Cassandra deployment architectures
5 minute read
This section provides a summary of the deployment architectures.
Standalone
One API Gateway instance only. This is the default.
Usage:
- Development environment
- Production environment with one API Gateway instance
High availability with local storage
Multiple API Gateway instances in a group, each API Gateway instance on different hosts, with a Cassandra storage node local to each API Gateway host.
Usage:
- Pre-production environment
- Production environment
High availability with remote storage
Multiple API Gateway instances in a group, each API Gateway instance on different hosts, with Cassandra storage nodes on remote hosts.
- Pre-production environment
- Production environment
You can use one Cassandra cluster to store data from one or multiple API Gateway groups and one or multiple API Gateway domains. Your Cassandra topology does not need to match your API Gateway topology.
Multiple API Gateway groups can also be deployed on the same host, each host running an API Gateway instance for each group. This applies to both local and remote storage.
Note
Windows is supported only for a limited set of developer tools. API Gateway and API Manager do not support Windows. You can continue using an existing remote Cassandra installation running on Windows that you have configured with your API Gateway installation.For details on hosting Cassandra in datacenters, see Configure API Management in multiple datacenters.
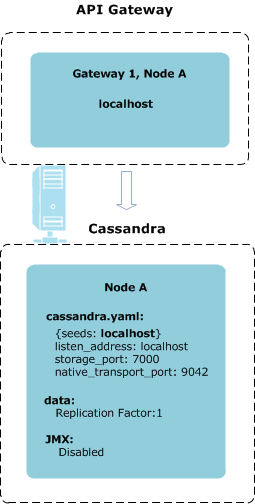
Cassandra in standalone mode
Cassandra is configured in non-HA standalone mode when deployed alongside a single API Gateway instance on the same host (for example, in a demonstration or development environment with one API Gateway instance). This is the default mode.
To configure Cassandra in standalone mode, perform the following steps:
- Ensure Cassandra is installed on the local node along with API Gateway.
- Start Cassandra before starting API Gateway.
- Start API Gateway.
The next steps depend on your installation setup type:
- In a Standard or Complete setup that includes the QuickStart tutorial, the default configuration attempts to connect to Cassandra running on
localhost. - In a Custom setup without the QuickStart tutorial, you must configure the connection in Policy Studio. For more details, see Connect to API Gateway for the first time.
To use Cassandra with API Manager, see Configure a highly available Cassandra cluster. This is configured by default when API Manager is installed along with the QuickStart tutorial.
To use Cassandra with OAuth, see Configure OAuth.
The following diagram shows Cassandra in standalone mode with a default standard setup:
Cassandra in High Availability mode
For both local and remote Cassandra HA, Cassandra runs on multiple hosts. This section describes both scenarios.
HA with local storage
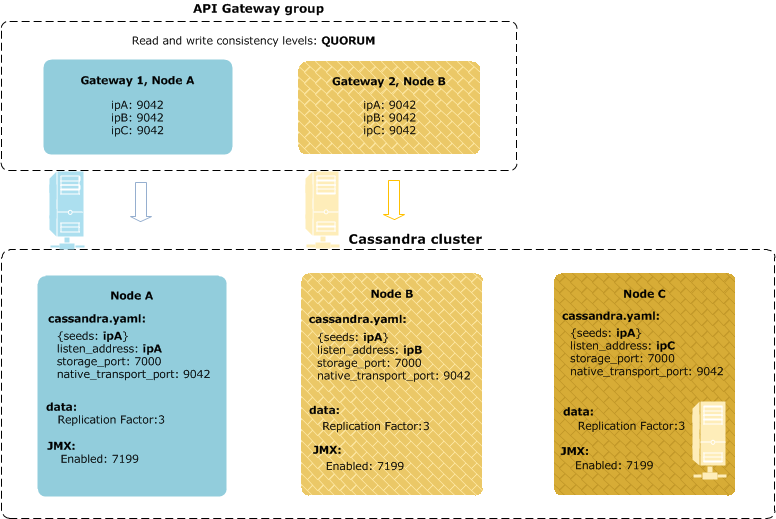
In local Cassandra HA, Cassandra runs alongside API Gateway on the same host. This means that you do not need to provision separate host machines for Cassandra and API Gateway, or open ports in your firewall. However, the data will be stored in the DMZ. Local Cassandra HA enables minimum cost of ownership.
The following diagram shows local Cassandra HA mode:
Note
In this example, one of the Cassandra nodes runs without an API Gateway instance on the same host. This is because the minimum deployment architecture includes two API Gateway hosts and three Cassandra hosts. If you have three API Gateway instances, all Cassandra nodes are local..HA with remote storage
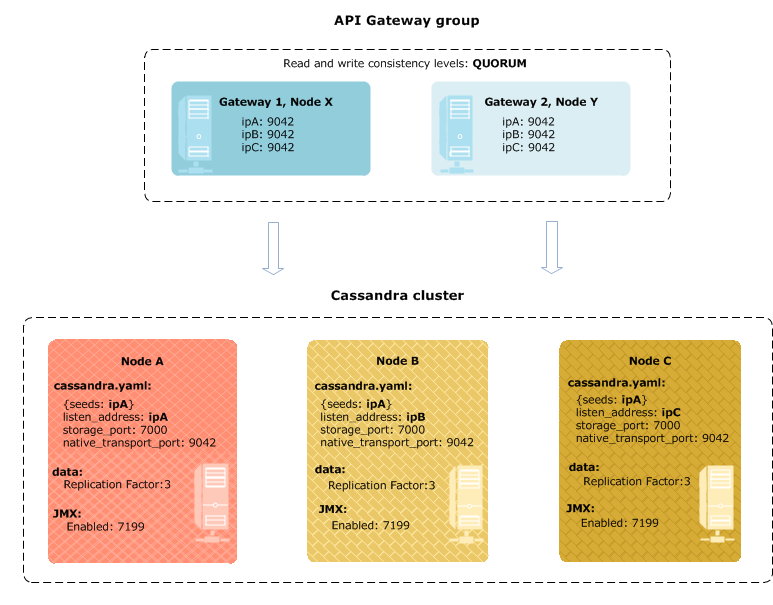
In remote Cassandra HA, Cassandra runs on a different host from API Gateway. The main differences when installing and configuring remote Cassandra are:
- You must provision separate host machines for Cassandra and API Gateway. However, the data can be stored outside the DMZ, and there might be improved performance.
- You might need to open ports in the firewall to connect to Cassandra outside the DMZ. For more details, see Configure a highly available Cassandra cluster.
- You do not have to use the Cassandra component supplied by the API Gateway installer.
- You can configure the remote node using the
setup-cassandrascript supplied by the API Gateway installation. For more details, see Configure Cassandra clusters with the setup-cassandra script. Alternatively, you can perform all necessary Cassandra configuration changes manually. - You must update the API Gateway Cassandra client settings in Policy Studio to connect to the remote Cassandra host nodes.
The following diagram shows remote Cassandra HA mode:
Cassandra HA configuration
You can use a local or remote Cassandra HA configuration. The example Cassandra HA configuration in the diagrams consists of the following:
- Three Cassandra nodes in a single cluster.
- Three host machines with network addresses:
ipA(seed node),ipB, andipC. - Replication factor of
3. Each node holds 100% of the data. - Default values in
cassandra.yamlfor:- Server-server communication:
listen_addressset to IP addressstorage_portset to7000ssl_storage_port:7001(when TLS v1.2 is configured) - Client-server communication:
native_transport_portof9042 - JMX monitoring on
localhost:7199
- Server-server communication:
More information:
ipA,ipB, andipCare placeholders for real host machines on your network. You can specify IP addresses or host names.- You must have at least one designated seed node. Seeds nodes are required at runtime when a node is added to the cluster. You can add more or change designation later.
- You can change the server-server port, but it must be the same across the cluster.
- For Cassandra administration, you must gain local access to the host machine (for example, using SSH) to perform administration tasks. This includes using
nodetoolto access the Cassandra cluster over JMX.
API Gateway configuration
API Gateway acts as a client of the Cassandra cluster as follows:
-
- Client failover
- API Gateway can fail over to any of the Cassandra nodes for service. Each API Gateway is configured with the connection details of each Cassandra host.
-
- Strong consistency
- Cassandra read and write consistency levels are both set to
QUORUM. This, along with the replication factor of3, enables full availability in the event of one node loss.
You can have any number of gateway instances (all running either locally or remote to Cassandra). However, you must have at least two gateway instances for HA. This also applies to API Manager.
For more details on Cassandra HA configuration, see Configure a highly available Cassandra cluster.