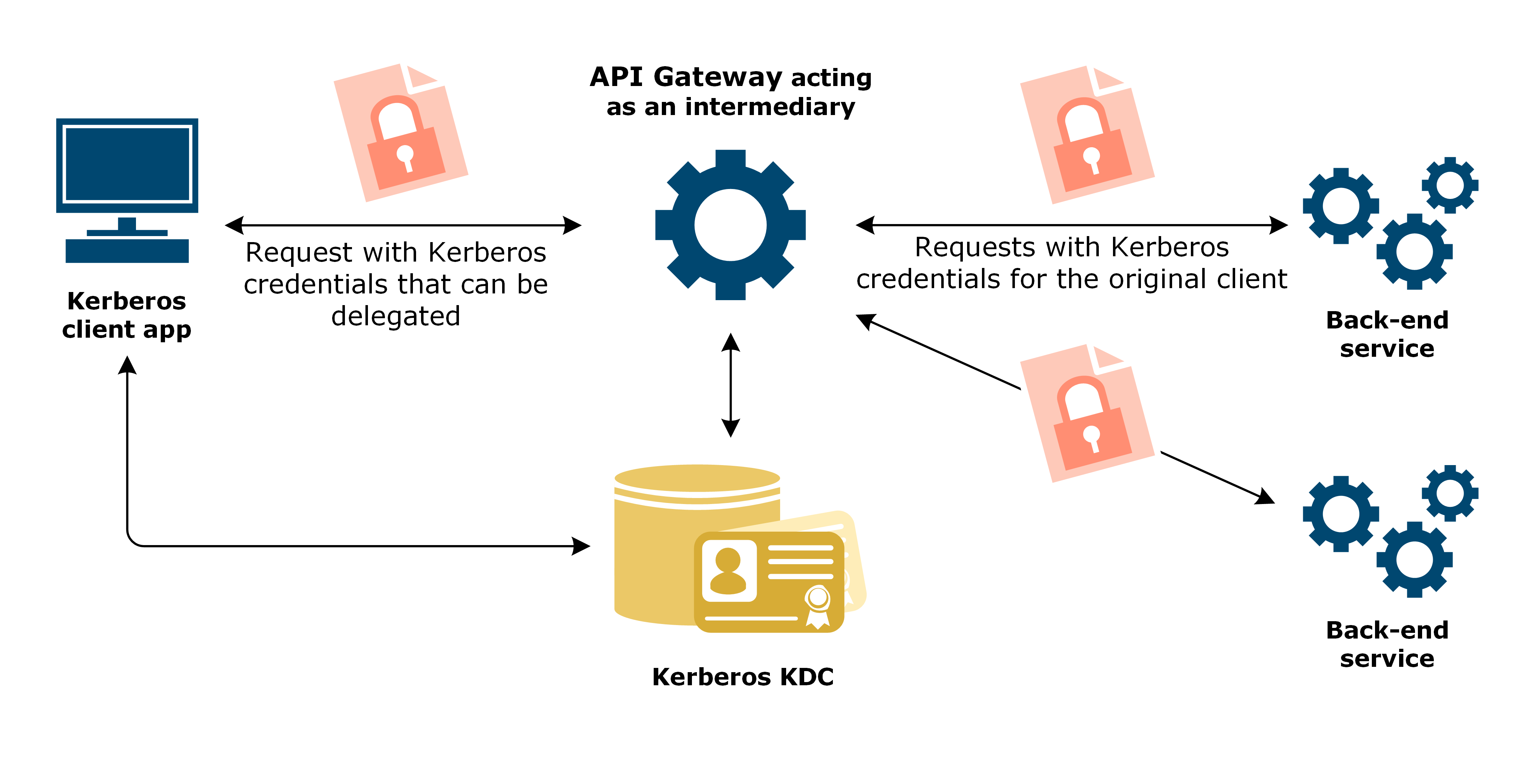
When authenticating to API Gateway using Kerberos, a client application can delegate its Kerberos credentials to API Gateway. API Gateway acts as an intermediary between a Kerberos client and Kerberos back-end services, and requests service tickets to any other Kerberos service in the same Kerberos realm on behalf of the client. These service tickets can then be used to authenticate the original end user to the other Kerberos services. This type of Kerberos delegation is often called unconstrained or open.
In this scenario:
- Client application: Supports Kerberos authentication.
- Back-end service: Requires Kerberos authentication with the end user’s credentials. Multiple back-end services may exist.
- API Gateway: Acts as both a Kerberos service and client, and authenticates to different back-end services as the end user.
API Gateway receives a request from the Kerberos client containing a SPNEGO token with the credentials to be delegated (the Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT)). The token also contains a service ticket that allows the Kerberos client to authenticate to API Gateway that is itself acting as a Kerberos service.
Using Kerberos authentication, API Gateway authenticates the Kerberos client. API Gateway then requests a service ticket to the back-end Kerberos service on behalf of the client, and authenticates to the back-end service as the original end user. The client application itself does not need to have any knowledge of any of the back-end services that API Gateway might invoke on its behalf.
A safer method for credentials delegation in Kerberos authentication is constrained delegation. In constrained delegation with protocol transition, the Kerberos service can obtain a Kerberos service ticket to itself on behalf of a Kerberos principal (end user) without requiring the principal to initially authenticate using Kerberos. Constrained delegation also restricts which back-end services the Kerberos service can request Kerberos service tickets on behalf of the client. The credential delegation is only allowed to a constrained set of Kerberos services that are configured in the Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC). For more details, see API Gateway in Kerberos constrained delegation.
Prerequisites
Before you start configuration, you must have API Gateway installed on any machine with access to the Windows Domain Controller. The machine does not have to be a Windows machine that is part of the Windows Domain.
Example names
The example name for the intermediary Kerberos service used in this guide is IntermediaryGateway.
The example Kerberos realm name AXWAY.COM is specific to the examples in this guide. Replace the example realm name with your own realm name.
The next sections describe the steps to configure the gateway in unconstrained credentials delegation.
Configure Active Directory
This section describes how to configure a Kerberos service principal for API Gateway in Active Directory acting as the Key Distribution Center (KDC).
-
On the Windows Domain Controller, click Control panel > Administrative Tools > Active Directory User and Computers.
-
Right-click Users, and select New > User.
-
Enter a name for the Kerberos principal (such as
IntermediaryGateway) in the First Name and User Logon Name fields, select your Active Directory domain from the drop-down menu (@axway.com), and click Next. -
Enter the password, and do the following:
- User must change password at next logon: Deselect this.
- User cannot change password: Select this.
- Password never expires: Select this.
This ensures that a working API Gateway configuration does not stop working when a user chooses, or is prompted to change their password. API Gateway does not track these actions.
If these options are not suitable in your implementation and a user password changes in Active Directory, you must then update the password or keytab of the Kerberos client or service related to the user in Policy Studio, and redeploy the configuration to API Gateway. If you cannot deselect User must change password at next logon, ensure the user changes the password and that the new password or keytab is deployed to API Gateway before API Gateway attempts to connect as this user.
You can store Kerberos passwords in a KPS table to update a changed password in runtime. For more details, see Use KPS to store passwords for Kerberos authentication.
-
Click Next > Finish.
-
Map a Service Principal Name (SPN) to the user account. The Kerberos client uses the SPN to uniquely identify a service. To map the SPN, open a command prompt on the Windows Domain Controller, and enter the following command:
ktpass -princ HTTP/<host>@<Kerberos realm> -mapuser <user> -pass password -out <user>.keytab -crypto rc4-hmac-nt -kvno 0The SPN is of the format
HTTP/<host>@<Kerberos realm>, where<host>is the name of the host running the Kerberos service,IntermediaryGatewayin this case:ktpass -princ HTTP/IntermediaryGateway.axway.com@AXWAY.COM -mapuser IntermediaryGateway -pass Axway123 -out IntermediaryGateway.keytab -crypto rc4-hmac-nt -kvno 0Replace the example Kerberos realm name with your own realm name. Note that the realm name is uppercase.
The command creates an SPN
HTTP/IntermediaryGateway.axway.com@AXWAY.COM, which is mapped to theIntermediaryGatewayuser account. The command also creates a keytab file for the account that you can use later when configuring a Kerberos service for API Gateway in Policy Studio. See Configure API Gateway policy.If you do not want to create a keytab file, you can use the following command:
setspn -A HTTP/<host> <user>As a Kerberos service, API Gateway authenticates the client application using Kerberos authentication. For the authentication to succeed, the client application or end user must also have an account configured in your Active Directory. For an example configuration for the client account, see Configure a user account in Active Directory. You must also configure user accounts and Service Principal Names (SPN) for the back-end services you want API Gateway to request service tickets for.
-
Right-click on the new user, and select Properties > Delegation. Then, select the Trust this user for delegation to any service (Kerberos only) option.
This is required for the API Gateway to extract delegated credentials when using unconstrained delegation where the client is the browser.
Configure Kerberos principals
This section describes how to add Kerberos principals for the intermediary Kerberos service, and back-end Kerberos service for unconstrained credentials delegation using Policy Studio.
- In the node tree, click Environment Configuration > External Connections > Kerberos Principals.
- Add a new Kerberos principal for the intermediary Kerberos service account as follows:
- Name:
IntermediaryGateway - Principal Name:
IntermediaryGateway@AXWAY.COM - Principal Type:
NT_USER_NAME
- Name:
- Add a new Kerberos principal for the back-end Kerberos service account as follows:
- Name:
<Back-end service name>(for example,Back-end Kerberos Service) - Principal Name:
<Service Principal Name for the back-end service>(for example,HOST/BackEndService.axway.com@AXWAY.COM) - Principal Type:
NT_USER_NAME
- Name:
For more details on the fields and options in this configuration window, see Configure Kerberos principals.
Configure API Gateway policy
This section describes for unconstrained credential delegation using Policy Studio.
Configure an intermediary Kerberos service
- In the node tree, click Environment Configuration > External Connections > Kerberos Services.
- Click Add a Kerberos Service, and enter a name for your Kerberos service (
IntermediaryGateway Kerberos Service for Unconstrained Delegation). - On the Kerberos Endpoint tab, set the following:
- Kerberos Principal:
IntermediaryGateway. - Enter Password: Enter the password for
IntermediaryGateway@AXWAY.COM. - Enabled: Select this option.
- Kerberos Principal:
- On the Advanced tab, set the following:
Mechanism:
SPNEGO_MECHANISM. Extract delegated credentials: Select this option.
Selecting Extract delegated credentials means that API Gateway extracts the Kerberos client’s TGT from the SPNEGO token after the client has been authenticated. API Gateway can then use the TGT to request service tickets to other Kerberos services on behalf of the Kerberos client. For more details on the fields and options in this configuration window, see Configure Kerberos services.
Configure a Kerberos client for the delegated credentials
- In the node tree, click Environment Configuration > External Connections > Kerberos Clients.
- Click Add a Kerberos Client, and enter a name for your client (
Kerberos Client for Unconstrained Delegation). - On the Kerberos Endpoint tab, set the following:
- Load from delegated credentials: Select this option.
- Enabled: Make sure this option is selected.
- On the Advanced tab, set the following:
- Mechanism:
SPNEGO_MECHANISM. - Context Settings: Select the following options:
- Mutual authentication
- Integrity
- Confidentiality
- Anonymity
- Replay Detection
- Sequence Checking
- Synchronize to Avoid Replay Errors at Service: Deselect this option to improve performance.
- Refresh when remaining validity is
<value>seconds: Set to300.
- Mechanism:
For more details on the fields and options in this configuration window, see Configure Kerberos clients.
Configure a Kerberos profile for the intermediary Kerberos service
- In the node tree, click Environment Configuration > External Connections > Client Credentials > Kerberos.
- Add a Kerberos profile as follows:
- Profile Name:
Authenticate to Back-End Service using Delegated Credentials. - Kerberos Client:
Kerberos Client for Unconstrained Delegation. - Kerberos Service Principal:
<Back-end Kerberos Service>. - Send token with first request: Select this option.
- Profile Name:
Configure an intermediary policy
The following section describes how to configure the policy for API Gateway delegating the credentials.
To start, add a new policy named, for example, Kerberos Intermediary for Unconstrained Credentials Delegation.
Configure a Kerberos service filter
- Open the Authentication category in the filter palette, and drag a Kerberos Service filter onto the policy canvas.
- Set Kerberos Service to the intermediary Kerberos service you created (
IntermediaryGateway Kerberos Service for Unconstrained Delegation). - Change Kerberos Standard to SPNEGO Over HTTP, and click Finish.
- Right-click the Kerberos Service filter, and select Set as Start.
Configure retrieving the end user credentials
- Open the Attributes category in the palette, and drag a Retrieve from HTTP Header filter onto the policy canvas.
- Set the HTTP Header name to
WWW-Authenticateand Attribute ID toouter.www.authenticate, and click Finish. - Open the Conversion category in the palette, drag a Remove HTTP Header filter onto the policy canvas.
- Set HTTP Header Name to
WWW-Authenticate.
Configure authentication to the back-end service
- Open the Routing category in the palette, and drag a Connect to URL filter onto the canvas.
- Enter the URL used to invoke the back-end Kerberos service.
- On the Authentication tab, select the Kerberos profile you configured (
Authenticate to Back-End Service using Delegated Credentials), and click Finish.\ - Open the Conversion category in the palette, and drag an Add HTTP Header filter onto the policy canvas.
- Set the following, and click Finish:
HTTP Header Name:
WWW-Authenticate. HTTP Header Value:${outer.www.authenticate}. Override existing header: Select this option. Add header to HTTP headers attribute: Select this option. - Open the Utility category in the palette, and drag a Reflect Message filter onto the canvas.
Build the policy
-
Click on the Add Relative Path icon to create a new relative path
/intermediarythat links to this policy. -
Connect the filters with success paths.
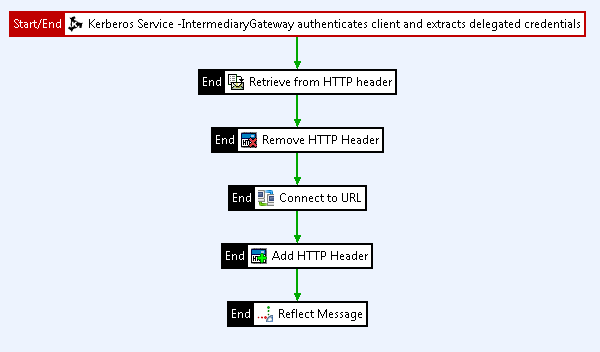
The policy has the following flow:
- API Gateway receives a request from the end user, and uses the Kerberos token in the
AuthorizationHTTP header to authenticate the end user. - API Gateway extracts the value of the
WWW-AuthenticateHTTP header and saves the value to a message attribute, so it can be reinstated later. This token is the response to the original token the end user sent. - API Gateway retrieves a service ticket for the end user to access the back-end Kerberos service, connects to the back-end Kerberos service, and authenticates using the Kerberos credentials relating to the original end user.
- API Gateway reinstates the value of the
WWW-AuthenticateHTTP Header, overriding the value the back-end Kerberos service set. - API Gateway sends the response to the Kerberos client.
Configure Kerberos system settings
-
In the node tree, click Environment Configuration > Server Settings > Security > Kerberos, and click Add Kerberos Configuration.
-
On the krb5.conf tab, add the Kerberos settings as follows:
[libdefaults] default_realm = AXWAY.COM [realms] AXWAY.COM = { kdc = dc.axway.com }Replace the realm settings in the example code with your Kerberos realm, and set the
kdcsetting to the host name of your Windows Domain Controller.
Deploy the configuration
To deploy the configuration to API Gateway, click the Deploy icon.
You have now configured and deployed a policy for the authenticating Kerberos service on API Gateway that delegates the SPNEGO credentials to the back-end Kerberos service. The client application calls the policy on relative path /intermediary.
For demonstration purposes, you may want to add API Gateway as the client application and the back-end service. For example configurations, see Demo setup: API Gateway as both Kerberos client and service. When configuring API Gateway as the client application for credentials delegation, the setting forwardable on the krb5.conf tab in the Kerberos system settings must be true:
[libdefaults]
default_realm = AXWAY.COM
forwardable=true
[realms]
AXWAY.COM = {
kdc = dc.axway.com
}
Test the configuration
Use a client application to call the policy in API Gateway.
The back-end Kerberos service should send a confirmation on a successful authentication.
The Traffic Monitor tab on the API Gateway Manager (https://localhost:8090) is an excellent place to view and troubleshoot the message flows. For more details, see Monitor services in API Gateway Manager.