JWT flow
3 minute read
A JSON Web Token (JWT) is a JSON-based security token encoding that enables identity and security information to be shared across security domains.
The X.509 certificate that matches the client’s private key must be registered in the Client Application Registry. The API Gateway uses this certificate to verify the signature of the JWT claim.
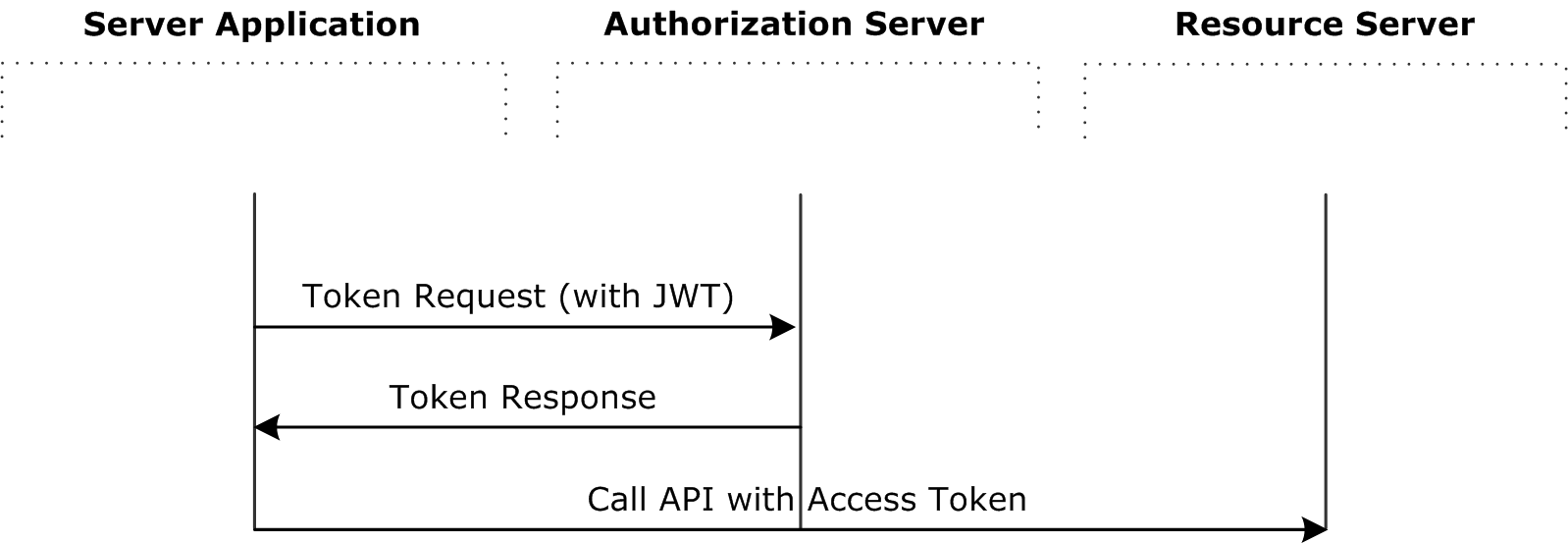
For more details on the OAuth 2.0 JWT flow, see: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7523
Create a JWT bearer token
To create a JWT bearer token, perform the following steps:
-
Construct a JWT header in the following format:
{"alg":"RS256"} -
Base64url encode the JWT header, which results in the following:
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiJ9 -
Create a JWT claims set, which conforms to the following rules:
-
Issuer (
iss) must be the OAuthclient_id, or the remote access application for which the developer registered their certificate. -
Audience (
aud) must match the value configured in the JWT filter. By default, this value is as follows:http://apigateway/api/oauth/token -
Validity (
exp) must be the expiration time of the assertion, within five minutes, expressed as the number of seconds from1970-01-01T0:0:0Zmeasured in UTC. -
Time when assertion was issued (
iat) is measured in seconds after00:00:00UTC, January 1, 1970. -
JWT must be signed (using RSA SHA256). For more details, see: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7515
-
JWT must conform with the general format rules specified in: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7519 For example:
{ "iss":"SampleConfidentialApp", "aud":"http://apigateway/api/oauth/token", "exp":"1340452126", "iat":"1340451826" }
-
-
Base64url encode the JWT claims set, resulting in:
eyJpc3MiOiJTYW1wbGVDb25maWRlbnRpYWxBcHAiLCJhdWQiOiJodHRwOi8vYXBpc2VydmVyL2FwaS9vYXV0aC90b2tlbiIsImV4cCI6IjEzNDA0NTIxMjYiLCJpYXQiOiIxMzQwNDUxODI2In0= -
Create a new string from the encoded JWT header from step 2, and the encoded JWT claims set from step 4, and append them as follows:
Base64URLEncode(JWT Header) + . + Base64URLEncode(JWT Claims Set)This results in a string as follows:
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiJ9.eyJpc3MiOiAiU2FtcGxlQ29uZmlkZW50aWFsQXBwIiwgImF1ZCI6ICJodHRwOi8vYXBpc2VydmVyL2FwaS9vYXV0aC90b2tlbiIsICJleHAiOiAiMTM0MTM1NDYwNSIsICJpYXQiOiAiMTM0MTM1NDMwNSJ9 -
Sign the resulting string in step 5 using SHA256 with RSA. The signature must then be base64url encoded. The signature is then concatenated with a
.character to the end of the base64url-encoded representation of the input string. The result is the following JWT:{Base64url-encoded header}. {Base64url-encoded claim set}.This results in a string as follows:
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiJ9.eyJpc3MiOiAiU2FtcGxlQ29uZmlkZW50aWFsQXBwIiwgImF1ZCI6ICJodHRwOi8vYXBpc2VydmVyL2FwaS9vYXV0aC90b2tlbiIsICJleHAiOiAiMTM0MTM1NDYwNSIsICJpYXQiOiAiMTM0MTM1NDMwNSJ9.ilWR8O8OlbQtT5zBaGIQjveOZFIWGTkdVC6LofJ8dN0akvvD0m7IvUZtPp4dx3KdEDj4YcsyCEAPhfopUlZO3LE-iNPlbxB5dsmizbFIc2oGZr7Zo4IlDf92OJHq9DGqwQosJ-s9GcIRQk-IUPF4lVy1Q7PidPWKR9ohm3c2gt8
Request an access token
The JWT bearer token should be sent in an HTTP POST to the token endpoint with the following parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
grant_type |
Required. Must be set to urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer. |
assertion |
Required. Must be set to the JWT bearer token, base64url-encoded. |
format |
Optional. Expected return format. The default is json. Possible values are urlencoded, json, and xml. |
The following is an example POST request:
POST /api/oauth/token HTTP/1.1
Content-Length:424
Content-Type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8
Host:192.168.0.48:8080
grant_type=urn%3Aietf%3Aparams%3Aoauth%3Agrant-type%3Ajwt-bearer&assertion=eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiJ9.eyJpc3MiOiAiU2FtcGxlQ29uZmlkZW50a WFsQXBwIiwgImF1ZCI6ICJodHRwOi8vYXBpc2VydmVyL2FwaS9vYXV0aC90b2tlbiIsI CJleHAiOiAiMTM0MTM1NDYwNSIsICJpYXQiOiAiMTM0MTM1NDMwNSJ9.ilWR8O8OlbQt T5zBaGIQjveOZFIWGTkdVC6LofJ8dN0akvvD0m7IvUZtPp4dx3KdEDj4YcsyCEAPhfop UlZO3LE-iNPlbxB5dsmizbFIc2oGZr7Zo4IlDf92OJHq9DGqwQosJ-s9GcIRQk-IUPF4lVy1Q7PidPWKR9ohm3c2gt8
Handle the response
API Gateway returns an access token if the JWT claim and access token request are properly formed, and the JWT has been signed by the private key matching the registered certificate for the client application in the Client Application Registry.
For example, a valid response is as follows:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Cache-Control:no-store
Content-Type:application/json
Pragma:no-cache
{
"access_token":“O91G451HZ0V83opz6udiSEjchPynd2Ss9......",
"token_type":"Bearer",
"expires_in":"3600",
}
Run the sample client
The following Jython sample creates and sends a JWT bearer token to the authorization server:
INSTALL_DIR/samples/scripts/oauth/jwt.py
To run the sample, open a shell prompt at INSTALL_DIR/samples/scripts, and execute the following command:
run oauth/jwt.py