Configure multi-datacenter high availability
5 minute read
Configure API Portal
This topic describes how to deploy API Portal in multiple datacenters using the recommended deployment architecture (Multi-datacenter deployment with shared file system).
Configure the database cluster for multiple datacenters
You must configure a relational database management system (RDBMS) to store API Portal data. Use a RDBMS cluster solution that supports connectivity across geographically distributed datacenters.
Note
You must install and configure the database on each database node in both datacenters before installing and configuring API Portal.The database cluster has the following requirements in a multi-datacenter production environment:
- The database must be supported by API Portal. For more information on supported databases, see Software requirements.
- For high availability (HA), it is best to have at least three database nodes in each datacenter (for example, to prevent data corruption due to split-brain syndrome). Install the database on each node.
- Choose a unique name for the database cluster.
- Do not start any of the databases until the database cluster is fully configured.
- You must synchronize time on all servers.
- Renaming a datacenter is not possible, so choose names carefully, and determine a naming convention for each datacenter and rack. For example:
- DC1, DC2
- RACK1, RACK2, RACK3
- To avoid firewall issues, you must open the RDBMS ports needed to allow bidirectional communication among the database nodes.
For more details on installing and configuring your database, see MySQL documentation or MariaDB documentation.
Configure the shared file storage
You must set up a shared file system between API Portal instances to keep them synchronized. For better performance, it is best to have a local shared file system in each datacenter, and sync the shared file systems between datacenters.
Configure API Portal
After setting up the database cluster, install API Portal. For HA, you must have at least two API Portal instances per datacenter.
Install API Portal for HA in multiple datacenters as a software installation
For HA, install API Portal on the first node, and then install it on each of the other nodes.
-
Install API Portal on the first node as detailed in Install API Portal as software installation.
- When prompted for database connection settings during the API Portal software installation, enter the access host of the database you created for this node.
- When asked if this is going to be HA setup with database replication, enter
y.
-
Install the EasyBlog and EasyDiscuss components on the first node as detailed in Install Joomla! components.
Note
When you change the Joomla! admininstrator password on the first node, the password is changed for all nodes. -
Install API Portal on each of the other nodes as detailed in Install API Portal as software installation. For each node:
- When prompted for database connection settings, use the same database server or cluster you used for the first API Portal instance.
- The installation checks the database connection and if it is successful for any node other than the first node, it asks you to confirm that this is a HA setup. Enter
y.
-
Install the EasyBlog and EasyDiscuss components on each other node as detailed in Install Joomla! components.
Upgrade API Portal for HA in multiple datacenters as a software installation
For HA upgrade, upgrade API Portal and perform the post-upgrade steps on each node as detailed in Upgrade API Portal software installation.
Configure load balancers
Configuring the load balancer may vary depending on the load balancer in question. Set up and configure the load balancer as instructed in the documentation of your load balancer.
You must situate the external load balancer to route traffic between the datacenters, and an internal load balancer in each datacenter to route the traffic between the API Portal instances.
Failover scenarios
This topic describes the expected behavior in case of a failover in API Portal multi-datacenter deployment.
One API Portal instance is down
In this scenario, one of the API Portal instances in a datacenter goes down:
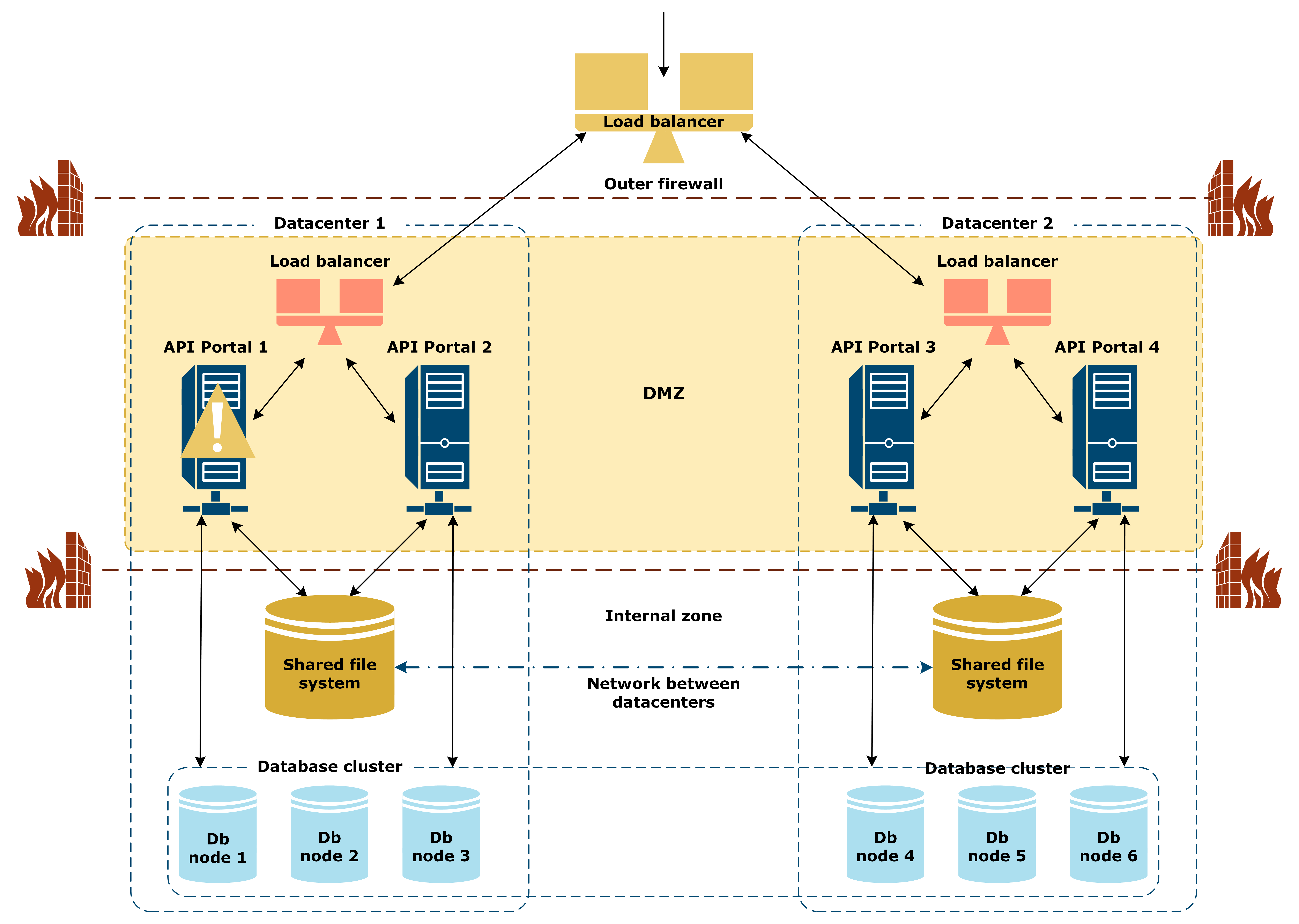
The following applies on this scenario:
- The API Portal instance that is down can no longer handle requests.
- All requests are handled by the remaining API Portal instances in the datacenter.
- You must restart the API Portal instance that is down.
One database node is down
In this scenario, one database node in a database cluster goes down:
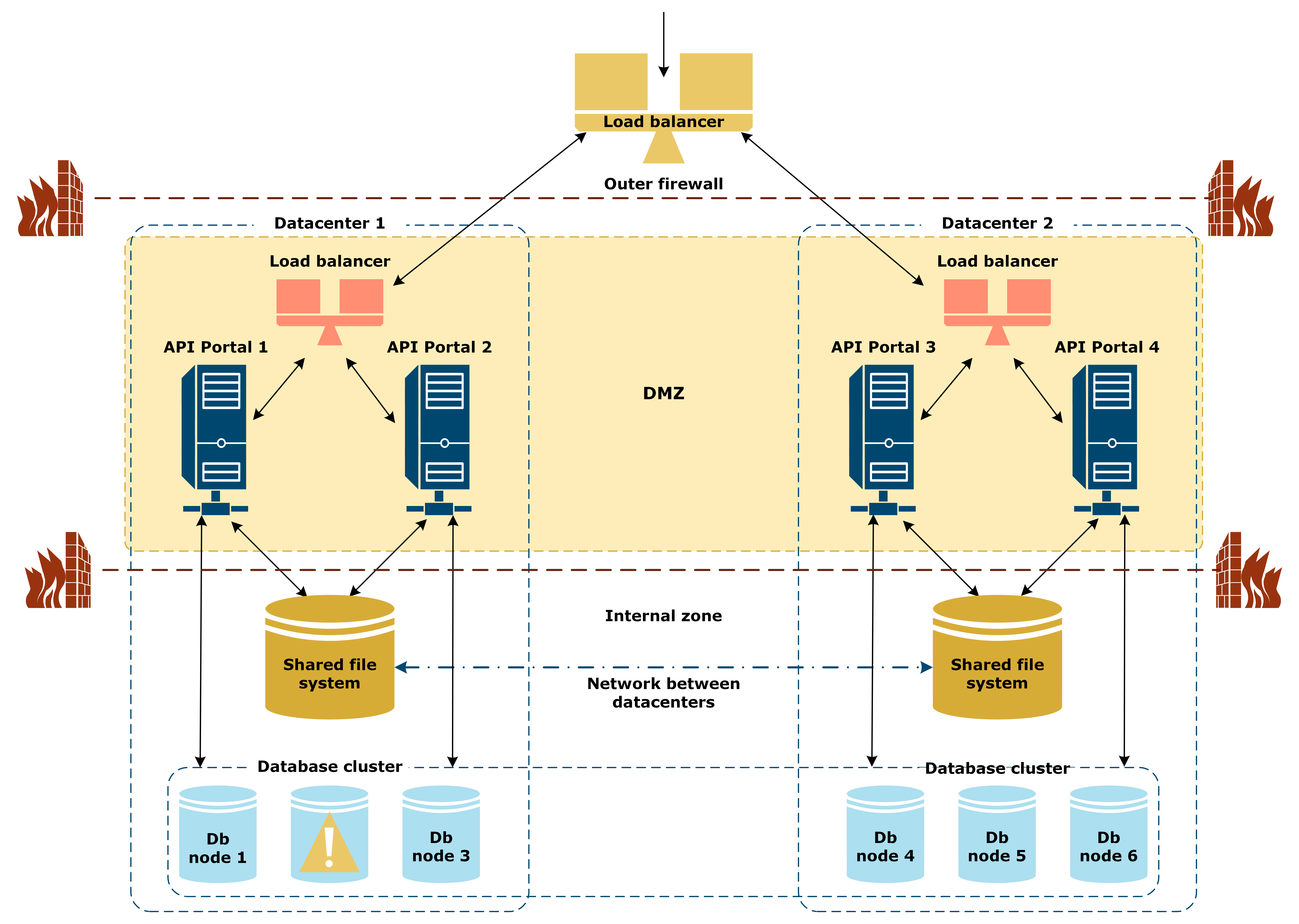
The following applies in this scenario:
- The database cluster tolerates the loss of a node in the cluster, and ensures 100% data consistency when the database cluster is configured for multiple datacenters.
- You must restart the database node that is down, and connect it to the cluster to synchronize and start operation.
Note
When a database node has been down and absent from a cluster for a time, you must repair the node after re-integrating it into the cluster. By design, the database node eventually becomes consistent with the other nodes.A full datacenter is down
In this scenario, a full datacenter goes down:
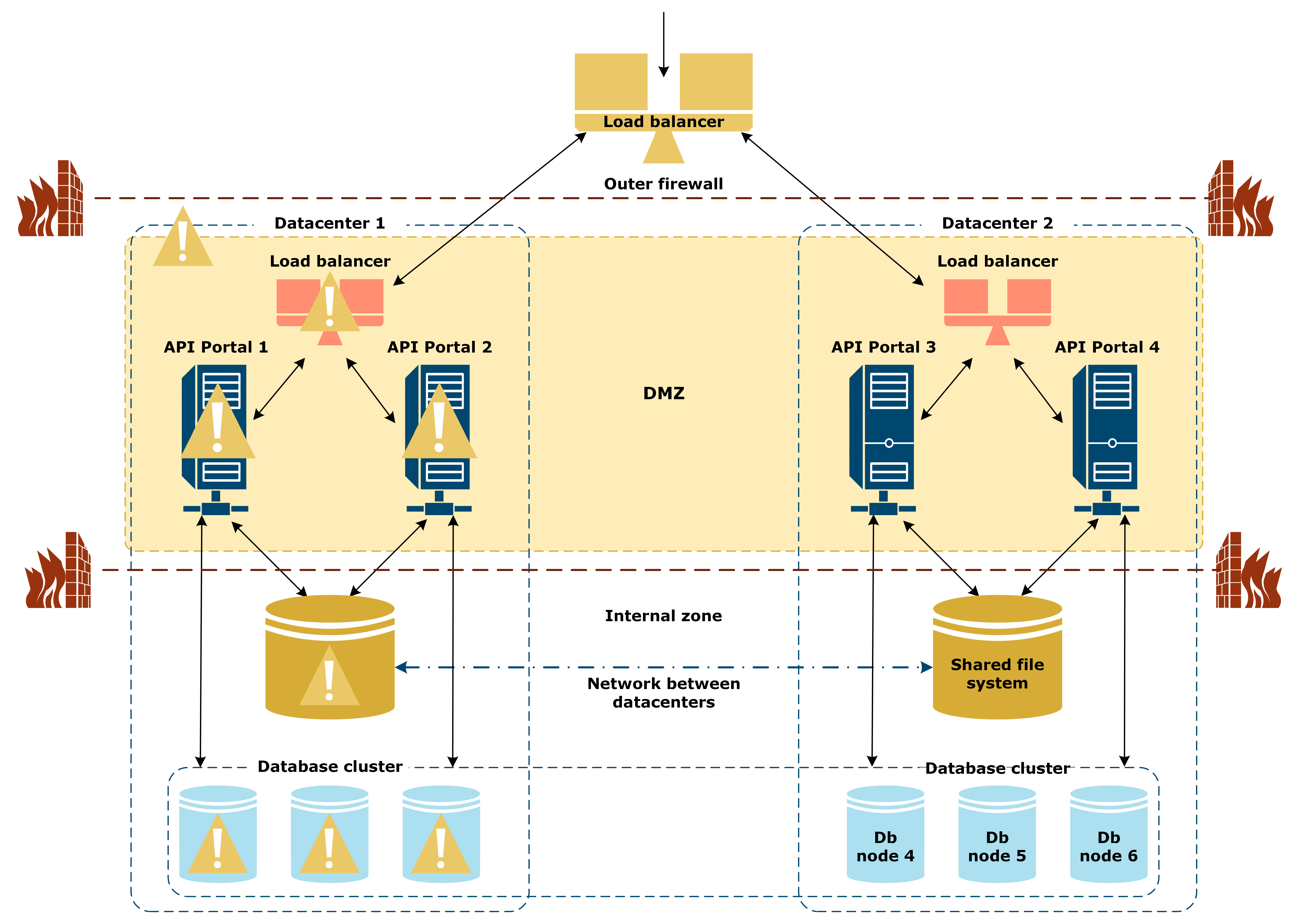
The following applies in this scenario:
- The datacenter that is down can no longer handle requests.
- Load balancer automaticalle routes all requests to the remaining datacenters.
- API Portal quotas remain the same but over less servers.
- Do not deploy more data to the remaining API Portal instances until the system is back to normal.
Restart the datacenter
Restart the failed datacenter in the following sequence:
- Restart the database nodes on the failed datacenter.
- When all database nodes are running and synchronized with rest of the clusters in the running datacenters, restart the API Portal instances on the failed datacenter.
- Synchronize the shared file system on in the failed datacenter with the other datacenters.
The network between two datacenters is down
In this case, the network between DC 1 and DC 2 is down, while both datacenters remain active:
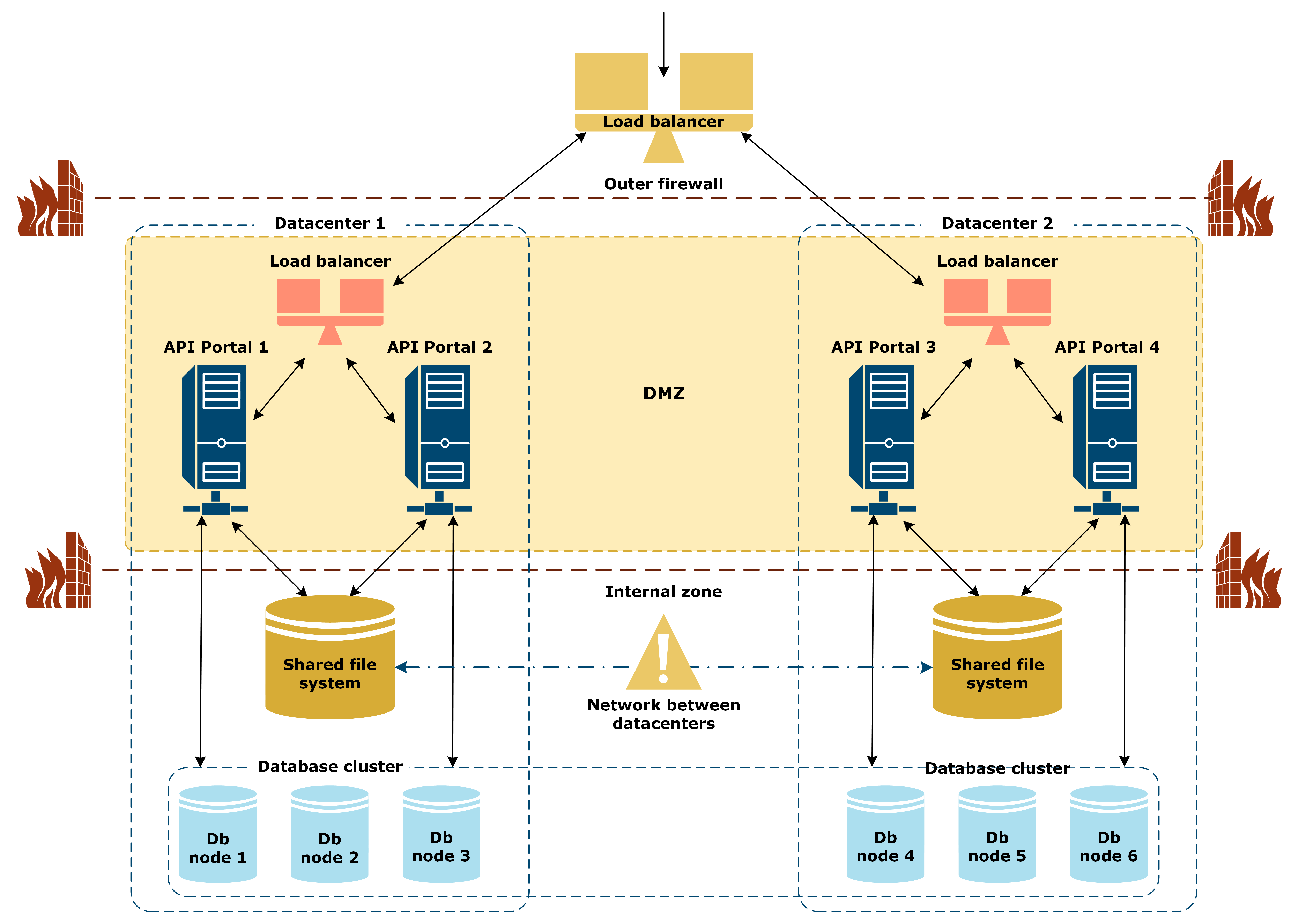
The following applies in this scenario:
- Datacenters are still operating independently.
- The data in the database clusters or in the shared file system is not synchronized between the datacenters until the network recovers. Do not deploy any updates to data.
- When the network recovers, all data is resynchronized automatically.