API management use cases
4 minute read
Cloud application connector use cases
This topic introduces the primary use cases for the cloud application connectors provided by API Manager.
API management for digital transformation
Companies are focusing on ways to open up their existing business, deliver new channels, and support new business models using REST APIs. They are adopting API management capabilities such as web service and REST API registration and API catalog. Companies need to deliver new initiatives much faster, reducing cost, and improve overall business performance.
To deliver these new initiatives, companies need an easy and fast way to register their application APIs and expose them safely to their employees, customers, and partners. The following architecture diagram shows how companies can manage their cloud application APIs using API Manager:
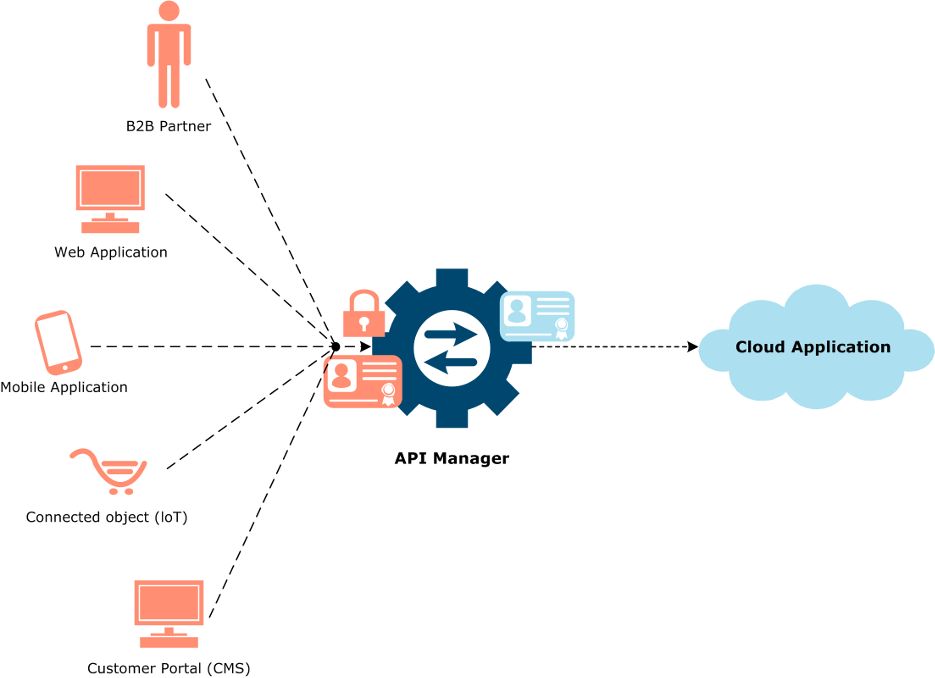
The primary user role in this use case is the API administrator. The policy developer is a secondary role. In some organizations, both roles may be performed by the same person.
API administrator role
The API administrator performs the following tasks:
- Registers specific cloud application APIs
- Browses the APIs exposed by a selected cloud application
- Registers the required APIs for the business objects to expose
- Virtualizes the registered cloud application APIs
- Chooses the authentication profile to connect to the cloud application
- Sets the security profile to secure the exposed APIs to end users
Policy developer role
The policy developer performs the following tasks:
- Defines the cloud application connection details to enable API registration from the application
- Defines the connection parameters to connect API Manager to the cloud application
- Sets the authentication configuration to enable API Manager to connect to the cloud application
- Defines the cloud application connection details to enable end-user API consumption
- Sets the authentication configuration to enable API Manager to connect to the cloud application on behalf of the end user
Hybrid application integration platform
Companies are now more and more willing to extend their application integration across and beyond the firewall to leverage the benefits of their cloud services. They are now adopting simple and web-based approaches to integrate and hide the complexity of orchestration, data transformation, and error handling with pre-built application connectors. These support the most common integration patterns for both cloud services and on-premise applications.
Cloud service integration
The following architecture diagram shows an overview of using API Manager to integrate two cloud services:
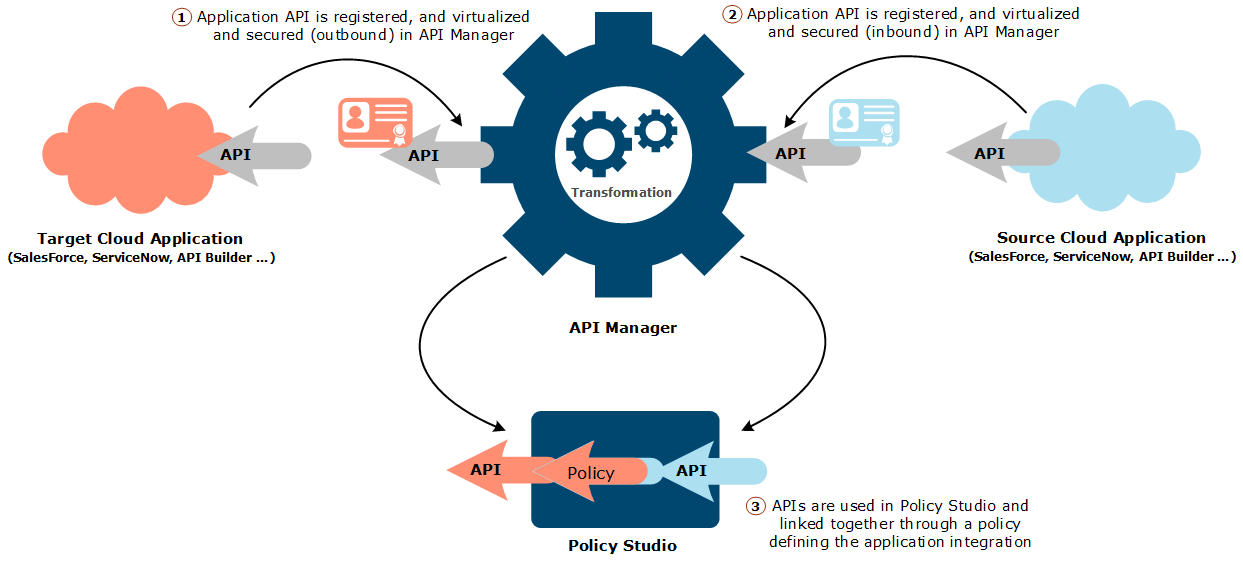
In this scenario, the target and source cloud applications both expose their APIs. The policy developer performs the following tasks:
- Defines the connection and authentication settings to connect API Manager to those applications for browsing, and registers their APIs so that applications can send and receive data
- Virtualizes and sets the runtime authentication configuration of both applications so that API requests can be sent by the source application to API Manager, and received by the target application from API Manager
- Links the source application API to the transformation policy, which sends transformed API requests to the target application API
Cloud service and on-premise application integration
The following architecture diagram shows an overview of using API Manager to integrate a cloud service with an on-premise application:
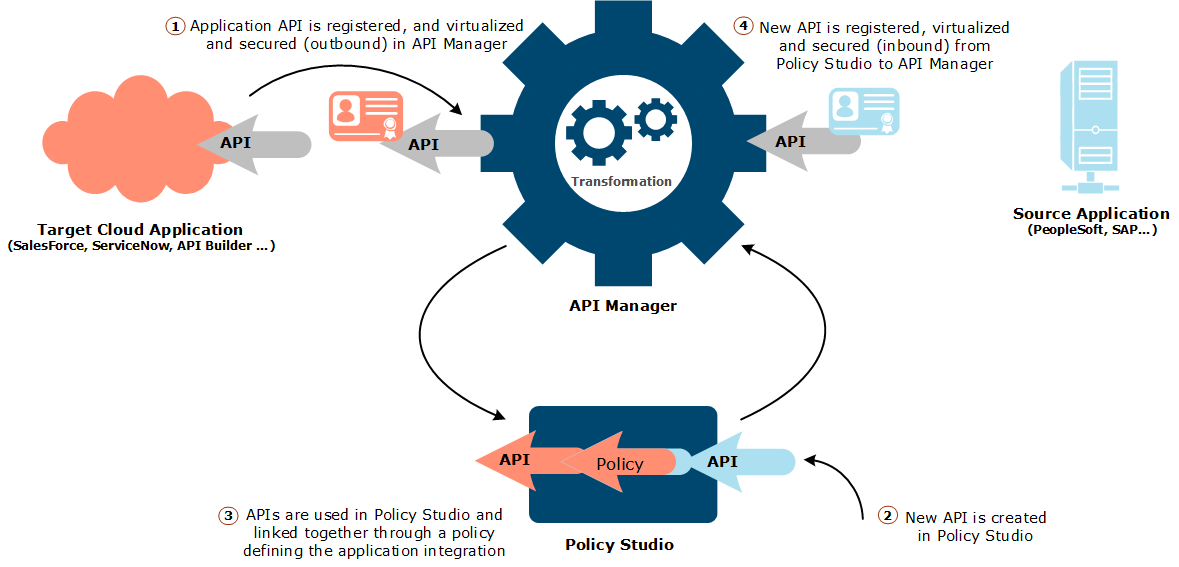
In this scenario, only the target cloud application exposes its APIs. The policy developer performs the following tasks:
- Defines connection and authentication settings to connect API Manager to the target cloud application so that it can browse and register its APIs and send it data
- Virtualizes and sets the runtime authentication configuration of the target cloud applications so that API requests can be received by the target application from API Manager
- Creates a new API to be exposed to the source application (specific development may be required in the source on-premise application to use the newly created API)
- Links this new API to the transformation policy, which will send transformed API requests to the target application API
- Registers, secures, and exposes this new API in API Manager so that it can be consumed by the source application