Install and configure database server
7 minute read
Installation
For details on how to install a database using yum, see the following:
If your database is on a remote host, you must configure a MySQL client or a MariaDB client on the API Portal host.
Configure the database server settings
Connect to your MySQL or MariaDB database, and configure the database for API Portal in the /etc/my.cnf configuration file as follows:
- To restrict the interfaces the database listens on, add
bind-address = 127.0.0.1under the[mysqld]line. - Set the value for
expire_logs_days. The default is0, no automatic removal. - Set the maximum size of the binary log file in
max_binlog_size. - Set the maximum number of connections in
max_connections. The default is151. - Set the size of the buffer pool in
innodb_buffer_pool_size. - Set the size of the log files in a log group in
innodb_log_file_size. - Set the size of database storage to a minimum of 100 MB. This is the recommended value for the most common environments, which include the use of blog posts, forums, comments, and so on.
- Enable the creation of non-deterministic stored functions by setting
log_bin_trust_function_creatorsto1.
For more details on the variables and how they affect the performance of the database server, see MySQL Server System Variables or MariaDB Server System Variables.
Configure the database server for secure connection
If you have a remote MySQL or MariaDB database server, you must configure it to use a secure connection between the database and your API Portal installation. After configuring your database server, you are prompted during the API Portal installation to use the secure connection.
To generate the SSL-RSA certificates and enable SSL in the MySQL or MariaDB server, connect to your database server and perform the following steps.
Generate RSA certificates
You must first create the database server and the client certificate and key files. During the process, you must respond to several prompts from the Open SSL commands:
- To generate test files, press
Enterto all prompts except the one for Common Name (CN) of the server certificate (server-cert.pem). The CN must match the host you will use for connecting, and it must differ from the root and client hosts certificates. - To generate files for production use, you must provide (non-empty) responses.
-
To create the RSA certificates, enter the following commands in the given order, and respond to any prompts you receive:
mkdir -p /etc/mysql/certs cd /etc/mysql/certs openssl genrsa 2048 > ca-key.pem openssl req -new -x509 -nodes -days 3600 -key ca-key.pem > ca.pem openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -days 3600 -nodes -keyout server-key.pem > server-req.pem openssl x509 -req -in server-req.pem -days 3600 -CA ca.pem -CAkey ca-key.pem -set_serial 01 > server-cert.pem openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -days 3600 -nodes -keyout client-key.pem > client-req.pem openssl x509 -req -in client-req.pem -days 3600 -CA ca.pem -CAkey ca-key.pem -set_serial 01 > client-cert.pem -
To verify the generated certificate, enter the following command:
openssl verify -CAfile ca.pem server-cert.pem client-cert.pem -
Verify that the MySQL user have access (ownership, or at least read rights) to the generated certificates, otherwise MySQL could not use them and enable TLS configuration.
chmod -R a+r /etc/mysql/certs
Enable secure connection in the database server
To enable secure connection in the MySQL or MariaDB server-side configuration, do the following:
-
To start the database server so that it permits clients to connect securely, use options that identify the certificate and key files the server uses when establishing a secure connection:
ssl-caidentifies the CA certificate.ssl-certidentifies the server public key certificate. This can be sent to the client and authenticated against the CA certificate the client has.ssl-keyidentifies the server private key.
-
Edit the
/etc/my.cnffile as follows to configure the certificates:[mysqld] ... ssl-ca=/etc/mysql/certs/ca.pem ssl-cert=/etc/mysql/certs/server-cert.pem ssl-key=/etc/mysql/certs/server-key.pem -
Save the file and restart the database:
systemctl restart mysql
Verify the configuration
After configuring the MySQL or MariaDB database server with certificates, you need to make sure SSL is enabled on the server side.
-
Log in to the database server as the
rootuser:mysql -u root –p -
Enter the following command:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE '%ssl%';
You should get an output similar to the one below:
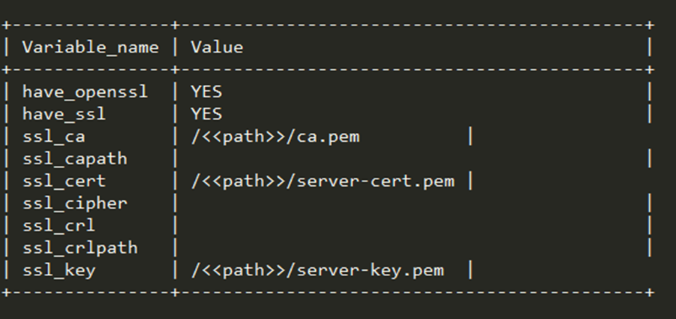
After you have successfully enabled SSL on the server, you must configure a user account with TLS authentication before you can use the secure connection.
Create a database and a user account for API Portal
You must create a database for API Portal to store your configuration data on the database server. Log in to the database server and enter the following:
CREATE DATABASE <database name>;
Make a note of your database name and port, as you must provide them when installing API Portal. For more details, see MySQL documentation or MariaDB documentation.
In addition, for API Portal to be able to connect to the MySQL or MariaDB database, you must configure a user account for API Portal on your database.
We recommend a strong password for this user account, which:
- is at least 10 characters long
- contains at least one digit
- contains at least one uppercase letter
- contains at least one lowercase letter
- contains at least one special character
!@#$%^&*
Configure a user account
If you do not want to use a secure connection, you can configure API Portal to use a user account without TLS authentication.
-
Connect to your database server.
-
To configure a user account, enter the following:
CREATE USER '<user name>'@'<API Portal host>' IDENTIFIED BY '<your password>'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON <database name>.* TO '<user name>'@'<API Portal host>' WITH GRANT OPTION; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Configure a user account with TLS authentication
MariaDB and MySQL 5.7 support one-way and two-way authentication modes. Authentication modes are handled based on the User Grant.
- One-way (Server CA) authentication: One-way authentication mode expects the client to provide a CA file generated in database server.
- Two-way (mutual) authentication: Two-way authentication mode expects the client to provide both the CA and the client certificates generated in database server.
Configure one-way authentication
To enable one-way authentication, create a user with the option REQUIRE SSL.
-
Log in to the database server as the
rootuser and enter the following:CREATE USER '<user name>'@'<API Portal host>' IDENTIFIED BY '<password>' REQUIRE SSL; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON <database name>.* TO '<user name>'@'<API Portal host>' WITH GRANT OPTION; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Replace the placeholders with the user name and password you want to use.
-
Copy the
ca.pemCA certificate to/etc/mysql/certson the machine on which you will install API Portal. -
Test the connection to the database server from the API Portal machine:
# for MySQL client installed with MySQL package mysql -h <database host> -u <user name> -p \ --ssl-ca=/etc/mysql/certs/ca.pem \ --ssl-mode=VERIFY_IDENTITY # for MySQL client installed with MariaDB package mysql -h <database host> -u <user name> -p \ --ssl-ca=/etc/mysql/certs/ca.pem \ --ssl-verify-server-certThe
database hostmust be the CN of the server certificate that you have previously generated.
Configure two-way (mutual) authentication
To enable two-way authentication, create a user with the option REQUIRE X509.
-
Log in to the database server as the
rootuser and enter the following:CREATE USER '<user name>'@'<API Portal host>' IDENTIFIED BY '<password>' REQUIRE X509; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON <database name>.* TO '<user name>'@'<API Portal host>' WITH GRANT OPTION; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; -
Copy the following client certificates to
/etc/mysql/certson the machine on which you will install API Portal:client-key.pemclient-cert.pemca.pem
-
Test the connection to the database server from the API Portal machine:
# for MySQL client installed with MySQL package mysql -h <database host> -u <user name> -p \ --ssl-ca=/etc/mysql/certs/ca.pem \ --ssl-cert=/etc/mysql/certs/client-cert.pem \ --ssl-key=/etc/mysql/certs/client-key.pem \ --ssl-mode=VERIFY_IDENTITY # for MySQL client installed with MariaDB package mysql -h <database host> -u <user name> -p \ --ssl-ca=/etc/mysql/certs/ca.pem \ --ssl-cert=/etc/mysql/certs/client-cert.pem \ --ssl-key=/etc/mysql/certs/client-key.pem \ --ssl-verify-server-certThe
database hostmust be the CN of the server certificate that you have previously generated.