Manage privacy and personal data
5 minute read
View audit logs
Joomla creates audit logs from the activities performed on your API Portal website. All data gathered from a user must be exportable. This does not include derived fields that were created by the organization, such as customer segmentation fields. API Portal allows JAI Administrators to view, export, and delete audit logs.
To view the list of audit logs, log in to the Joomla! Administrator Interface (JAI), and click Users > User Actions Log. You can filter by extension, by user, and by date or period. Sorting by all fields is also available.
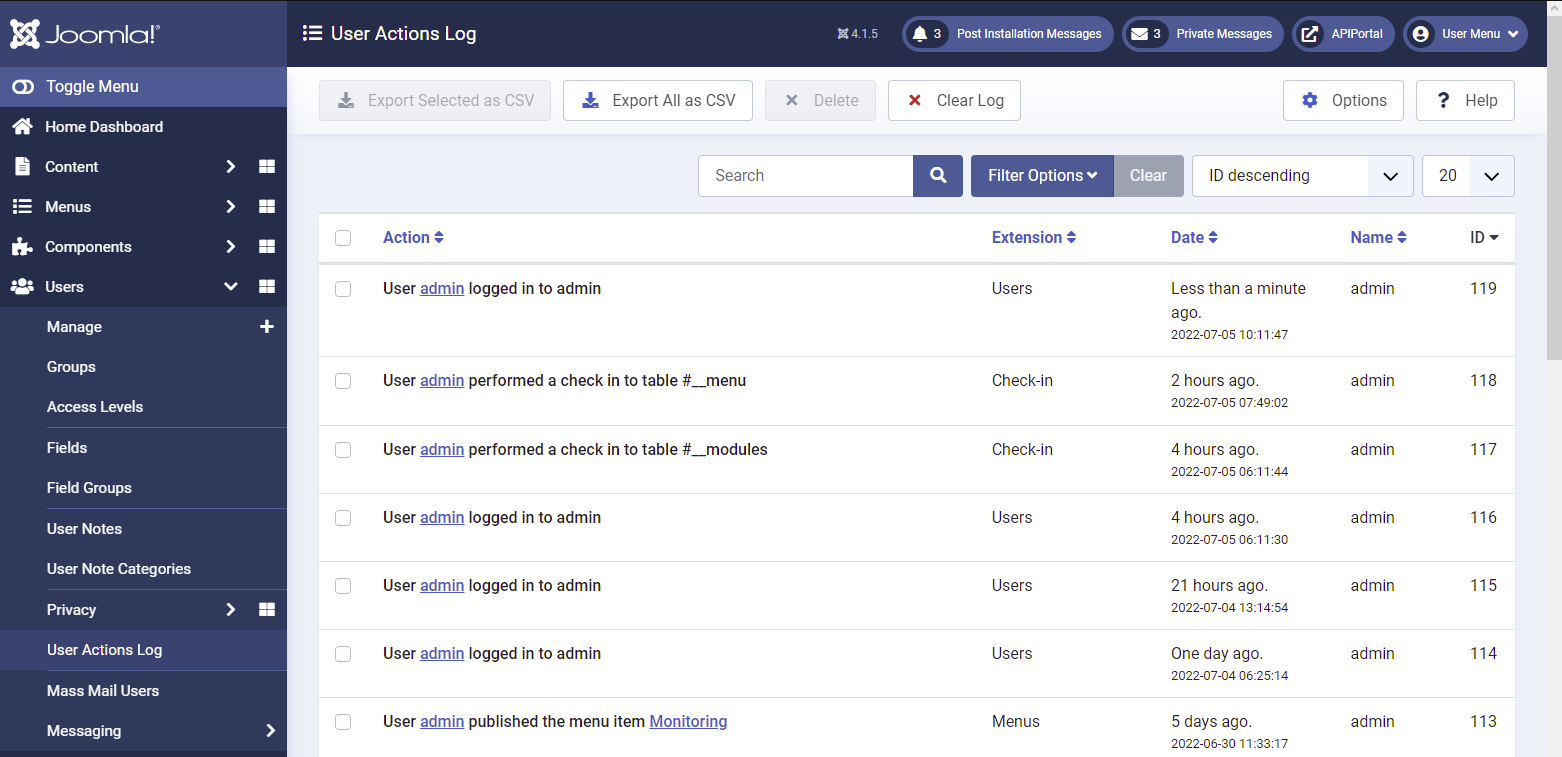
- You must enable both Action Log- Joomla and Action Log - API Portal plugins to view the list of audit logs.
- This view is available only for Super Users.
Export and delete user data
To export, delete, or purge audit logs:
-
In JAI, click Users > User Actions Log.
-
Use the search or the filters to limit your search, if needed.
-
Select one or more items from the list:
- Click either Export Selected as CSV to export the selected items, or Export All as CSV to export all items from the list.
- Click either Delete to delete the selected items, or Purge to purge the selected items.
Configure audit logs options
On the User Actions Log page, click Options to enable or disable the IP logging, select a CSV delimiter, and select from which components to gather the logs based on their events.
Set the number of days to keep audit logs
To set the number of days after which the logs will be deleted:
- In JAI, click System > Plugins.
- Search for System - User Actions Log, and click it from the list.
- Select Enabled from the Status dropdown list.
- You must enabled the Privacy - Action Logs to export the action log data for user’s privacy requests.
Manage data requests
The users of API Portal can request their data export or removal.
To use the data request feature, you must to set up a SMTP server. To configure the SMTP server settings, in JAI, click System > Global Configuration > Server > Mail Settings.
The data request feature is enabled by default. To disable it, in JAI, click Menus > Main menu > Data Request and set Status to Unpublished.
The dashboard of privacy requests is located in the Joomla Privacy Component Users > Privacy. It provides a summary of the information requests for the website and a status of recommended actions that you can take. The request count module on the left is a summary of the information requests on a website. The health check module shows whether there are any recommended actions to take. For example, it will show you whether there are any urgent requests (which are older then configurable amount of time under the Options button) or the mail sending is disabled.
In the Requests menu there is a list of all requests made in the site along with their status and available actions.
After the user requests the export or removal of their data, both user and site admin will receive an email notification for the request. The user must confirm the request by following a link sent into the email. When the request is confirmed, the site owner can either export or delete the data, or invalidate the request. Once the status of the request is updated, the request can be completed by the admin.
Note
For Joomla versions older than 3.9.22 the removal of the data from the request view is not possible.Removal of personal data
After the request to remove data is completed all user’s sessions are deleted and the user is anonymized, but not deleted. This means that the logs of the user are still present, but they could not be linked to the user anymore. The user is blocked and is not able to login anymore.
Additional recommendations
Additional recommendations to manage privacy and personal data.
Define retention periods for personal data
For General Data Protection (GDP) compliance, you should define retention periods within the design phase for all data fields taking into account the defined purpose. You should also include retention periods for backups.
If you are a small organization, you may not need a documented retention policy. However, if you do not have a retention policy, you should still regularly review the data you hold and delete or anonymize any data that you no longer need.
You must include your Data Protection Officer (DPO) or Legal department to define the retention periods as other laws may impact the retention requirements.
Permanently delete unnecessary data
When the retention periods expire, you must ensure that all of the data which is no longer needed has been deleted. This may require automatic identification of the latest activities and a data deletion functionality or manual work.
Develop a log retention policy and archival procedures
We recommend that you develop a log retention policy to identify storage requirements for device logs, and appropriate archival procedures to ensure that the audit logs are available for a security response in the case of an incident or investigation.
The audit logs must be collected for the last 30 days, in an easily accessible storage media. Older logs should be archived in a protected storage and should be accessible in the future as required for incidents or investigations.