Elastic deployment overview
4 minute read
Deploy API Gateway and API Manager in Docker containers on a cloud platform hosted by infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) providers, and use the elastic capability that their automation tools and techniques provide. This enables you to manage the load on your system easily, adding and removing nodes as needed.
Deployment process
To deploy your API Gateway or API Manager topology in containers, you must have an automated continuous integration (CI) pipeline spanning all your environments from development to production. The CI pipeline moves a Docker image from one environment to another. However, the image is always specific to a single environment, and you use the promoted image as the base image when creating the Docker image. You must update the configuration files to match the configuration of the environment (for example, certificates, ports, and back-end URLs often change between environments). If you are using API Manager, during promotion APIs are exported from the previous environment, environmentalized, and imported into the new environment.
You can download Docker scripts for API Gateway and Admin Node Manager from Axway Support, and use these scripts to create the Docker images. You can then include your .fed and other configuration files in the API Gateway base image in your development environment to create a customized API Gateway Docker image.
Because the .fed files are not separately deployed but included in the Docker image, after the image is created, it is immutable. However, you can create multiple Docker images with different .fed files as needed and deploy them as required. Containers from each image (containing the same .fed file) form a group that scales independently from other groups, and you can use a load balancer to route traffic from one group to another.
Example containerized topology
In the classic, non-containerized deployment, the topology is managed internally through an Admin Node Manager communicating with Node Managers in API Gateway nodes.
However, in a container deployment the topology is externally managed. Instead of the Admin Node Manager, a cluster manager, such as Openshift or Kubernetes, manages the topology and communicates directly with each API Gateway. The API Gateway Docker images do not include a Node Manager.
The following diagram shows an example of the topology in container deployment:
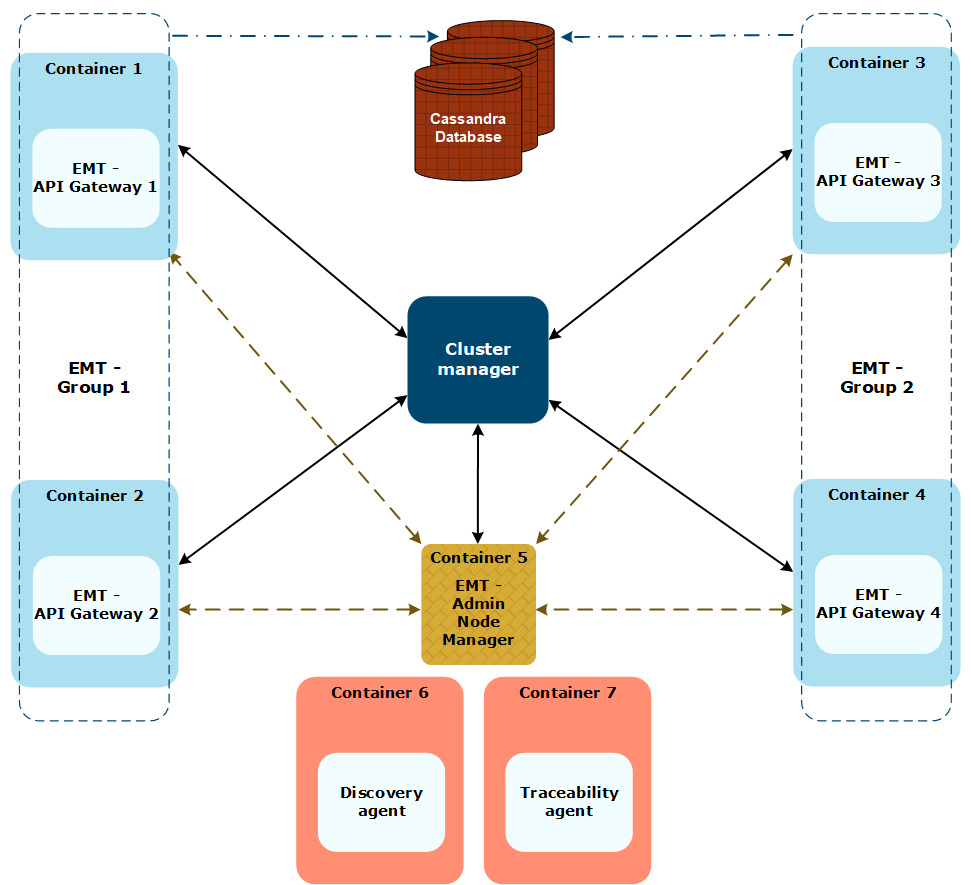
API Gateway containers
In this example, four API Gateway nodes run in Docker containers:
- The containers have been deployed from two images that use different
.fedfiles (file1.fedandfile2.fed), thus forming two groups,EMT - Group 1andEMT - Group 2. - Because there are no Node Managers, each API Gateway node exposes the management interface directly on port
8085.
Admin Node Manager container
The topology includes an Admin Node Manager, but with a different role than in the classic deployment:
- Admin Node Manager does not manage the topology, but is managed by the same cluster manager as the API Gateway nodes.
- Admin Node Manager provides access to monitoring data and runtime settings.
- Admin Node Manager builds a dynamic picture of the topology:
- New API Gateway nodes automatically start sending transaction event logs to Admin Node Manager when they are started.
- Admin Node Manager listens to the API Gateway nodes, processes the received logs and writes them to the metrics database.
- The Admin Node Manager container uses a shared volume to access the transaction event logs from API Gateway containers.
Cluster manager
A cluster manager such as Openshift or Kubernetes manages the topology and adds or removes nodes as the load on the system changes:
- When a node is added, the image for the new node is passed to the cluster manager that starts the required number of containers.
- When a node is removed, the cluster manager waits for the traffic to the node to stop before removing it.
Apache Cassandra
If the deployment includes API Manager, Apache Cassandra is configured for high availability (HA) to store API Manager data and Key Property Store (KPS) tables. For more details, see Configure a Cassandra HA cluster.
Discovery and Traceability agents
If the deployment includes API Manager, Discovery and Traceability agents can be used to send information to Amplify Central. For more information, see Set up Discovery agent and Set up Traceability agent.