Troubleshooting API Portal
2 minute read
General troubleshooting steps
- Check if your issue and a workaround for it is listed as a known issue in the Release Notes for your installed API Portal version.
- Restart the failing servers or clients.
- Collect the log files, screen shots, and any other data related to the issue, and contact Axway Support.
Logging and error reporting
The Apache error_log file is located at /var/log/apache2/.
To enable Joomla! error reporting, in JAI, click System > Global Configuration > Server and set the error reporting to the desired level. However, use caution, because this may lead to warnings and errors on the API Portal pages. We recommended you to enable the error reporting only in critical situations, and not in a production environment.
For more information, see Supported log files.
API response class details missing
The following is an example of missing response class details. An array[null] value is displayed instead of details:
![An example of an “array[null]” Response Class with missing details](/Images/APIPortal/troubleshooting1.png)
The following is an example of the expected response class details:
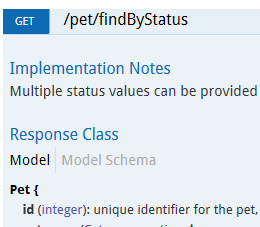
To solve this issue, set the correct return type for any APIs causing the error, and then republish them:
- Log in to API Manager, and click API Registration.
- Select the API causing the error, click Manage selected, and select Unpublish. You can unpublished multiple APIs at one go.
- Click the API, select the API Methods tab, set Response type for the method causing the error, and click Save.
- Go back to API Registration, select the edited API, click Manage selected, and select Publish.
Random session logout
If API Portal is randomly terminating users sessions, the session Hijacking plugin running in the API Portal might be the cause of the issue.
This plugin checks, for example, the x-forwarded-for HTTP header, which is typically set by an upstream reverse proxy, to check whether the header remains the same during a session. If the header changes, the user is logged out. To solve this issue, check if a reverse proxy is in use, and if and how it sets the X-Forwarded-For header.
For example, if the X-Forwarded-For changes a port from 89.211.212.232:50238 to 89.211.212.232:50239, the user is logged out. In this case, you can reconfigure your reverse proxy so that the X-Forwarded-For header is not sent without the port number, or not sent at all.