Configure API Portal for HA in single or multiple datacenters
5 minute read
You can configure API Portal for high availability (HA) deployment to ensure that there is no single of point of failure in the system. This helps to eliminate any potential system downtime in production environments.
API Portal supports HA deployment in both a single datacenter or multiple datacenters. In either case the deployment is always done in active-active mode that ensures data is constantly backed up when it is replicated between API Portal instances and datacenters.
Note
API Portal running standalone has been validated in a HA scenario. However, API Portal running in Docker containers has not been fully tested or validated in a HA scenario yet.API Portal HA in a single datacenter
The HA deployment provides both high availability and horizontal scalability. To achieve a API Portal high-availability (HA) deployment, you must deploy at least two API Portal instances with a shared file system for data storage behind a load balancer.
This section describes the infrastructure and the steps required for deploying API Portal HA configuration in a single datacenter.
Deployment architecture single datacenter
The load balancer performs Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) checks at the network level on both active API Portal instances. If either of the crucial services (Apache or MySQL) becomes unavailable in one instance, the load balancer redirects traffic to another available instance. When the failed instance returns to normal operation, the traffic is again evenly distributed between all instances.
The following diagram illustrates the HA setup with two API Portal instances:
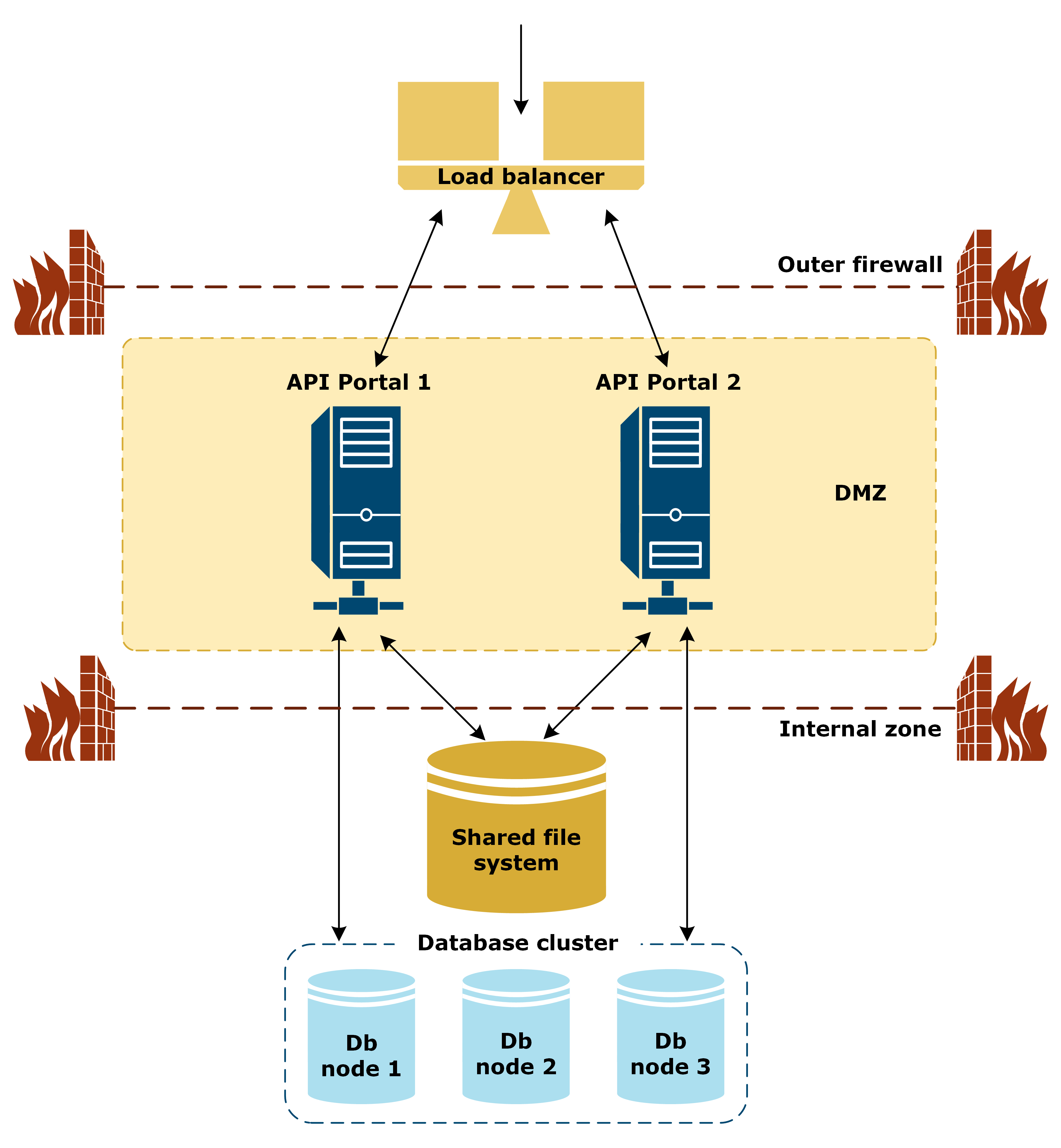
A load balancer sits outside the external firewall and routes the traffic from the Internet and end users to the API Portal instances. The Apache web servers are located in the demilitarized zone (DMZ), and communicate with the shared file system and the database cluster located in the internal zone.
The shared file system synchronizes static files (such as images uploaded by users) between the API Portal instances. The database cluster stores data (for example, configuration data) that API Portal queries as required. You must have at least three database nodes for HA.
For more details on data storage in API Portal HA configuration, see Data storage for high availability.
API Portal HA in multiple datacenters
You can distribute your environment across multiple datacenters to improve the availability, reliability and performance. If one datacenter fails, the others continue to operate, so there is no break in service. The active-active model ensures that data is continuously backed up when data is replicated between the datacenters. If you distribute your datacenters globally, you can provide a datacenter geographically close to your operations and your customers to diminish the latency in traffic.
This section describes the infrastructure and the steps required for deploying API Portal across multiple datacenters.
Deployment architecture multiple datacenters
Deploying API Portal in multiple datacenters has two architecture options: with either shared file system or local data storage.
Using shared file system is the recommended option, because syncing static files between all API Portal instances provides more flexibility to enhance your API Portal later. However, when taking into account the limitations that using local data storage imposes, in some cases (for example, if you do not plan on using blogs or discussion forums in API Portal), using the local data storage may be a viable option.
Note
It is not recommended to use separate databases for API Portal instances instead of the database clusters, because the benefits of the HA deployment are practically lost.For more details on what data API Portal stores and where, see Data storage.
Multi-datacenter deployment with shared file system
The following diagram shows a reference architecture on API Portal multi-datacenter deployment with a shared file system:
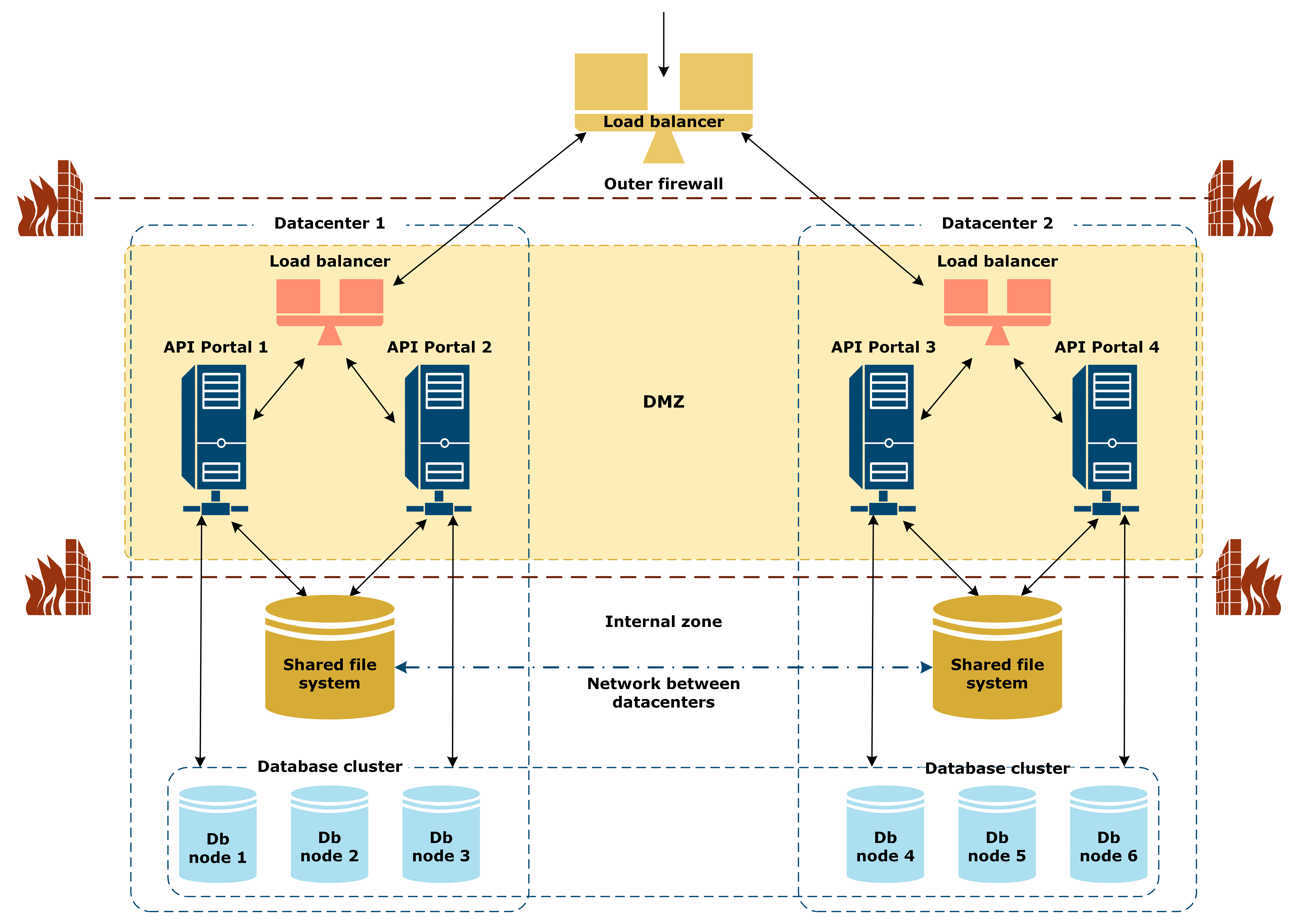
The example deployment includes four API Portal instances deployed in two datacenters. An external loadbalancer sits outside the external firewall and routes the traffic from the Internet and end users to the datacenters.
Each datacenter includes the same components deployed in active-active mode, and can handle all of the traffic load and scale in the same way. An internal load balancer distributes the traffic to the datacenter between the two API Portal instances. The Apache web servers are located in the demilitarized zone (DMZ) and communicate with the shared file system and the database cluster located in the internal zone.
The shared file system synchronizes static files (such as images uploaded by users) between all API Portal instances, both within the datacenter and between the datacenters over the network between the datacenters. The database cluster stores data (for example, configuration data) that API Portal queries as required.
The API Portal instances, the database nodes, and the shared file storage in each datacenter are all configured for HA. This means that you must have at least two API Portal instances and three database nodes per datacenter.
Multi-datacenter deployment with local data storage
The following diagram shows a reference architecture on API Portal multi-datacenter deployment with a local data storage:
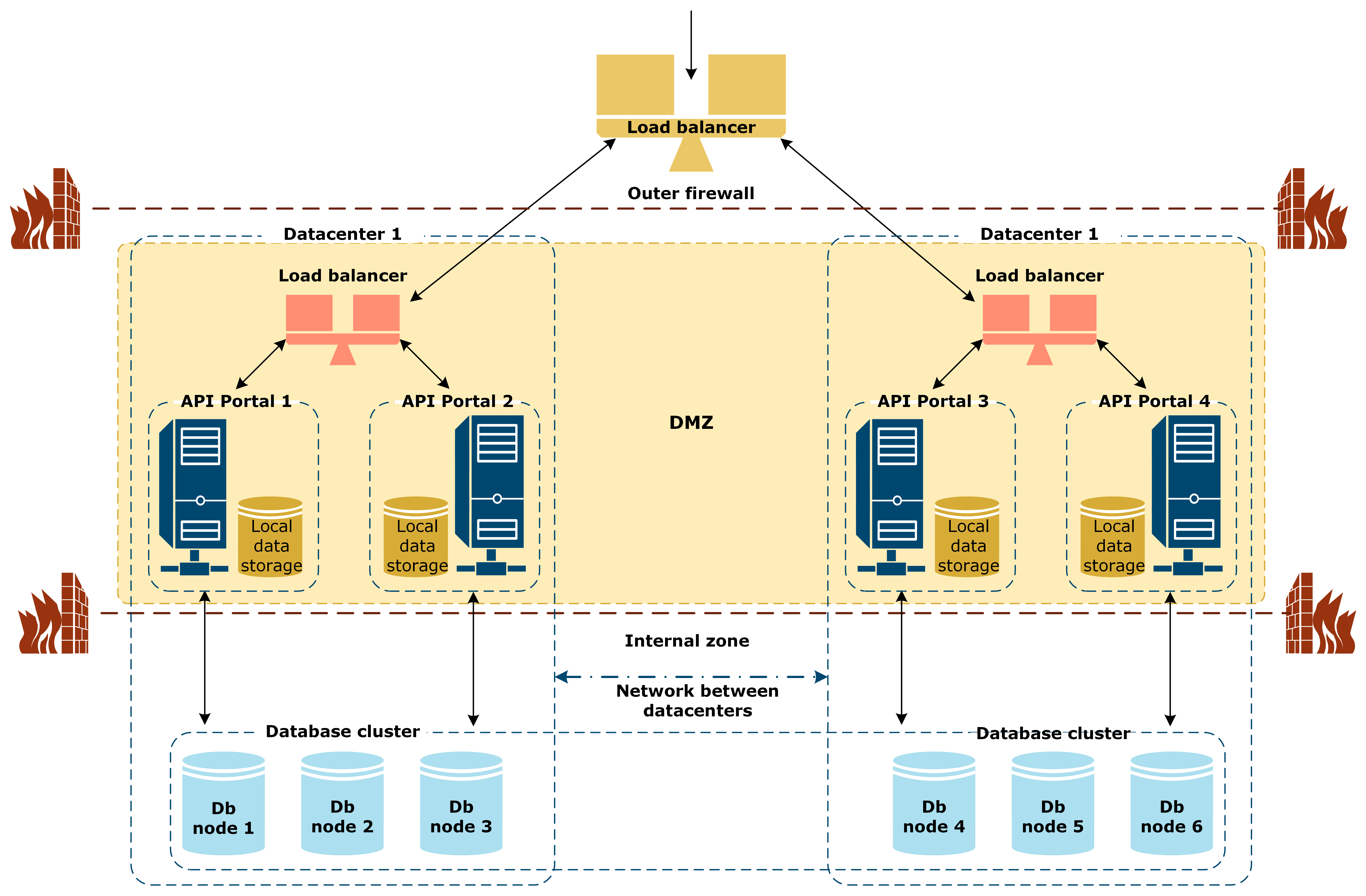
The setup is otherwise like with the shared file system, except that the local data storage is co-located with the Apache web server on each API Portal instance in the DMZ.
Because there is no shared file system, the attachments uploaded the content (Joomla! articles, blog posts, discussions forums) are not synchronized between the datacenters. The attachments are only accessible only from the datacenter and the API Portal instance where they were uploaded.
Without the shared storage, if a user creates a blog post with an attachment and refreshes or reloads the page, the attachment might not be visible because the user was redirected to another API Portal instance. Similarly, other users might not see the attachments, because they are not in the same API Portal instance.