API Portal single sign-on
5 minute read
API Portal supports single sign-on (SSO). This enables users to use the same login details for API Portal and other Axway platform products, such as API Manager or Decision Insight, and eliminates the need to log in multiple times to different web-based UIs.
API Portal uses API Manager as the service provider in SSO, but they can be configured separately. This means that you can have SSO in just API Portal, in API Manager, or in both. API Portal SSO is controlled in the service-provider-apiportal.xml file, while API Manager SSO uses the service-provider.xml.
Caution
SSO does not work when you have multiple API Managers configured with API Portal.SSO concepts
Single sign-on (SSO) is a session/user authentication process where a user enters one user name and password to access multiple applications. API Portal supports SAML-based SSO.
The SAML 2.0 standard describes how to exchange authentication and authorization data between entities. This section describes some key concepts.
Service Provider
A Service Provider (SP) protects access to requested resources, such as web sites and applications by applying a security policy. For example, the SP blocks all access to an unauthenticated user and routes the request to the Identity Provider. API Manager acts as an SP.
Identity Provider
An Identity Provider (IdP) is a system that creates, maintains, and manages identity information for users, services, or systems, and provides authentication to other service providers (applications) within a network. An IdP is a trusted entity that users and servers can rely on when they are establishing a dialog that must be authenticated. The IdP sends an attribute assertion containing trusted information about the user to the SP. In an Axway deployment, the IdP is a third-party product.
User agent
A user agent is usually a web browser. The person who uses the browser can be referred to as a user or as a principal.
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML)
The Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an XML-based solution for exchanging user security information (authentication, authorization) between an IdP and SP. SAML is a product of the OASIS Security Services Technical Committee.
SAML assertion
A SAML assertion is a package of information that contains one or more statements made by a SAML authority. The SAML standard defines three types of assertion statement:
- Authentication: The specified subject was authenticated by a particular means at a particular time. This kind of statement is typically generated by an IdP.
- Attribute: The specified subject is associated with the supplied attributes.
- Authorization: A decision to grant or deny the specified subject access to the specified resource.
SSO message flows
As a client, API Portal uses “external” single sign-on (SSO) to authenticate to API Manager that acts as the Service Provider (SP).
API Portal client acts as a reverse proxy. The Identity Provider (IdP) sends SAML assertions to API Portal. API Portal forwards the assertions to API Manager. API Manager processes the assertions and manages the authentication and authorization process.
The following sections describe the message flows between API Portal, API Manager acting as the SP and the IdP.
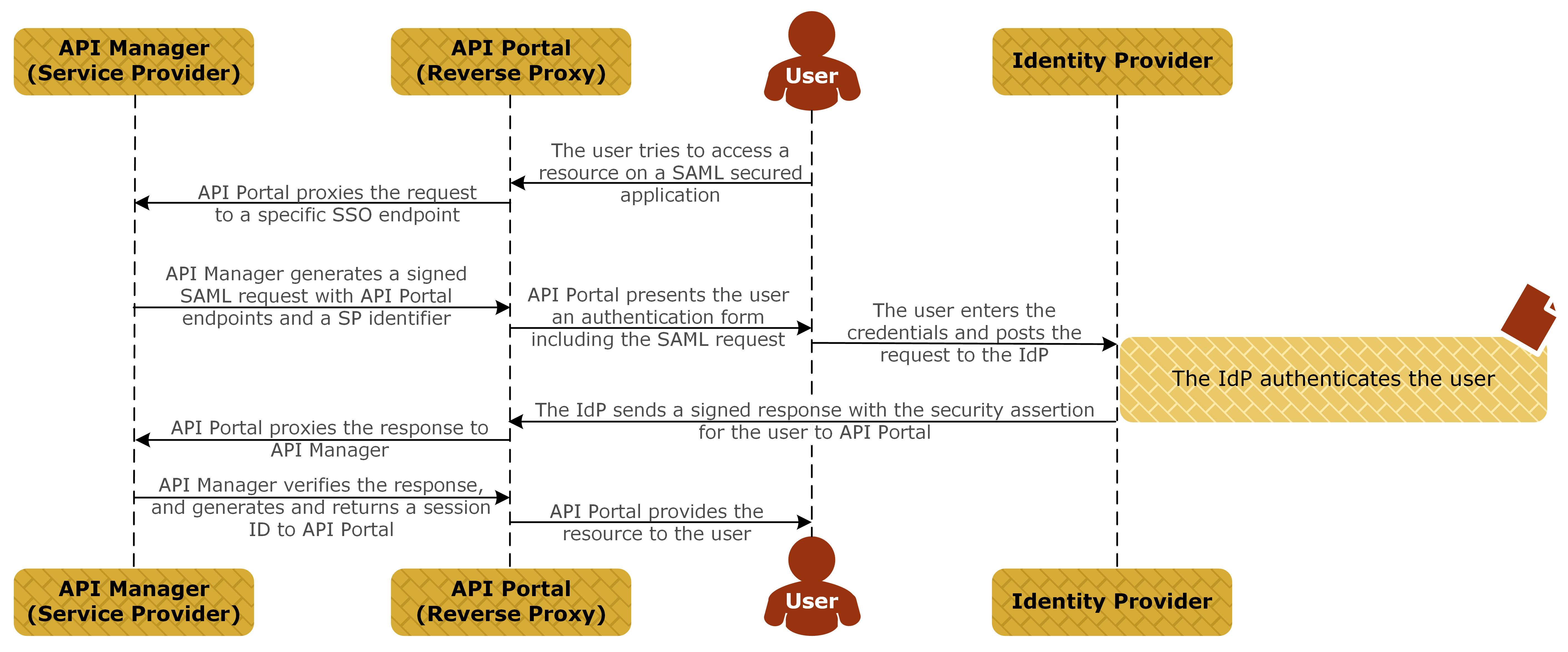
Authentication sequence
The following diagram shows a simplified message flow for SSO using SAML:
-
The end user tries to access the API Portal UI using a web browser:
- For non-SSO login, use the default URL (for example,
https://<FQDN>:<port>). - For SSO login, use the SSO URL (for example,
https://<FQDN>:<port>/sso).
The
<FQDN>is the fully qualified domain name of the machine where API Portal is running, and<port>is the API Portal listening port. You can change the SSO URL in the Joomla! Admin Interface (JAI). For more details, see Enable SSO in API Portal.The SSO login URL must be used even if the user has already logged in using SSO (for example, if they have already logged in to API Manager or Decision Insight).
- For non-SSO login, use the default URL (for example,
-
API Portal proxies the request to API Manager.
-
API Manager builds a SAML Authentication Request message and sends it to the IdP.
-
The IdP checks if there is an active session for the user.
- If no session for the user exists on the IdP, the user is prompted to enter their credentials. The IdP analyzes the credentials, and upon successful authentication sends a SAML Response message to API Portal, asserting that the user is authenticated.
- If a session for the user exists, the IdP sends the session ID to API Portal.
-
API Portal immediately proxies the message to API Manager.
-
API Manager processes and verifies the response, and maps the user’s IdP role to an API Portal-specific role. For more details, see Mapping syntax.
-
When successful, API Manager generates and returns a session ID to API Portal.
-
API Portal provides the requested resource to the user.
Logout sequence
The logout sequence is as follows when logout is initiated by API Portal:
- The end user tries to log out of API Portal by clicking the Logout button in the UI.
- The IdP removes the user session and returns a SAML Logout Response to the browser.
- The browser posts the HTML form containing the SAML Logout Response to the API Portal single logout service URI.
- API Portal redirects to the logout redirect URI.
When the end user tries to log out of API Portal, API Manager session remains active.