Wireshark tracing for Kerberos authentication
4 minute read
You can use Wireshark, a third-party trace tool, to view the SPNEGO token data sent between a Kerberos client and service when the client authenticates to the service. For more details on Wireshark and to download and install the program, go to Wireshark web page.
In SPNEGO Kerberos authentication, Kerberos tokens are sent between the client and service using the Authorization HTTP header. Wireshark can parse, decrypt, and view the content of these tokens.
Because Wireshark can trace any application acting either as the Kerberos client or service, the information in this section is applicable for both API Gateway and third-party applications.
Use Wireshark to trace authentication between the client and service
SPNEGO tokens are used only for the Client-Server Authentication Exchange (the AP_REQ and AP_REP Kerberos messages) between the client and service. The AP_REP the Kerberos client sends to the Kerberos service contains a service ticket encrypted with the service’s secret key. To view this data decrypted, you must import the service’s keytab to Wireshark.
The messages sent between the client and the KDC to acquire TGTs and service tickets are not covered by SPNEGO. For information on how to view these messages in Wireshark, see Use Wireshark to trace Authentication Service Exchange and Ticket-Granting Service Exchange.
Import a Kerberos service keytab file into Wireshark
-
If you do not yet have a keytab file for your Kerberos service, create one by running the following command on the Windows Domain Controller:
ktpass -princ <Kerberos service>@<Kerberos realm> -pass ****** -out wireshark.keytab -ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPALFor example:
ktpass -princ ServiceGateway@AXWAY.COM -pass ****** -out wireshark.keytab -ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL -
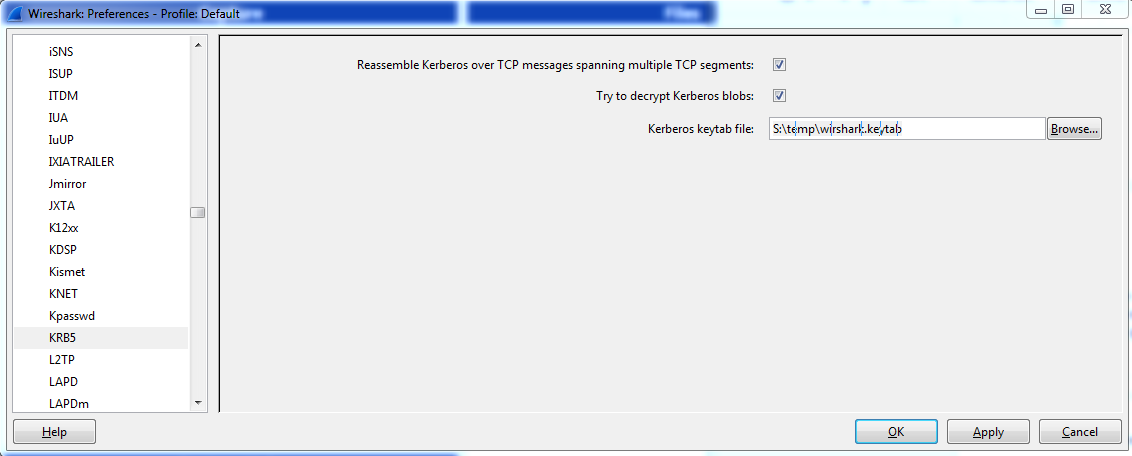
In Wireshark, click Edit > Preferences > Protocols > KRB5.
-
Click Browse, and select the keytab file of your Kerberos service.
-
Select Try to decrypt Kerberos blobs, and click Apply.
-
Click OK.
Capture and analyze a Wireshark trace
If you have the Kerberos client and Kerberos service running on separate machines, run Wireshark on the same machine as the Kerberos client.
-
Start a Wireshark capture with the following filter:
ip.addr==<ip address of the machine running Kerberos service> and kerberosFor example:
ip.addr==10.142.9.178 and kerberos -
Send a message from the Kerberos client to the Kerberos service.
The Kerberos client calls the Kerberos service on the configured path (for example,
POST /servicein the Wireshark trace details).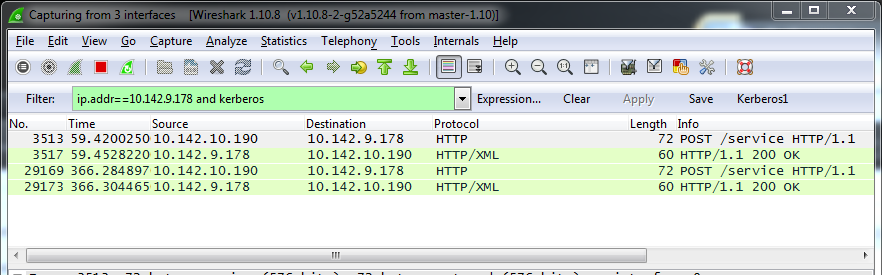
-
Select one of the
POST /<path>lines in the top panel, and open theHypertext Transfer Protocolin the lower panel. -
To view the contents of the SPNEGO token sent from the Kerberos client to the Kerberos service, open the
AuthorizationHTTP header. For example: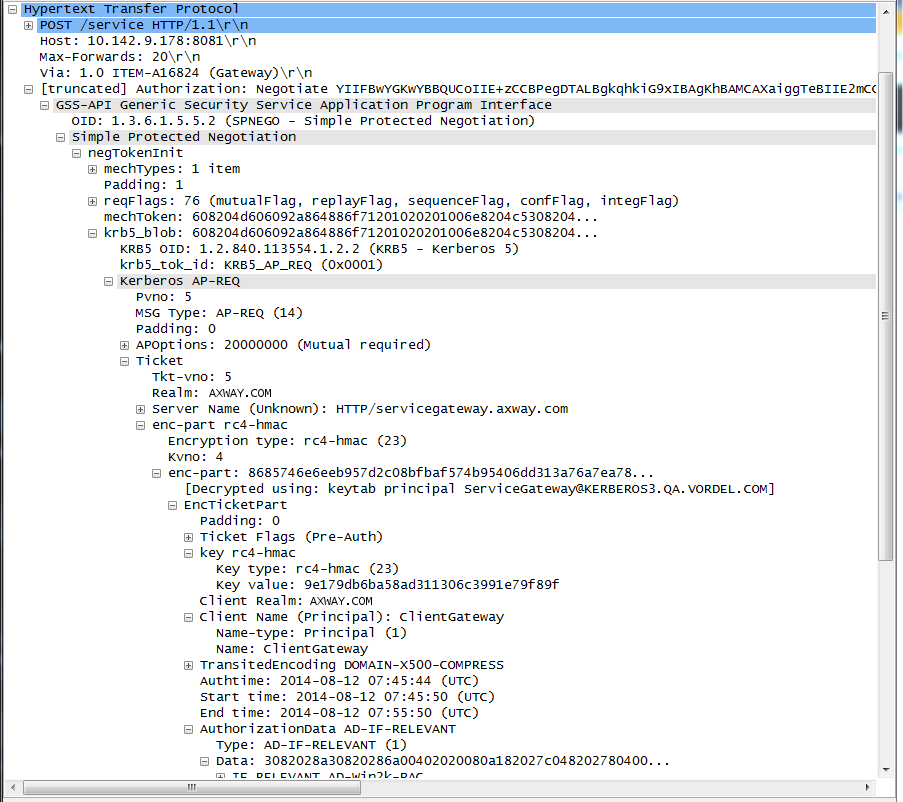
-
To view the response SPNEGO token the Kerberos service sends to the Kerberos client in the
WWW-Authenticate HTTPheader, select one of theHTTP/1.1 200 OKlines in the top panel, and expand theHypertext Transfer Protocolin the lower panel. For example: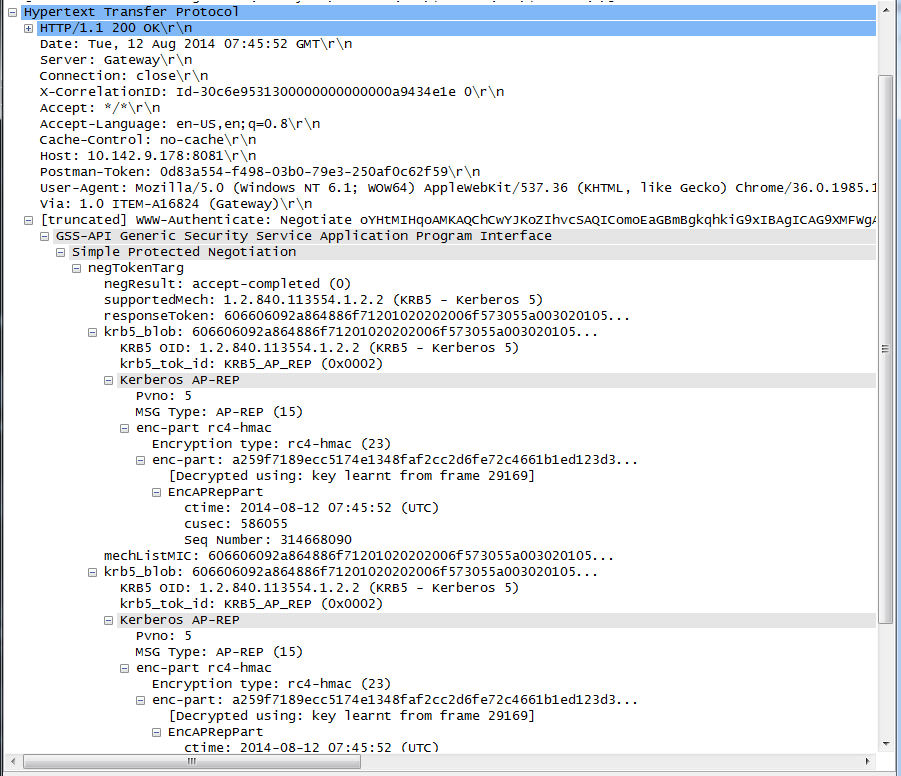
-
When tracing credential delegation, you must set the
forwardableflag and thedelegFlagin thereqFlagtotruein the tickets.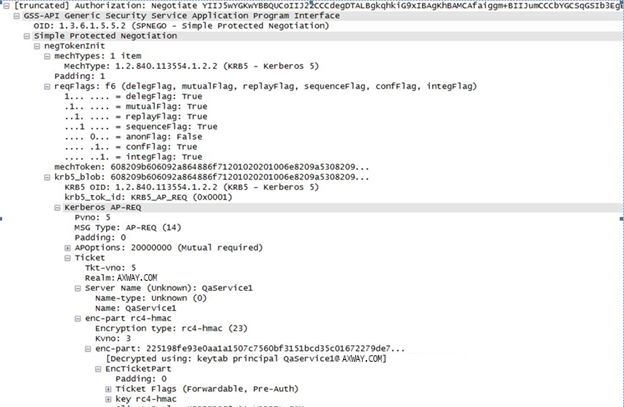
Use Wireshark to trace Authentication Service Exchange and Ticket-Granting Service Exchange
You can use Wireshark to trace the Kerberos traffic between the Kerberos client and the Kerberos KDC (Windows Domain Controller). This traffic relates to the Kerberos Authentication Service Exchange (AS-REQ and AS-REP) and the Ticket-Granting Service Exchange (TGS-REQ and TGS-REP) when the client requests the TGT and service ticket.
If you have the Kerberos client and Kerberos service running on separate machines, run Wireshark on the same machine as the Kerberos client.
-
Start a Wireshark capture with the following filter:
ip.addr==<ip address of the Windows Domain Controller> and kerberosFor example:
ip.addr==10.0.7.78 and kerberos -
Restart API Gateway running the Kerberos client. If the Kerberos client is a 3rd party application, you most likely need to restart the application as well to ensure that a cached TGT and service ticket are not used.
-
Send a message from the Kerberos client to the Kerberos service.
The Kerberos traffic is as follows:
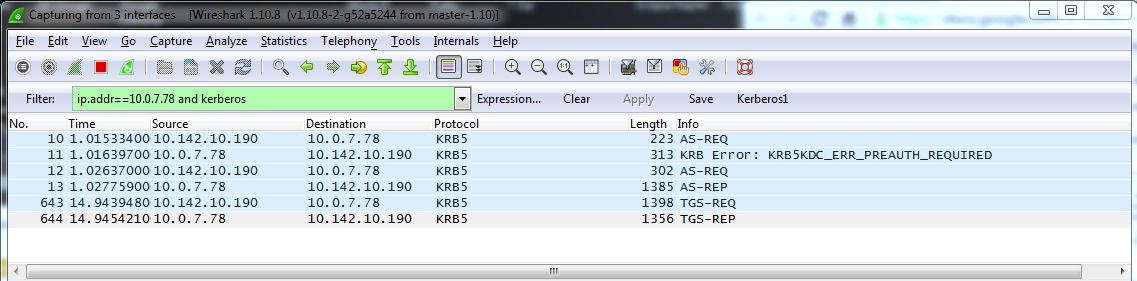
- The
AS-REQandAS-REPare generated at the startup of API Gateway, because this is when the TGT for the Kerberos client is requested from the KDC. The TGT is only re-requested when it expires, because the TGT is cached in API Gateway. - The
TGS-REQandTGS-REPare created when the Kerberos client sends a message to the Kerberos service to request the service ticket for the Kerberos service. TheTGS-REQis only sent from the Kerberos client on the first request, or when the service ticket has expired, because the service ticket is cached in API Gateway. - The service ticket is encrypted with the secret key of the Kerberos service. To view the content decrypted, you must have the keytab of the Kerberos service imported in the Wireshark. See Use Wireshark to trace SPNEGO Kerberos authentication between the client and service.