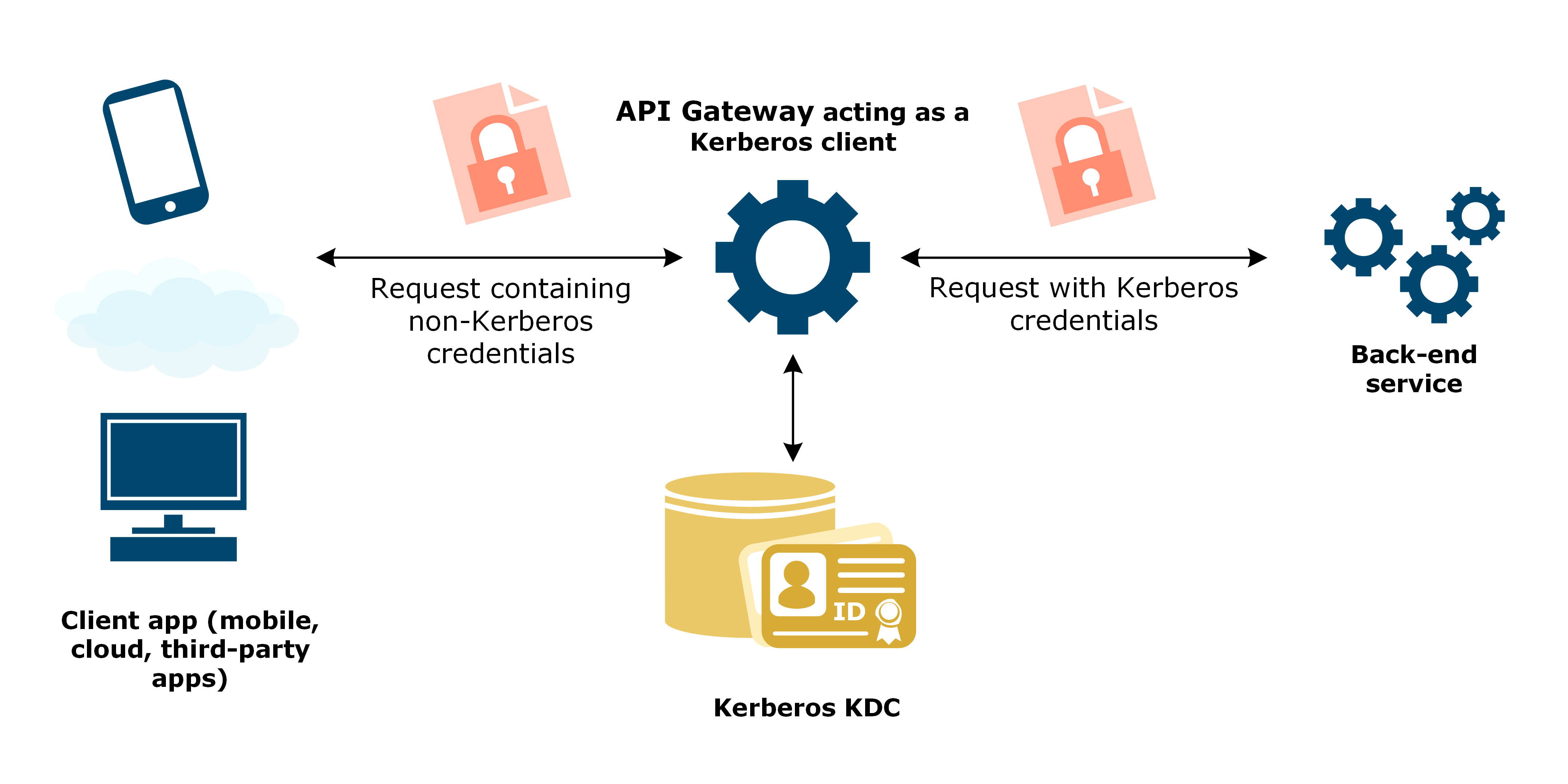
API Gateway as a Kerberos client
6 minute read
In this scenario:
- Client application: Does not support Kerberos authentication.
- Back-end service: Requires Kerberos authentication, but not the end user’s credential.
- API Gateway: Acts as a Kerberos client and authenticates to the back-end service as itself.
The client application can only authenticate using some non-Kerberos authentication mechanism. The back-end service requires Kerberos authentication, but does not need to authenticate the real user associated with the client application. API Gateway sits between the client application and back-end service, and authenticates the client using a non-Kerberos authentication mechanism. The back-end service authenticates API Gateway as the Kerberos client, and trusts that API Gateway has authenticated the real user.
Prerequisites
Before you start configuration, you must have API Gateway installed on any machine with access to the Windows Domain Controller. The machine does not have to be a Windows machine that is part of the Windows Domain.
Example names
For the example in this section, the Kerberos client ClientGateway connects to an existing back-end service.
The example Kerberos realm name AXWAY.COM is specific to the examples in this guide. Replace the example realm name with your own realm name.
The next sections describe the steps to configure the gateway as a Kerberos client.
Configure a user account in Active Directory
Configure a Kerberos client principal for API Gateway in Active Directory acting as the Key Distribution Centre (KDC).
-
On the Windows Domain Controller, click Control panel > Administrative Tools > Active Directory User and Computers.
-
Right-click Users, and select New > User.
-
Enter a name for the user (such as
ClientGateway) in the First Name and User Logon Name fields, ensure the Active Directory domain is set to your domain, and click Next. -
Enter the password, and do the following:
- User must change password at next logon: Deselect this.
- User cannot change password: Select this.
- Password never expires: Select this.
This ensures that a working API Gateway configuration does not stop working when a user chooses, or is prompted to change their password. API Gateway does not track these actions.
If these options are not suitable in your implementation and a user password changes in Active Directory, you must then update the password or keytab of the Kerberos client or service related to the user in Policy Studio, and redeploy the configuration to API Gateway.
If you cannot deselect User must change password at next logon, ensure the user changes the password and that the new password or keytab is deployed to API Gateway before API Gateway attempts to connect as this user.
You can store Kerberos passwords in a KPS table to update a changed password in runtime. For more details, see Use KPS to store passwords for Kerberos authentication.
-
Click Next > Finish.
As a Kerberos client, API Gateway authenticates to an existing back-end Kerberos service. For the authentication to succeed, the back-end Kerberos service must have an account and any SPNs configured in your Active Directory. For an example configuration, see Configure a user account in Active Directory.
Configure Kerberos principals
Add Kerberos principals using Policy Studio when API Gateway is the Kerberos client.
- In the node tree, click Environment Configuration > External Connections > Kerberos Principals.
- Add a Kerberos principal for API Gateway acting as the Kerberos client as follows:
- Name:
ClientGateway - Principal Name:
ClientGateway@AXWAY.COM - Principal Type:
NT_USER_NAME
- Name:
- Add a Kerberos principal for the back-end service as follows:
- Name: Enter the name of the back-end service.
- Principal Name: Enter the Service Principal Name (SPN) for the back-end service (for example,
HTTP/backend.axway.com@AXWAY.COM). - Principal Type:
NT_USER_NAME.
Configure API Gateway policy
This section describes how to configure API Gateway as the Kerberos client using Policy Studio.
Configure a Kerberos client
- In the node tree, click Environment Configuration > External Connections > Kerberos Clients.
- Click Add a Kerberos Client, and enter a name for your client (such as
ClientGateway Kerberos Client). - On the Kerberos Endpoint tab, set the following:
- Load via JAAS Login: Select this option and the Request from KDC option.
- Kerberos Principal: Your API Gateway principal (
ClientGateway). - Enter Password: Enter the password for
ClientGateway@AXWAY.COM. - Enabled: Make sure this option is selected.
- On the Advanced tab, set the following:
- Mechanism:
SPNEGO_MECHANISM. - Context Settings: Select the following options:
- Mutual authentication
- Integrity
- Confidentiality
- Anonymity
- Replay Detection
- Sequence Checking
- Synchronize to Avoid Replay Errors at Service: Deselect this option to improve performance.
- Mechanism:
Configure a Kerberos profile for the Kerberos client
- In the node tree, click Environment Configuration > External Connections > Client Credentials > Kerberos.
- Add a Kerberos profile as follows:
- Profile Name:
Authenticate to back-end service. - Kerberos Client: Your Kerberos client (
ClientGateway Kerberos Client). - Kerberos Service Principal: Your back-end service Kerberos service principal.
- Send token with first request: Select this option.
- Profile Name:
Configure a Kerberos policy
This section describes how to configure the Kerberos policy for API Gateway as the Kerberos client.
To start, add a new policy named, for example, Kerberos Client SPNEGO.
Configure the end user authentication method
In this example, API Gateway authenticates the end user application using HTTP Basic. Depending on your environment, you may want to use a different authentication mechanism.
- Open the Authentication category, and drag a HTTP Basic filter onto the policy canvas.
- Set Credential Format to User Name, and select Allow client challenge.
- Set Repository Name to
Local User Store, and click Finish.\ - Right-click the HTTP Basic filter, and select Set as Start.
API Gateway does not authenticate the end user to the back end. The back-end service only sees API Gateway’s Kerberos credentials regardless of how the end user authenticates to API Gateway.
Configure connection to the back-end service
- Open the Routing category in the filter palette, and drag a Connect to URL filter onto the policy canvas.
- Enter the URL used that invokes the back-end service.
- On the Authentication tab, choose the Kerberos credential profile configured earlier (
Authenticate to back-end service), and click Finish.
If the back-end service requires an SSL/TLS connection, SSL must be configured on the Connect to URL filter.
Build the policy
- Click on the Add Relative Path icon to create a new relative path (for example,
/gw-client-to-back-end) that links to this Kerberos policy. - Connect the filters with a success path.
The policy looks like this:
The policy has the following flow:
- Client application authenticates to API Gateway.
- API Gateway sends a request to the back-end service. The request contains a Kerberos SPNEGO token where the client principal is API Gateway.
- The back-end service authenticates API Gateway and returns a response to API Gateway.
Configure Kerberos system settings
-
In the node tree, click Environment Configuration > Server Settings > Security > Kerberos, and click Add Kerberos Configuration.
-
On the krb5.conf tab, change the following settings:
[libdefaults] default_realm = AXWAY.COM [realms] AXWAY.COM = { kdc = dc.axway.com }Replace the realm settings in the example code with your Kerberos realm, and set the
kdcsetting to the host name of your Windows Domain Controller. -
Click the Deploy icon to deploy the configuration to API Gateway.
You have now configured and deployed a simple Kerberos policy for SPNEGO authentication.
Test the configuration
Use a third-party application, such as POSTMan or similar, to call the Kerberos policy in API Gateway.
The back-end Kerberos service should send a confirmation on a successful authentication.
The Traffic Monitor tab on the API Gateway Manager (https://localhost:8090) is an excellent place to view and troubleshoot the message flows. For more details, see Monitor services in API Gateway Manager.