Deploy API Portal in containers
3 minute read
Docker containers are software containers that wrap software in a complete file system containing everything the software in question needs to run properly, such as code, runtime, system tools, and system libraries. This guarantees that the software always runs the same way, regardless of environment. In addition, you can configure several containers to run on a single host machine, without the overhead of starting and maintaining separate virtual machines.
Docker containers enable you to run API Portal on any host operating system or cloud platform that supports Docker. Because API Gateway and API Manager also support Docker containers, you can run the full API Management solution in Docker containers. This makes it easy to quickly build, test, and run API Management solutions for standalone or high availability (HA) deployment.
For details on how to deploy your Docker infrastructure in the cloud, see the product documentation for your chosen third-party cloud platform or Platform as a Service (PaaS) environments, such as Amazon Web Services.
For more details on Docker, see the following:
Note
API Portal running standalone has been validated in a HA scenario. However, API Portal running in Docker containers has not been fully tested or validated in a HA scenario yet.Interaction example
The following diagram shows an example on how the different components interact in Docker containers:
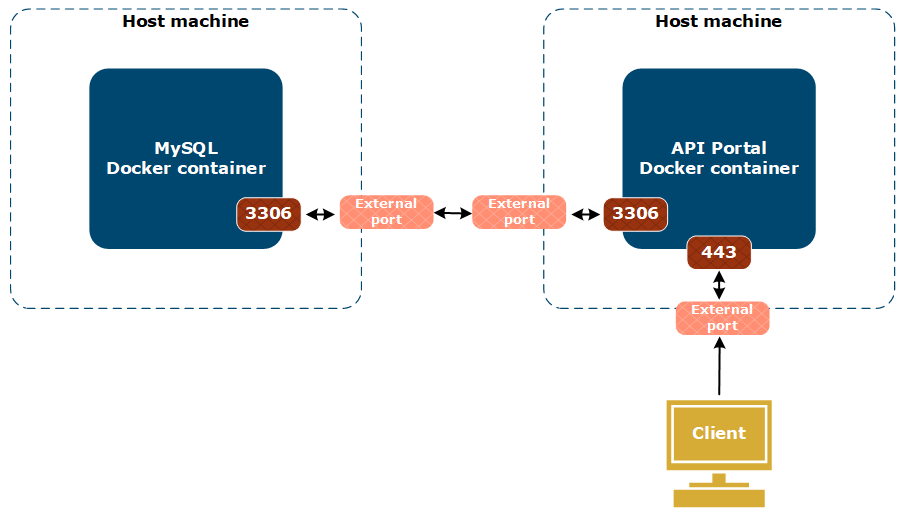
In this example, API Portal and MySQL containers are located on separate host machines but, you can also run API Portal and MySQL containers on the same host machine. However, separating the containers on different host machines allows for additional security measures.
The end user uses a browser to access API Portal using the host address and the host port of the host machine running the API Portal Docker container. The host machine interacts with the API Portal container using the port 443 to secure the connection. Behind the scenes, API Portal connects to the host address and the host port of the host machine running the MySQL Docker container. The MySQL host machine uses the port 3306 to interact with the MySQL database in the container.
Note
The example shows MySQL running in a container, but you can use any MySQL and Redis server installed on bare metal or in a virtual machine. Axway does not provide MySQL and Redis Docker images, but you can download these images from Docker Hub.Default ports
By default, API Portal uses port 3306 for the MySQL connection and ports 443 and 80 for http. To use different ports on the Docker containers, you can replace the default values in the code examples with your chosen ports. Ensure that you define the same MySQL port in both the MySQL and API Portal container. Additional configuration might also be required.
On the host machines running the Docker containers, you can expose any port you want. The examples in this guide use ports 443 on the API Portal host machine and port 3306 on the MySQL host machine.
API Portal resources
Axway provides a package containing a ready-made API Portal Docker image for running API Portal in Docker. You can get the API Portal packages from Axway Repository.
Data persistence
When you make changes that affect the file system of the API Portal container, such as customizations (template, logo), it is recommended to back up these changes.
Data is persistent as long as the Docker container exists:
- If you stop the container, all your changes are retained when you run the container again.
- If you remove the container, all your changes are lost, and you must either restore them from your backup, or redo them.
Non-root user
By default, API Portal container runs as a non-root container, which makes containers more secure but results in some volumes-related issues. For more information, see the data persistence section.