Introduction to API Builder
3 minute read
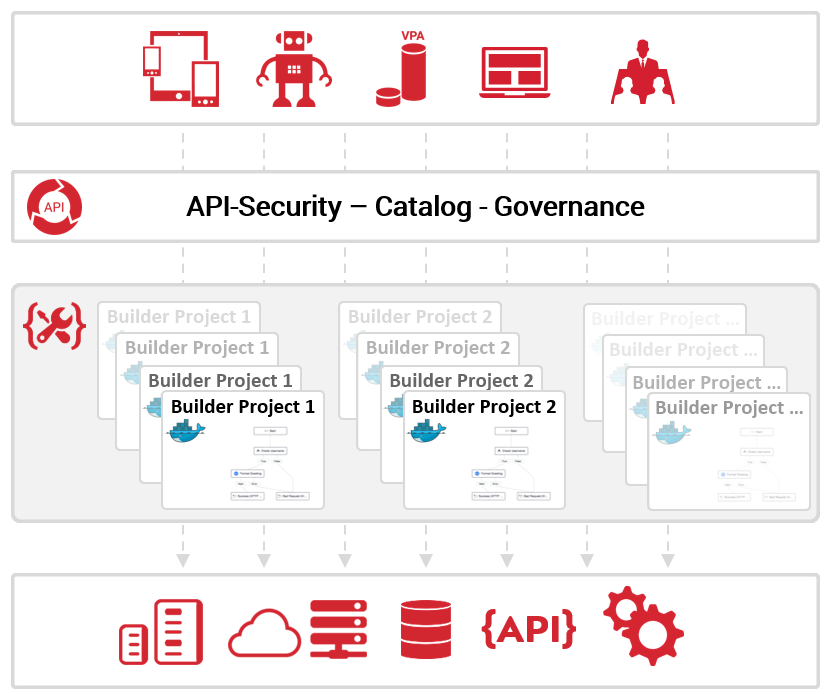
Axway API Builder is based on Node.js, and acts as an integration orchestration layer between existing service providers and the API management system, or governance layer.
API Builder can connect to different service providers:
- Databases
- REST API based on an OpenAPI 2.0 or 3.0 specification
- Cloud applications
- Using an SDK additional plugins or connectors can be added
Use API Builder
The basic principle of API Builder is to expose APIs in the same way as any other application, such as a Node.js or Spring Boot application. The main advantage of API Builder is the speed at which you can implement integration use cases, much faster than implementing them manually. Instead of having to deal with how to integrate into a system, you can install a ready-to-use plugin in the API Builder project.
API builder is not an API Gateway or security component but an integration and orchestration layer. The APIs exposed by API Builder are typically imported into the API management solution as back-end APIs.
API Builder offers:
- Low code/no code approach
- Based on standards (OpenAPI/Swagger, Node.js, Javascript, JSON)
- Powerful flow engine
- Optimized for use in containers
- Easily expandable using an available API Builder SDK
To expose and implement APIs, the API builder offers two different approaches.
Model approach
Connectors are the key in the model-based approach. Connectors have the task of generating a model from data sources such as databases. API Builder can generate a simple CRUD (create, read, update, delete) API for the model quickly and easily. With this approach, you can generate a CRUD API in minutes, and you can restrict it, for example, to read access only.
Watch this video to learn how to connect to a database and create a CRUD API based on it.
Learn more about API Builder Models.
API-first approach
In the API-first approach, you import a defined API specification (OpenAPI/Swagger) into API Builder as the initial step. This tells API Builder what endpoint should be exposed, what parameters each endpoint has, and so on. The API specification might come from the API design phase where you have used your preferred API design editor. All endpoints are disabled by default and you can implement each endpoint with a flow using the plugins, connectors, and model you need for your use case.
Watch this vide to learn how to implement an API design using flows.
Learn more about API Builder Flows.
Both approaches can also be mixed, for example, to combine the data from a model with the data from a REST service.
Mock an API
To mock an API with API Builder, follow the same steps as for the API-first approach and use the Create Mock option after you have imported your API specification.
Watch this video to learn how.
Deployment
API Builder projects are designed to run as Docker containers in a scalable environment such as a Kubernetes cluster. Although API Builder supports a low code/no code interface, a Node.js application with a set of JavaScript and configuration files is created in the background. These should be versioned like any other application, built via a pipeline, tested, and published as a Docker image. Based on the image, the API Builder application is provided as a Docker container. The APIs exposed in this way are registered in the API management system as back-end APIs.