KPS overview
4 minute read
Data in a KPS table is assumed to be read frequently and seldom written, and can be changed without incurring an API Gateway service outage. KPS tables are shared across an API Gateway group.
KPS architecture
The following diagram shows a simple role-based architecture:
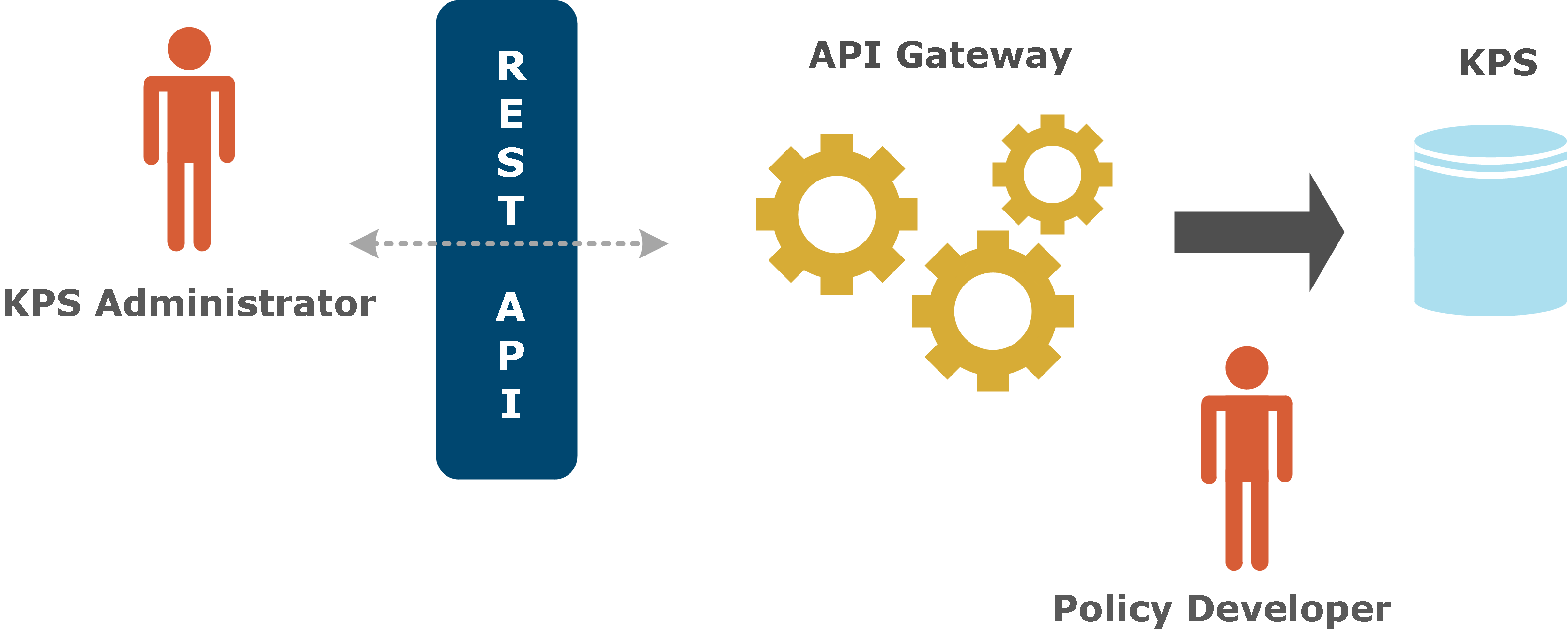
A KPS is typically used to store property values that are used in policies running on an API Gateway. KPS data is injected into policies using selectors that are first created in Policy Studio by policy developers. Selectors are evaluated and expanded dynamically at runtime. For example, a KPS table could contain authorization tokens for different users. A policy could look up the token for the current user and insert it into an HTTP request.
KPS tables are organized into collections. The tables in a collection typically have some sort of relationship to one another. For example, the OAuth collection contains a set of tables that store all OAuth-related data. Every KPS table is assigned an alias so that it can be easily referred to in a policy or a REST request. KPS collections and tables can be created by policy developers using Policy Studio.
KPS administrators can use the API Gateway Manager web console to view and modify KPS data at runtime. This is a business or operational role that manages dynamic policy configuration data in a KPS (for example, customer details, authorization levels, or quotas). This means that this information does not need to be configured at design time by policy developers.
KPS data stores
KPS data can be stored in one of the following locations:
- External Apache Cassandra database: Data can be distributed across multiple nodes to provide high availability. This is the default data store. See Configure Apache Cassandra KPS storage.
- Relational database: Accessible to all API Gateway instances in the gateway group. See Configure database storage
- JSON files: On the local file system (deprecated). See Configure file-based KPS storage
Note
Custom KPS data defined in Policy Studio supports Cassandra, database, and file data stores. API Manager KPS data (Client Registry and API Catalog) supports Cassandra only. File-based KPS is deprecated and will be removed in a future release.KPS client applications
API Gateway provides the following client applications:
- Policy Studio: Enables policy developers to create KPS collections and tables, and to configure data sources. See Configure KPS in Policy Studio.
- API Gateway Manager: Includes a visual web-based interface to enable KPS administrators to view and modify KPS data at runtime. See Get started with KPS
- kpsadmin command: Supports KPS data entry and other administrative functions. It is designed for use in a development environment. See Manage KPS using kpsadmin
- KPS REST API: Enables remote programmatic clients to read and write KPS data.
When to use a KPS
KPS provides a flexible data storage service that can be used to store any configuration data. Its primary function is to make this data available to selectors at runtime, and it is optimized for this purpose. This makes it most suitable for data with the following characteristics:
- Data is common to all API Gateways in an API Gateway group. KPS is not suitable for data that is specific to one particular API Gateway.
- The data schema is relatively simple. Each KPS table is assumed to be independent of all others, and referential integrity across tables is not supported.
- Data can change while API Gateways are running. Updating Cassandra-backed or database-backed KPS tables does not require an API Gateway restart. Changeable data should therefore be stored in KPS instead of hard-coded into policies.
- Queries always involve looking up a key value in a table to retrieve a single object. This is the usage model supported by selectors. Ad hoc queries that involve searching for non-key properties are not supported.
- Multi-operation transactions are not required. Each read or write to a KPS table is considered a standalone operation. Locking or rollback across multiple operations is not supported.