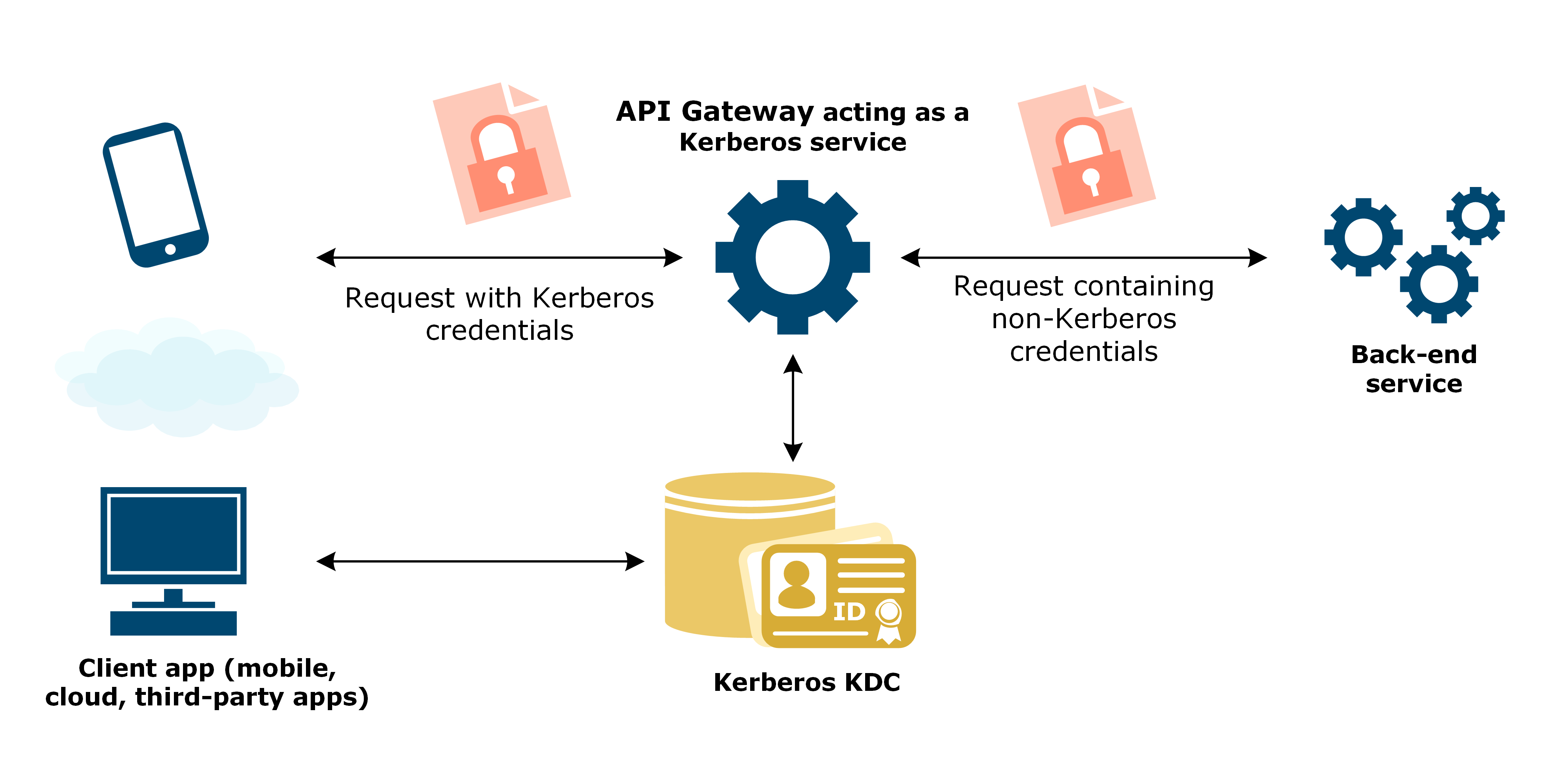
API Gateway as a Kerberos service
14 minute read
In this scenario:
- Client application: Supports Kerberos authentication.
- Back-end service: Requires non-Kerberos authentication (for example, OAuth or SAML).
- API Gateway: Acts as a Kerberos Service authenticating the client application, then authenticates to back-end service.
If the back-end service requires a non-Kerberos authentication, but the client application supports only Kerberos authentication, API Gateway can act as a Kerberos service, and mediate the authentication to the back-end.
A Kerberos client app, such as a standard browser, authenticates to API Gateway using Kerberos authentication. API Gateway then authenticates to the back-end service using a non-Kerberos authentication mechanism.
Prerequisites
Before you start configuration, you must have API Gateway installed on any machine with access to the Windows Domain Controller. The machine does not have to be a Windows machine that is part of the Windows Domain.
Example names
For the example in this section, a client application supporting Kerberos connects to the Kerberos service ServiceGateway running on the host machine gateway.axway.com connects to an existing back-end service.
The example Kerberos realm name AXWAY.COM is specific to the examples in this guide. Replace the example realm name with your own realm name.
The next sections describe the steps to configure the gateway as a Kerberos service.
Configuration process
The most common client application in this scenario is a browser, so this example focuses on that. For instructions on how to configure your browser, see Configure your browser to authenticate to API Gateway.
The connection between the client application and API Gateway acting as the Kerberos service is by default unsecured. For security reasons, it is recommended to enable SSL/TLS connection in the Kerberos service. SSL/TLS is configured in the SSL port on the Kerberos service, but you must also configure your browser separately to use SSL/TLS connection. For more details, see Configure browser authentication over SSL/TLS.
Configure a user account in Active Directory
This section describes how to configure a Kerberos service principal for API Gateway in Active Directory acting as the Key Distribution Centre (KDC).
Configure a user account for API Gateway
-
On the Windows Domain Controller, click Control panel > Administrative Tools > Active Directory User and Computers.
-
Right-click Users, and select New > User.
-
Enter the host name of the machine running API Gateway in the First Name and User Logon Name fields. For example, if the host name is
gateway.axway.com, entergateway. -
Click Next.
-
Enter the password, and do the following:
- User must change password at next logon: Deselect this.
- User cannot change password: Select this.
- Password never expires: Select this.
This ensures that a working API Gateway configuration does not stop working when a user chooses, or is prompted to change their password. API Gateway does not track these actions.
If these options are not suitable in your implementation and a user password changes in Active Directory, you must then update the password or keytab of the Kerberos client or service related to the user in Policy Studio, and redeploy the configuration to API Gateway.
If you cannot deselect User must change password at next logon, ensure the user changes the password and that the new password or keytab is deployed to API Gateway before API Gateway attempts to connect as this user.
You can store Kerberos passwords in a KPS table to update a changed password in runtime. For more details, see Use KPS to store passwords for Kerberos authentication.
-
Click Next > Finish.
-
Right-click the new user gateway, and select Properties.
-
On the Account tab, select Use DES encryption types for this account.
-
Click Apply > OK.
As a Kerberos service, API Gateway authenticates the client application using Kerberos authentication. For the authentication to succeed, the client application must have an account configured in your Active Directory. For an example configuration, see Configure a user account in Active Directory.
Map an SPN to the user account
You must map a Service Principal Name (SPN) to the user account you created (gateway@AXWAY.COM).
-
On the Windows Domain Controller, open a command prompt.
-
Enter the following
ktpasscommand:ktpass -princ HTTP/<host>@<Kerberos realm> -mapuser <user> -pass password -out <user>.keytab -crypto rc4-hmac-nt -kvno 0The SPN is of the format
HTTP/<host>@<Kerberos realm>, where<host>is the name of the host running the Kerberos service,gateway.axway.comin this case:ktpass –princ HTTP/gateway.axway.com@AXWAY.COM –mapuser gateway –pass Axway123 –out gateway.keytab –crypto des-cbc-md5 –kvno 0Replace
gateway.axway.comwith the full host name your browser will use when connecting to API Gateway.
ReplaceAXWAY.COMwith your Kerberos realm name. Note that the realm name should be uppercase.This command creates an SPN
HTTP/gateway.axway.com@AXWAY.COM, which is mapped to the user account (gateway).The command also creates a keytab file for the account that you can use later when configuring the Kerberos service in Policy Studio. See Configure Kerberos principal.
If you do not want to create a keytab file, you can use the following command:
setspn -A HTTP/<host> <user>
If you view the user properties, you see that the user logon name has changed.
DNS considerations
A web browser is the most likely client application authenticating to API Gateway acting as the Kerberos service.
When a browser requests a service ticket from the Kerberos KDC, the browser presents the SPN for the service it wants to connect to. The SPN is based on the host name in the URL entered in the browser.
For example, if the user enters http://gateway.axway.com:8080/kerberos, the SPN that the browser passes to the Kerberos KDC to acquire a service ticket is HTTP/gateway.axway.com@AXWAY.COM.
If the host name is defined in the DNS as a host (A-name), the SPN is directly resolved from the host:
The DNS server has the following DNS record defined:
HOST(A): gateway.axway.com
The following URL is entered in the client browser:
URL: http://gateway.axway.com:8080/kerberos
The requested SPN is:
HTTP/gateway.axway.com
If DNS aliases (C-names) are used as host names, the SPN is resolved by mapping the C-name to a DNS A-name:
The DNS server has the following records defined:
HOST(A): gateway.axway.com
Alias (CNAME): test -> gateway.axway.com
The following URL is entered in the client browser:
URL: http://test.axway.com:8080/kerberos
The requested SPN is:
HTTP/gateway.axway.com
If all host names are defined as hosts (A-names) in the DNS, you must map separate SPNs for the hosts to the user account you configured.
If the DNS uses aliases (C-names), it is not necessary to map additional SPNs.
Map additional SPNs to the user account
You can map more than one SPN to a user account, if many browser users need to refer to the API Gateway machine using different host names, for example, http://gateway.axway.com:8080/kerberos and http://test.axway.com:8080/kerberos.
-
To map additional SPNs to the user account, enter the following command:
setspn -A HTTP/test.com gatewayThe output looks like this:
Registering ServicePrincipalNames for CN=gateway,CN=Users,DC=axway,DC=com` HTTP/test.axway.com Updated object -
To list the SPNs mapped to a user account, enter the following command:
setspn –L gatewayThe output looks like this:
Registered ServicePrincipalNames for CN=gateway,CN=Users,DC=axway,DC=com: HTTP/test.axway.com HTTP/gateway.axway.com
Configure Kerberos principal
Add Kerberos principal for API Gateway acting as a Kerberos service using Policy Studio.
The client application can provide Kerberos token to API Gateway using Kerberos, and the back-end service supports some other authentication mechanism, so you do not need to configure Kerberos principals for them.
- In the node tree, click Environment Configuration > External Connections > Kerberos Principals.
- Click Add a Kerberos principal.
- Enter a name, such as
ServiceGateway. - In Principal Name, enter the SPN you mapped to the user account on Active Directory (
HTTP/gateway.axway.com@AXWAY.COM). - Ensure Principal Type is set to
NT_USER_NAME, and click OK.
Configure API Gateway policy
This section describes how to configure API Gateway as the Kerberos service using Policy Studio.
Configure a Kerberos service
- In the node tree, click Environment Configuration > External Connections > Kerberos Services, and add a new Kerberos service.
- Enter a name for the service, such as
ServiceGateway Kerberos Service, and select the Kerberos Principal you configured (ServiceGateway). - Click Enter Password, and enter the password for
gateway@AXWAY.COM. - On the Advanced tab, set Mechanism to SPNEGO_MECHANISM, and click OK.
Configure the Kerberos authentication
Configure the Kerberos policy for API Gateway as the Kerberos service.
To start, add a new policy named, for example, Kerberos Service SPNEGO.
- Open the Authentication category in the palette, and drag a Kerberos Service filter onto the policy canvas.
- Select the Kerberos service you configured (
ServiceGateway Kerberos Service), select SPNEGO Over HTTP, and click OK. - Right-click the Kerberos Service filter on the policy canvas, and select Set as Start.
Configure connection to the back-end service
- Configure the authentication mechanism the back-end service requires. The required filters and configuration details depend on the type of authentication. For more details on different authentication methods.
- Open the Routing category in the filter palette, and drag a Connect to URL filter onto the policy canvas.
- Enter the URL used that invokes the back-end service, and click Finish.
Build the policy
-
Click Add Relative Path icon, create a new relative path
/gw-service-to-back-endthat links to the Kerberos policy, and click OK. -
Connect the filters with success paths.
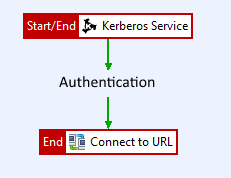
The policy has the following flow:
- API Gateway authenticates the client application, such as a browser, using Kerberos authentication.
- API Gateway creates the authentication tokens the back-end service requires.
- API Gateway connects and authenticates to the back-end service.
If API Gateway can map the Kerberos credentials received from the client app to the end-user-specific credentials in the non-Kerberos authentication mechanism, API Gateway can authenticate the actual end user to the back-end service.
-
Click the Deploy icon to deploy the configuration to API Gateway.
You have now configured and deployed a simple Kerberos policy for SPNEGO authentication.
The most common client application in this scenario is a standard browser. In addition to configuring API Gateway, you must also configure your browser to authenticate to API Gateway. For more details, see Configure your browser to authenticate to API Gateway.
By default, the connection between the browser and API Gateway acting as the Kerberos service is by default unsecured. For details how to change to a secured connection, see Configure browser authentication over SSL/TLS.
Configure your browser to authenticate to API Gateway
This section describes how to configure your browser to authenticate to API Gateway acting as the Kerberos service.
Configure Internet Explorer
-
Open Internet Explorer on a machine connected to your Kerberos realm (
AXWAY.COM). -
Click Tools > Internet Options.
-
On the Advanced tab, select Enable Integrated Windows Authentication, and click OK.
-
Restart Internet Explorer, and click Tools > Internet Options.
-
On the Security tab, click Local Intranet > Sites > Advanced.
-
In Add this website to the zone, enter your host name (
http://gateway.axway.com), and click Add.You do not have to enter the port or the relative path, and you can use wildcards for the host name (http://*.axway.com).Ensure the host name matches the SPN you mapped to the user account in Active Directory. The SPN must also match the host name the client browser authenticating to API Gateway specifies in the URL. See Map an SPN to the user account.
-
Click Close, and on the Security tab, click Local Intranet > Custom Level.
-
Select Automatic login only in Intranet zone, and click OK.
Configure Firefox
-
Open Firefox on a machine connected to your Kerberos realm (
AXWAY.COM). -
In the address bar, enter
about:config. If you get a warning prompt on changing the advanced settings, accept it. -
Right-click the preference name network.negotiate-auth.trusted-uris, and select Modify.
-
Enter your host name (
http://gateway.axway.com). If you have multiple entries, separate them with a comma.Ensure the host name matches the SPN you mapped to the user account in Active Directory. The SPN must also match the host name the client browser authenticating to API Gateway specifies in the URL. See Map an SPN to the user account.
-
Click OK.
Test the configuration
To test the policy, you need a client app that can get a Kerberos token, such as a standard browser.
- On a machine connected to your Kerberos realm (
AXWAY.COM), start the browser you want to test. - Enter the URL of API Gateway (
http://gateway.axway.com:8080/gw-service-to-back-end).
API Gateway authenticates the Kerberos user, passes the request to the back-end service, and passes the response from the back-end service back to the browser.
The Traffic Monitor tab on the API Gateway Manager (https://localhost:8090) is an excellent place to view and troubleshoot the message flows. For more details, see Monitor services in API Gateway Manager.
For details how to change the configuration to use a secure connection, see Configure browser authentication over SSL/TLS.
Configure browser authentication over SSL/TLS
The connection between the browser and API Gateway acting as the Kerberos service is by default unsecured. For security reasons, it is recommended to use a secure SSL/TLS connection when connecting to the API Gateway.
This section describes the additional configuration steps required to enable a browser to authenticate to the API Gateway using SPNEGO over a secure SSL connection.
The configuration of Kerberos principal, Kerberos service, and Kerberos service policy remains the same as with insecure connection. For details, see Configure Kerberos principal and Configure API Gateway.
The next sections describe how to enable SSL connection.
Configure API Gateway for SSL/TLS connection
This section describes how to import an existing SSL certificate for API Gateway and configure an HTTPS interface in Policy Studio.
Import an SSL certificate
To enable SSL/TLS connection, you must have a valid SSL certificate.
- In the node tree, click Environment Configuration > Certificates and Keys > Certificates.
- Click Create/Import.
- Click Import Certificate…, and select the certificate file you want to use.
- Enter an alias for the certificate or click Use Subject, and click OK.
For more details on the fields and options in this configuration window, see Manage certificates and keys.
Configure an HTTPS interface
- In the node tree, click Environment Configuration > Listeners > API Gateway > Default Services > Ports.
- Click Add > HTTPS Interface, and enter a name for the interface.
- On the Network tab, set Port to
8081. - Click X.509 Certificate, select your SSL certificate, and click OK.
- Click the Deploy icon to deploy the configuration to API Gateway.
For more details on the fields and options in this configuration window, see Configure HTTP services.
You must configure your browser to use secure connection as well. For more details, see Configure your browser to use SSL/TLS connection.
Configure your browser to use SSL/TLS connection
This section describes how to configure your browser to authenticate with SPNEGO over SSL/TLS connection.
Configure Internet Explorer to use SSL/TLS connection
-
Open Internet Explorer on a machine connected to your Kerberos realm (
AXWAY.COM). -
Click Tools > Internet Options.
-
On the Security tab, click Local Intranet > Sites > Advanced.
-
In Add this website to the zone, enter your host name (
https://gateway.axway.com), and click Add. You do not have to enter the port or the relative path, and you can use wildcards for the host name (https://*.axway.com).Ensure the host name matches the SPN you mapped to the user account in Active Directory. The SPN must also match the host name the client browser authenticating to API Gateway specifies in the URL. See Map an SPN to the user account.
-
Click Close.
Configure Firefox to use SSL/TLS connection
-
Open Firefox on a machine connected to your Kerberos realm (
AXWAY.COM). -
In the address bar, enter
about:config. If you get a warning prompt on changing the advanced settings, accept it. -
Right-click the preference name network.negotiate-auth.trusted-uris, and select Modify.
-
Enter your host name (
https://gateway.axway.com). If you have multiple entries, separate them with a comma.Ensure the host name matches the SPN you mapped to the user account in Active Directory. The SPN must also match the host name the client browser authenticating to API Gateway specifies in the URL. See Map an SPN to the user account.
-
Click OK.
Test the SSL/TLS configuration
This section describes how to test the configuration for the browser SPNEGO authentication over SSL.
- On a machine connected to your Kerberos realm (
AXWAY.COM), start the browser you want to test. - Enter the URL of API Gateway (
https://gateway.axway.com:8081/gw-service-to-back-end).
When you start a new session, the browser might show some security alerts. Once the security alerts have been handled, the back-end Kerberos service should send a confirmation on a successful authentication.
Once the security alerts have been handled, API Gateway sends a response after authenticating the Kerberos user and passing the request to the back-end service.
The Traffic Monitor tab on the API Gateway Manager (https://localhost:8090) is an excellent place to view and troubleshoot the message flows. For more details, see .
Internet Explorer security alerts
When you start a new HTTPS session to API Gateway, Internet Explorer might show a security alert on the security certificate.
If you want to view the certificate details, click View Certificate. To proceed, click Yes.
To avoid the security alerts, you can import API Gateway’s SSL certificate to the trusted certificate store in the browser:
- In Internet Explorer, click Tools > Internet Options.
- On the Content tab, click the Certificates….
- Import the certificate, and close the dialog window.
Firefox security alerts
When you start a new HTTPS session to the API Gateway, Firefox may show a security alert for an untrusted connection.
If the security alert is displayed, follow these steps:
- Click I Understand the Risks.
- Click Add Exception > Get Certificate, and import the certificate.
- Click Close.
- Click Confirm Security Exception.
To avoid the security alerts, you can import API Gateway’s SSL certificate to the trusted certificate store in the browser:
- Open Firefox, and select Tools > Options > Advanced.
- On the Certificates tab, click View Certificates.
- Import the SSL certificate, and close the dialog window.