Configure Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
9 minute read
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) enables you to restrict system access to authorized users based on their assigned roles. Using the RBAC model, permissions to perform specific system operations are assigned to specific roles, and system users are granted permission to perform specific operations only through their assigned roles. This simplifies system administration because users do not need to be assigned permissions directly, and instead acquire them through their assigned roles.
The API Gateway uses the RBAC permissions model to ensure that only users with the assigned role can access parts of the management services exposed by the Admin Node Manager. For example, this includes access to traffic monitoring data or making a configuration change by deploying to a group of API Gateways. The following diagram shows an overview of the RBAC model in the API Gateway:
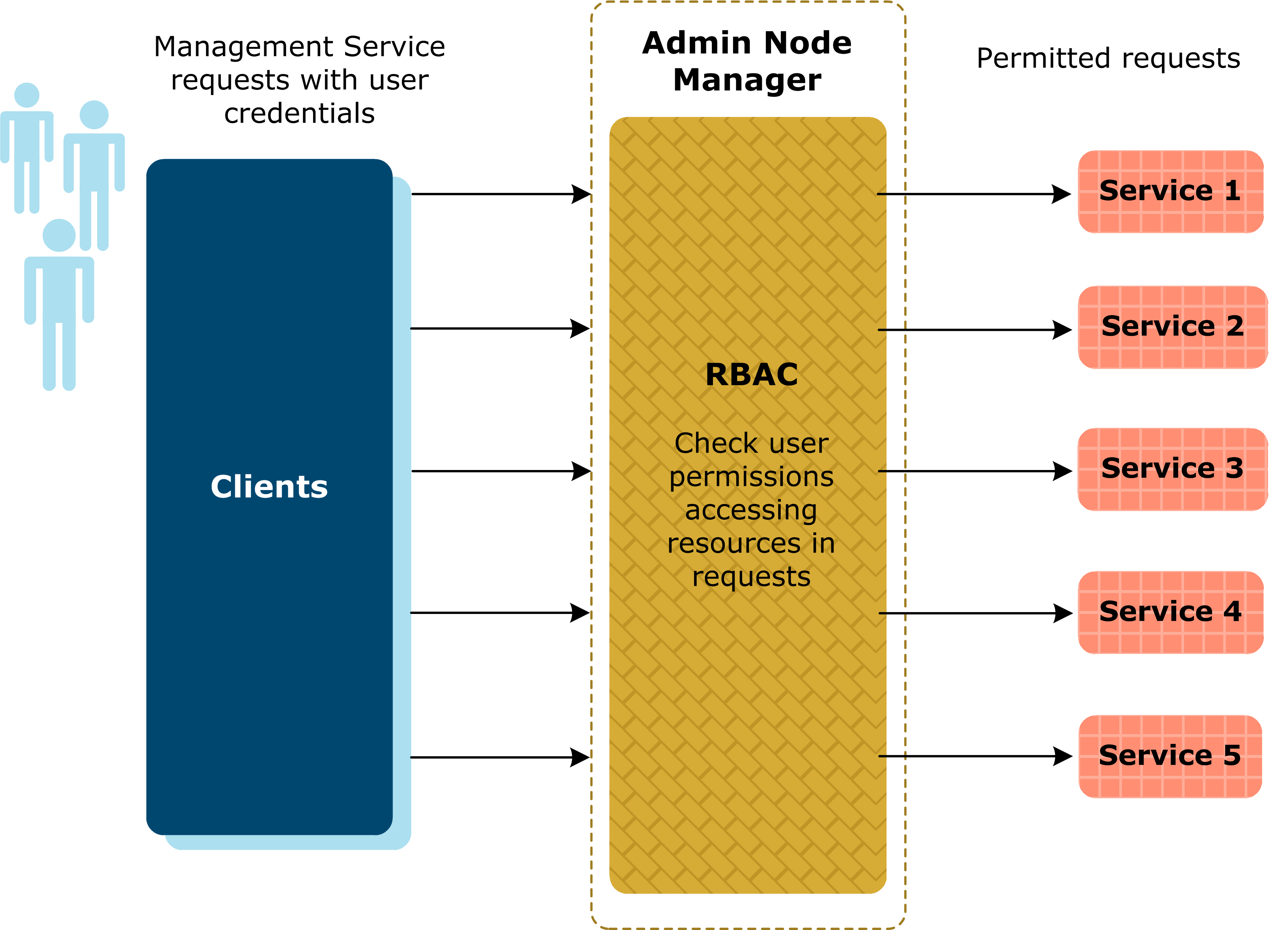
API Gateway Manager
The web-based API Gateway Manager tool (https://localhost:8090) is a centralized dashboard for managing and monitoring the gateway, and is controlled by RBAC. Users connecting to this URL with different roles results in different features being displayed.
For example, users with the API Server Administrator role has read/write access in the API Gateway Manager tool. However, users in the API Server Operator have only read access in the API Gateway Manager tool.
For more details on the tools and privileges assigned to specific user roles, see Manage Admin users.
Protected management services
The Admin Node Manager exposes a number of REST management services, which are all protected by RBAC. For example, the exposed services and the associated tools that use them include the following:
| Protected Service | Tool | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Traffic Monitoring Service | API Gateway Manager | Displays HTTP, HTTPS, JMS, and FTP message traffic processed by the API Gateway. |
| Configuration Service | API Gateway Manager | Adds and removes tags on the API Gateway. |
| Topology API | API Gateway Manager | Accesses and configures API Gateway domains. |
| Static Content Resources | API Gateway Manager | Manages UI elements in a browser. |
| Deployment API | Policy Studio | Deploys configurations to the API Gateway. |
| KPS Service | Policy Studio | Manages a Key Property Store. |
RBAC user roles
User access to management services is determined by their roles. Each role has a defined set of management services that it can access. A Management Service is defined by the URI used to access it, for example:
Role Name: API Server Operator
Service Name: Topology API
API Type: REST
Example URI: /api/topology/hosts
For full details on the default roles that have access to each Management Service, see Management service roles and permissions.
Local admin user store
By default, all the user credentials are stored in a local admin user store in the following file:
INSTALL_DIR/conf/adminUsers.json
INSTALL_DIR is the directory where API Gateway is installed as Admin Node Manager.
The following shows an example file:
{
"productVersion" :"7.7",
"version" :1,
"timestamp" :0,
"adminUsers" :[ {
"id" :"user-1",
"name" :"admin",
"roles" :[ "role-1", "role-6", "role-7" ]
} ],
"credentials" :{
"user-1" :"$AAGQAAAAAQAC$DxlhcXQ2FTZ3mjErhGDEEQ==$0/hQdegidtOyrX2QuUnmEWIzknx4bsf0iPr3HydpbyY="
},
"adminUserRoles" :[ {
"id" :"role-1",
"name" :"API Server Administrator"
}, {
"id" :"role-2",
"name" :"API Server Operator"
}, {
"id" :"role-5",
"name" :"Deployer"
}, {
"id" :"role-6",
"name" :"KPS Administrator"
}, {
"id" :"role-7",
"name" :"Policy Developer"
} ],
"uniqueIdCounters" :{
"Role" :8,
"User" :2
},
"adminUsersVersion" :{
"version" :1,
"timestamp" :0
}
}
The credentials from this file are used to authenticate and perform RBAC on all accesses to the management services. This store holds the user credentials, so their passwords can be verified, and also holds their roles. Credentials and associated roles can also be retrieved from an LDAP Directory Server (for example, Microsoft Active Directory or OpenLDAP).
Admin user password storage algorithm
Admin user passwords are in stored in the adminUsers.json file as a base64-encoded salted hash of the plaintext password. To authenticate a user password, the incoming password value is digested in the same way, and compared against the value in the file. If they match, the user is authenticated.
The salt is a 16 byte value generated using the SHA1PRNG pseudo-random number generator algorithm. This algorithm is provided by the Java Cryptography Extension (JCE) and is PBKDF2 with HMAC SHA2. The algorithm repeats the digest of the password along with the salt for 102400 iterations. The salt is stored with the digest allowing for password verification in the following format:
<version-value>$<salt-value>$<password-digest>
For example:
AAGQAAAAAQAC$DxlhcXQ2FTZ3mjErhGDEEQ==$0/hQdegidtOyrX2QuUnmEWIzknx4bsf0iPr3HydpbyY=
Because the salt is generated each time a password is stored, the same plaintext password will have a different salt and digest value. For example, the following stored passwords are all digests of the default password:
AAGQAAAAAQAC$qqlNVeQ6eAGnBDK0VcU1oQ==$uzK6wvSLjVTdO0/qP9I4d72P6yRG1XbI3KRQIPpZjwA=
AAGQAAAAAQAC$mJbacNzCfoeJ1Ukixyj/xw==$hw7uwm5/D/7HIKKH4mUoM76xnYvqOSDfucKI0U9yndk=
AAGQAAAAAQAC$a3EP3mKkWpJm4flYacTtnQ==$Czke56xcmk9xbjw+KZhi26jpPoXV7fgE0CWp4WBz9kg=
Configure an LDAP repository to store credentials
Alternatively, for details on how to configure an LDAP repository to store user credentials, see the following topics:
- Active Directory for authentication and RBAC of management services
- OpenLDAP for authentication and RBAC of management services
RBAC access control list
The access control list file (acl.json) is located in the conf directory of your API Gateway installation. This file lists each role and the management services that each role may access. By default, this file defines the following roles:
API Server AdministratorAPI Server OperatorDeployerKPS AdministratorPolicy Developer
The default admin user is assigned the API Server Administrator, KPS Administrator, and Policy Developer roles by default, which together allow access to everything. For full details on the management services that each role has access to, and the permissions that must be listed in the acl.json file to have access to them, see Management service roles and permissions.
Note
The roles defined in theacl.json file should exist in the user store used to authenticate the users and load their roles and groups. The default roles are defined in the local Admin User store, which is used to control access to the management services using the Protect Management Interfaces policy.
If a different user store is used (for example, an LDAP repository), the LDAP groups should be listed in the acl.json and adminUsers.json files.
Access control list file format
Each role entry in the acl.json file has the following format:
"role-name" :[ <list_of_permission_names>]
The permissions consist of operations that are defined by HTTP methods and URIs:
“permission-name” : { <list_of_operation_names }
“operation-name” : {
"methods" :[ <list of HTTP Methods>],
"paths" :[ <list of path-names>]
}
“path-name” : {
"path" :<URI>
}
This file entry format is described as follows:
- The permissions line is repeated for each permission the role has. To determine which permissions should be listed for each Management Service, see Management service roles and permissions.
- You can place a wildcard (
*) at the end of thepathfield. For example, see the path fordojo resourcesin the example that follows. This means the role has access to all URIs that start with the URI content that precedes the*. - In some cases, you must protect a Management Service by specifying a query string after the URI. Exact matches only are supported for query strings.
Example access control list file
The following example shows roles and permissions to URIs:
"paths" : {
"root" :{ "path" :"/" },
"emc pages" :{ "path" :"/emc/*" },
"site images" :{ "path" :"/images/*" },
"dojo resources" :{ "path" :"/dojo/*" },
....
}
},
"operations" : {
"emc_read_web" : {
"methods" :[ "GET" ],
"paths" :[ "emc pages", "dojo resources" ]
},
"common_read_web" : {
"methods" :[ "GET" ],
"paths" :[ "root", "site images" ]},
....
},"permissions" : {
"emc" :[ "common_read_web", "emc_read_web" ],
"config" :[ "configuration" ],
"deploy" :[ "deployment", "management" ],
...
},
“roles” : {
"Policy Developer" :[ "deploy", "config"]
...
}
Configure RBAC users and roles
You can use the API Gateway Manager to configure the users and roles in the local Admin User store. Click the Settings > Admin Users to view and modify user roles (assuming you have a role that allows this). This screen is displayed as follows:
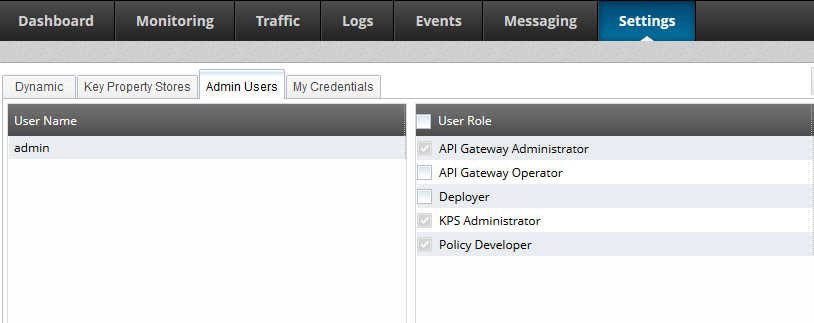
Manage RBAC user roles
When you click Create to create a new user, you can select the roles to assign to the that new user. New users are not assigned a default role. While users that are replicated from an LDAP repository do not require a role to be assigned to them. You can click Edit to changed the roles assigned to a selected user.
Add a new role to the user store
When you add a new role to the Admin User store, you must modify the available roles in the adminUsers.json and acl.json files in the conf directory of your Admin Node Manager installation. You must add the new role to the roles section of the acl.json file, which lists all the permissions that the new role may have.
Note
You must update theacl.json before you add the roles to the Admin User store. The RBAC policy object automatically reloads the acl.json
file each time you add or remove a role in the Policy Studio.
When you update the acl.json file, you must restart the Admin Node Manager to reload the acl.json file. However, the Admin Node Manager does not need to be rebooted or refreshed if a user’s roles change.
For more details on managing user roles, see Manage Admin users.
Management service roles and permissions
You can use the following for reference purposes when making changes to the acl.json file. It defines each Management Service, and the default roles that have access to them. It also lists the permissions that must be listed in the acl.json file to have access to the Management Service.
API Gateway Manager (https://localhost:8090):
-
Default Roles
- API Server Administrator
- API Server Operator
-
Permissions
emcmgmt
API Server Administrator:
-
Default Roles
- API Server Administrator
-
Permissions
emcmgmtmgmt_modifydashboarddashboard_modifydeployconfig
API Gateway Manager Dashboard (read-only access):
-
Default Roles
- API Server Operator
-
Permissions
emcmgmtdashboarddashboard_modify
API Gateway Manager Monitoring:
-
Default Roles
- API Server Administrator
- API Server Operator
-
Permissions
emcmgmtmonitoringeventstraffic_monitorsettingssettings_modifylogs
API Gateway Manager Traffic:
-
Default Roles
- API Server Administrator
- API Server Operator
-
Permissions
emcmgmttraffic_monitor
API Gateway Manager Logs:
-
Default Roles
- API Server Administrator
- API Server Operator
-
Permissions
emcmgmtlogs
API Gateway Manager Events:
-
Default Roles
- API Server Administrator
- API Server Operator
-
Permissions
emcmgmtmonitoringevents
API Gateway Manager Settings:
-
Default Roles
- API Server Administrator
-
Permissions
emcmgmtmgmt_modifysettingssettings_modify
API Gateway Manager Settings (read-only access):
-
Default Roles
- API Server Operato
-
Permissions
emcmgmtsettings
Documentation:
-
Default Roles
- API Server Administrator
- API Server Operator
-
Permissions
emcmgmt
KPS:
-
Default Roles
- KPS Administrator
-
Permissions
kpsmgmt
Policy Studio:
-
Default Roles
- Policy Developer
-
Permissions
mgmtdeployconfig
API Gateway Configuration Deployment:
-
Default Roles
- API Server Administrator
- Policy Developer
- Deployer
-
Permissions
mgmtdeployconfig
Concurrent sessions
Concurrent sessions are allowed in API Gateway Manager by default. The approach to handling concurrent sessions is subject to context and depends on the end users particular needs. There are valid reasons for supporting multiple logins for a single entity, such as in DevOps environments or for different account types, and the approaches to handling concurrent sessions are varied. The gateway’s policy engine supports session management, and handling of concurrent sessions is left to the end users discretion, which provides greater flexibility for the end user.