Configure API Manager custom policies
35 minute read
API Manager custom policies are optional policies developed in Policy Studio that can be applied to APIs registered in API Manager. For example, these include custom policies for inbound security, request or response processing, or routing. These custom policies enable policy developers to implement enterprise-specific policies in Policy Studio that can be applied to multiple APIs in API Manager.
This page describes the API Manager HTTP request flow, and explains the different custom policies that you can add at different stages in the flow. It also provides examples of why you would use custom policies and explains what happens when they are executed at runtime.
HTTP request flow
When custom policies are configured for front-end APIs in API Manager, the request flows in the following order:
- Client request
- Default inbound security or optional inbound security policy
- Optional request policy
- Outbound authentication profile and/or default routing or optional routing policy
- Back-end service
- Optional response policy
- Client response
This HTTP client request flow is shown in the following swim lane diagram:
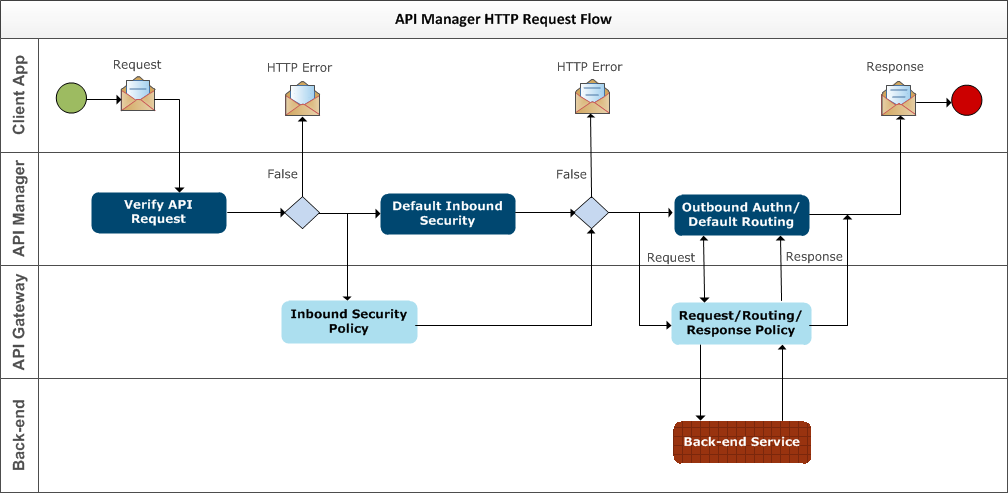
The API Manager policy flow is described as follows:
When the client makes an API call to API Manager, and the API request is first verified. If the request is not valid or not permitted, API Manager returns an HTTP error such as:
HTTP 400 Bad RequestHTTP 404 Not FoundHTTP 405 Method Not AllowedHTTP 429 Too Many Requests
When the API request has been verified, the optional custom inbound security policy is invoked if configured. This means that the default security no longer applies, and all authentication and access to the API by the API Manager organization must be provided by the custom policy. When inbound security returns false, API Manager returns an HTTP error such as:
HTTP 401 UnauthorizedHTTP 403 Authentication FailedHTTP 500 Internal Server Error
If an optional request policy is configured, it could perform some customization on the client request, which is controlled by the API Manager administrator, before sending it to the routing policy.
The default routing uses a Connect to URL filter to route to the back-end service. If you need to customize this, you can configure an custom routing policy instead.
The client request is then routed to the back-end service.
When the response is returned from the back-end service to API Manager, if an optional response policy is configured, it processes the response and can customize it as needed before the response is returned to the client.
Custom policy execution
The following image shows the order of execution of the different custom policies:
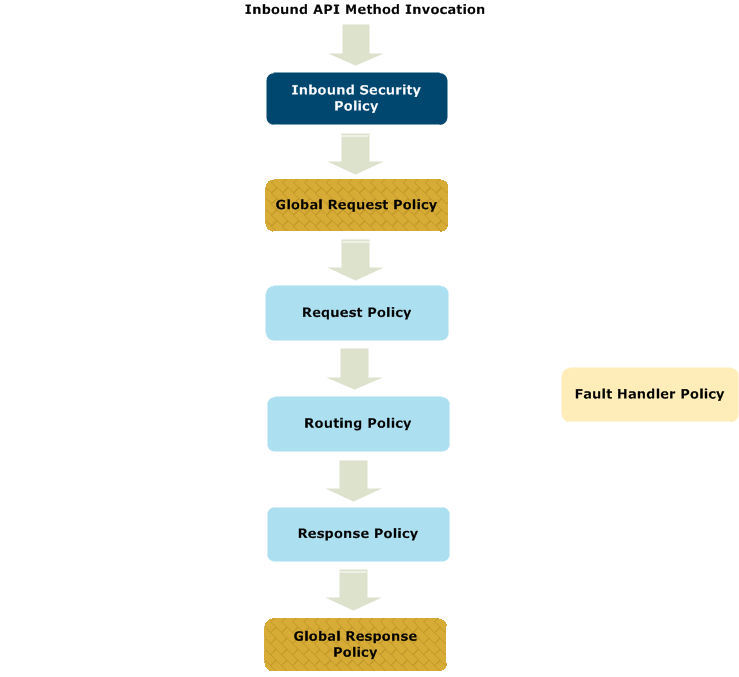
The following general rules apply when API Manager custom polices are executed:
If a filter in a custom policy is aborted, the execution flow is interrupted, and an HTTP 500 Internal Server Error is returned to the client. You can add an API Gateway Generic Error fault handler filter to a policy, but this will print the stack trace and the execution flow will continue to the next policies.
If a filter in a custom policy returns false, and there is no false flow defined in the policy, an HTTP 500 Internal Server Error is returned to the client. However, in this case, you can customize the false flow and return a custom HTTP code and error message. For example, you could use a Set Attributes or Copy/Modify Attributes filter to set the following message attributes when your request policy fails:
request.policy.failure = true
request.policy.httpcode = 403
request.policy.error.msg = something happened
You can then use a custom routing policy to control processing and routing to the back-end. For example, you can test the value of the request.policy.failure attribute to check if the request policy succeeded, and then route to back-end. If the request policy failed, you can stop processing, and use the values from request.policy.httpcode and request.policy.error.msg to create a custom message that is reflected to the end user.
You can define API Manager fault handler policies at the API Manager, API, and method level. However, if a local fault handler is configured for any custom policies, and an exception occurs in any of these policies, the local fault handler is executed for the exception. The flow then continues as if the exception did not occur, which may not be the desired behavior. A workaround is to define a policy that acts as the fault handler using an API Gateway Policy Shortcut filter, and for that policy to return false. This ensures that any API Manager fault handler policies also get executed. For more details, see Add API Manager fault handler policies.
In the case of failure, an HTTP 500 Internal Server Error response code is always returned for a SOAP 1.1 response, or an HTTP 400 and HTTP 500 for a SOAP 1.2 response with the corresponding SOAP fault code in the SOAP response body.
Custom policy types
API Manager custom policies are described as follows:
Inbound Security Policy
Enables you to configure optional security policies to perform custom authentication for front-end APIs. API Manager provides a number of built-in authentication policies (for example, API key, OAuth, and SSL), which you can select when creating front-end APIs. You can extend the list of built-in authentication mechanisms by using the Inbound security > Invoke policy setting to select a custom authentication policy that has been developed in Policy Studio.
For example, you could configure a custom authentication policy that uses CA SiteMinder to authenticate client requests. In addition, custom authentication policies can specify a message displayed in the API Catalog informing application developers of the authentication mechanism to use when accessing the API. By default, no inbound security policies are configured. When you configure an inbound security policy, this means that the default security no longer applies, and all authentication and access to the API by the API Manager organization must be provided by the custom policy.
The inbound security policy must set the authentication.subject.id message attribute to the client ID set in the external credentials of the client application, and return true for successful authentication. By default, Invoke policy > Use client registry specifies that authentication.subject.id must match one of the application’s external credentials in the API Manager client registry. This setting is also required for API Manager to check if the organization has access to the API. If you do not select this setting, the API will have no client information, and API Manager will not check the organization access.
Custom policies developed for inbound security must always end on true or false. Returning true means successful authentication, and returning false means failed authentication. In this way, these policies behave like API Gateway Policy Shortcut filters, where the result is passed back to the calling policy and handled there.
Global Request Policy
Enables you to configure optional global enforcement policies for front-end APIs (for example, security, compliance, or governance policies executed as part of every API call). By default, no global policies are configured.
When global request policies have been configured in Policy Studio, the API administrator can select a global request policy on the API Manager settings page. The selected global request policy is executed after inbound security but before any request, routing, or response policies configured for the front-end API.
Global Response Policy
Enables you to configure optional global enforcement policies for front-end APIs (for example, security, compliance, or governance policies executed as part of every API call). By default, no global response policies are configured.
When global response policies have been configured in Policy Studio, the API administrator can select a global response policy on the API Manager settings page. The selected global response policy is executed last after any response policy configured for the front-end API.
Request Policy
Enables you to configure optional request processing policies for front-end APIs. For example, you could use a configured policy to check request messages for authentication or authorization. By default, no request policies are configured.
When request policies have been configured in Policy Studio, you can then apply them in API Manager on the Frontend API > Outbound > Advanced page. The selected request policy is executed after inbound security and any global request policy, but before any routing or response policies configured for the front-end API.
Routing Policy
Enables you to configure custom routing policies for front-end APIs. For example, you could use a configured policy to route to a specific back-end JMS service. By default, no routing policies are configured and a default routing policy template is used.
When routing policies have been configured in Policy Studio, you can apply them in API Manager on the Frontend API > Outbound > Advanced page. The selected routing policy is executed after any request policy and before any response policy configured for the front-end API.
When a routing policy is selected in the API Manager UI, the Backend service URL field might be overridden by a destination URL that is specified in the routing policy.
Response Policy
Enables you to configure optional response processing policies for front-end APIs. For example, you could use a configured policy to validate or transform outbound response messages. By default, no response policies are configured.
When response policies have been configured in Policy Studio, you can then apply them in API Manager on the Frontend API > Outbound > Advanced page. The selected response policy is executed after any routing policy configured for the front-end API, but before any global response policy.
Fault Handler Policy
Enables you to configure optional fault handler policies that are applied to front-end API invocations. The configured fault handler is executed when an error or exception occurs during the API Manager runtime API invocation. The API Manager Default Fault Handler policy is configured by default.
When fault handler policies are configured, an API administrator can select a global fault handler policy for all front-end APIs on the API Manager settings page. API developers can also select fault handler policies for specific front-end APIs and API methods on the Frontend API > Outbound > Advanced page.
Evaluate undefined parameters
When validating the parameters received from the client, API Manager runtime ignores any parameters that are not defined by the back-end API, and it does not generate any message attributes for these parameters. As a consequence, querying undefined parameters in custom policies results in an “invalid field”. To access undefined parameters in these policies, use the following selectors:
- Query -
${http.querystring.paramName} - Header/Cookie -
${http.headers.headerName} - Form -
${http.querystring.paramName}
You can also add undefined parameters as part of a method override. In such cases, you can use API Manager ${params.query}, ${params.form}, and ${params.header} selectors.
Add custom API Manager routing policies
This section explains advanced use-cases of how to configure custom API Manager routing policies. API Manager custom routing policies support all outbound API authentication profiles configured in API Manager (for example, HTTP Basic, HTTP Digest, API key, OAuth, and SSL). This topic shows detailed examples of using API key, OAuth, and SSL as the outbound authentication profile.
API Manager custom routing policy templates
API Manager provides reserved routing policy templates in Policy Studio under Policies > Generated Policies > REST APIs > Templates. For any customization, you should make copies of these reserved templates, which may be changed in future releases:
-
Default API Proxy Routing: API Manager custom routing is based on this template by default.
-
Default Profile-based Routing: This is used by the Default API Proxy Routing template to process the following outbound authentication profiles:
- Pass through
- HTTP Basic
- HTTP Digest
- API Key
-
Default OAuth-based Routing: This is used by the Default API Proxy Routing template to process the OAuth authentication profile.
-
Default SSL-based Routing: This is used by the Default API Proxy Routing template to process the SSL authentication profile.
-
Default URL-based Routing: This is used by API Gateway only since version 7.6.2.
Customize a template policy
You can customize a default routing policy by modifying its Connect To URL filter in Policy Studio. To edit a default policy, select Policies > Generated Policies > REST APIs > Templates > My Default Routing Policy, and double-click the Connect to URL filter in the policy canvas on the right.
For example, under Settings > Failure > Call connection policy on failure, you could configure a custom policy with a Reflect message filter that modifies the default HTTP 500 response code to HTTP 503 when the API Manager runtime cannot connect to a back-end service.
Updating a default routing policy modifies how API Manager manages connection failures globally for all APIs, without needing to modify each API.
After updating a default routing policy, you do not need to restart the underlying API Gateway, redeploying the updated configuration is sufficient.
Message attributes
The API Manager custom routing policy message whiteboard includes the following message attributes:
params.outcontains the API authentication profile for the policy customization.params.authncontains the connection handler to be consumed by the Connect To URL filter in the custom routing policy. To use the authentication handler, the${params.authn}value must be set in the required credential profile in the Connect To URL filter.- Additional message attributes are also set depending on the authentication profile used. For example, these include
params.ssl.cacertificatesfor SSL, andoauth.token.idandoauth.client.applicationfor OAuth
Note
API Manager custom routing policies designed for outbound SSL authentication profiles must include a Connect To URL filter namedapimanager.outbound.ssl. The corresponding SSL profile settings will apply only to such Connect To URL filters. For example, see the Default SSL-based Routing template policy.
Default TLS settings
The Connect To URL filters in the custom routing templates use TLS version 1.2 with strong FIPS-compliant ciphers by default for SSL/TLS connections. You can modify the SSL/TLS protocols and ciphers in custom routing policies as needed.
Add a custom routing policy with API key authentication
This section explains how to set up a custom API Manager routing policy that uses API key as the outbound authentication type. It shows how to create the policy in Policy Studio, and how to configure it for use in API Manager.
Create the custom API key routing policy in Policy Studio
You must first create a new policy in Policy Studio that will be used as the custom API key routing policy in API Manager.
Perform the following steps:
-
Right-click the Policies node in the tree, and select Add Policy.
-
Enter a meaningful Name for the new policy (for example, Custom routing policy for PetStore API).
-
Click the new policy in the tree to start configuring its filters. You can do this by dragging the required filters from the filter palette on the right, and dropping them on to the policy canvas. This example includes Trace and Connect to URL filters:
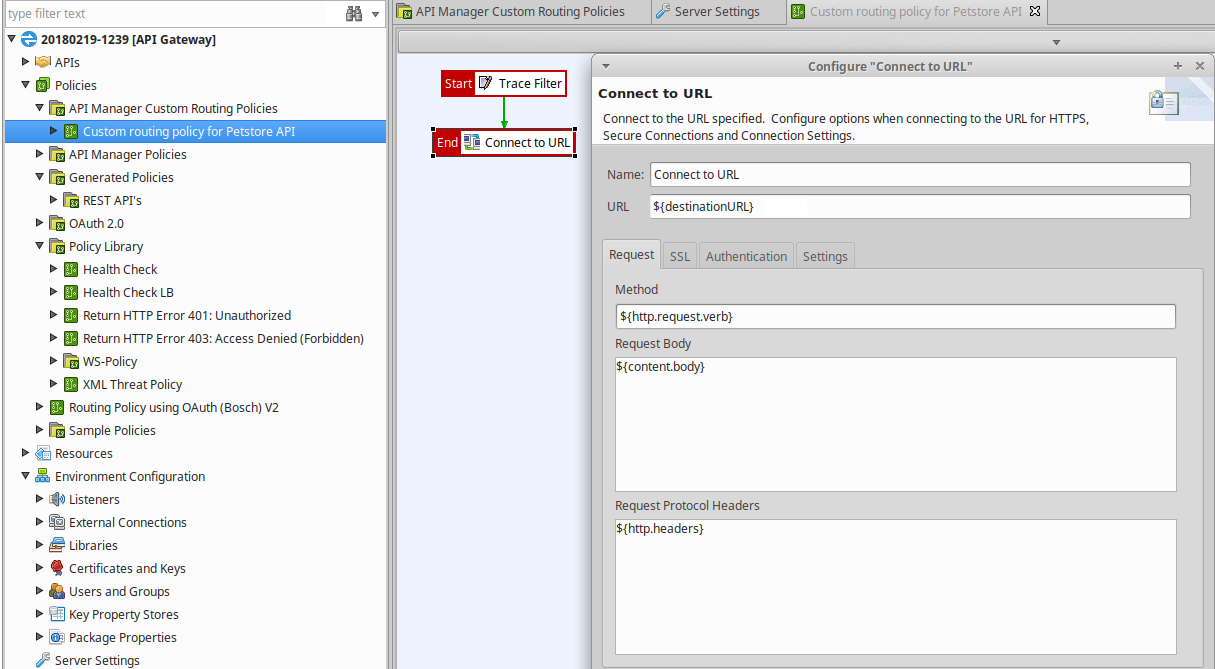
-
Open the Connect to URL filter, and in the URL field, enter
${destinationURL}. -
On the Authentication tab, the client credential is set to the
${params.authn}selector by default, but you can enter a different selector or select a credential profile if necessary: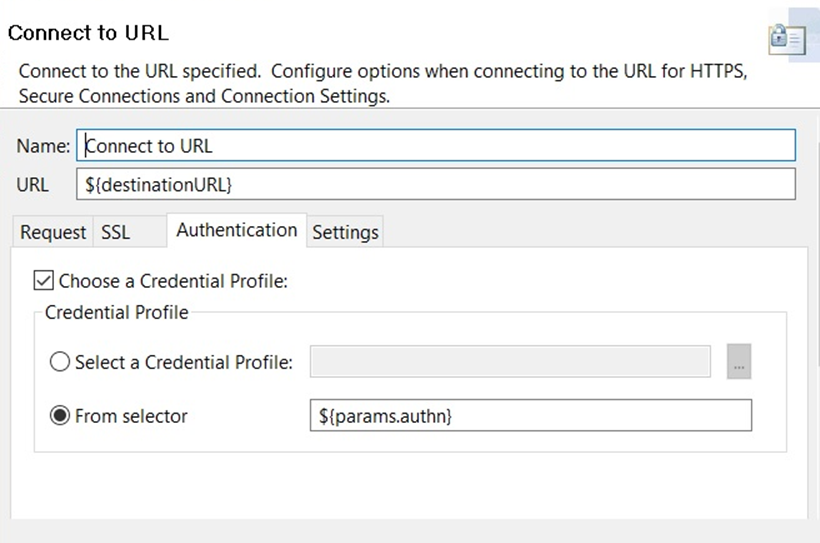
Configure the list of API Manager routing policies in Policy Studio
You must add the new custom API key routing policy to the list of available routing policies that APIs registered in API Manager can use.
Perform the following steps:
- Select Server Settings in the tree, and select API Manager > Routing Policies.
- Click Add on the right, and select the custom routing policy that you created (for example, Custom routing policy for PetStore API).
- Click OK, and click Save at the bottom right.
The following image shows how to configure routing policies:
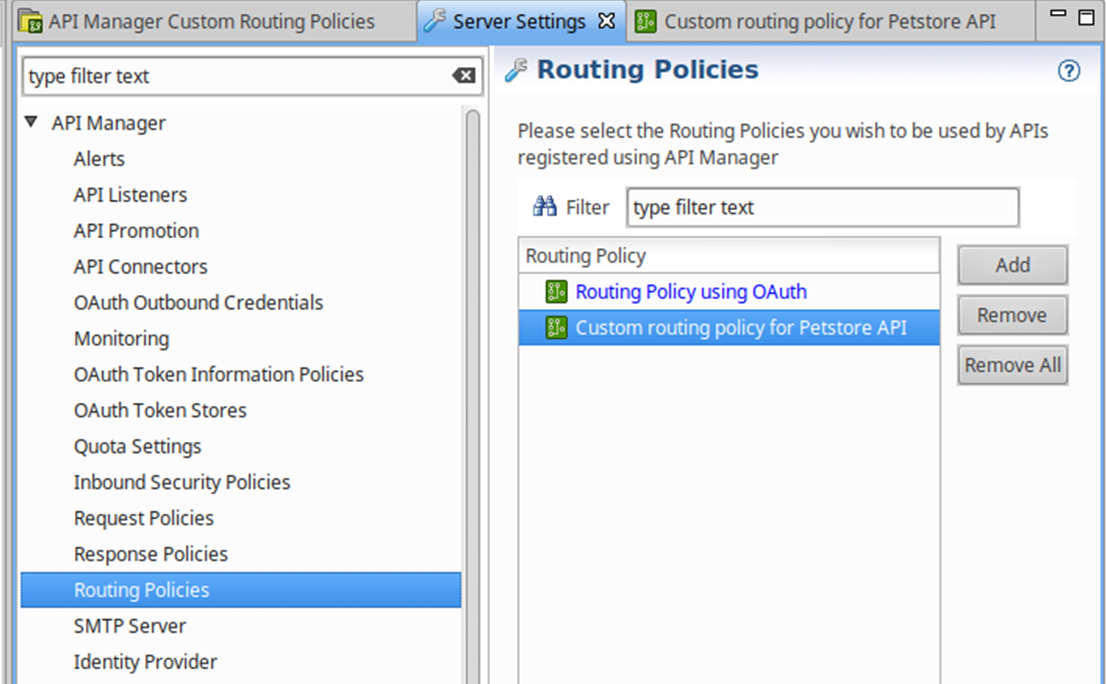
Configure the custom API key routing policy in API Manager
When the custom routing policy has been added to the list of available routing policies in Policy Studio, perform the following steps in API Manager:
-
Click API > Backend > New API to import a back-end API, and ensure the Base path URL is set to the API on the remote server.
-
Click API > Frontend > New API to create a front-end virtualized API from the back-end API.
-
On the Inbound tab, set Inbound security to Pass Through.
-
On the Outbound tab , set Outbound authentication profile to API Key, click Edit, and configure the following settings in the dialog box:
- API key field name: Use the default value of
KeyId. - API key: Enter the API key for your API.
- Pass credentials as HTTP: Select Header from the list
- API key field name: Use the default value of
-
Click Advanced on the right, and set Default method routing to use your custom routing policy. For example:
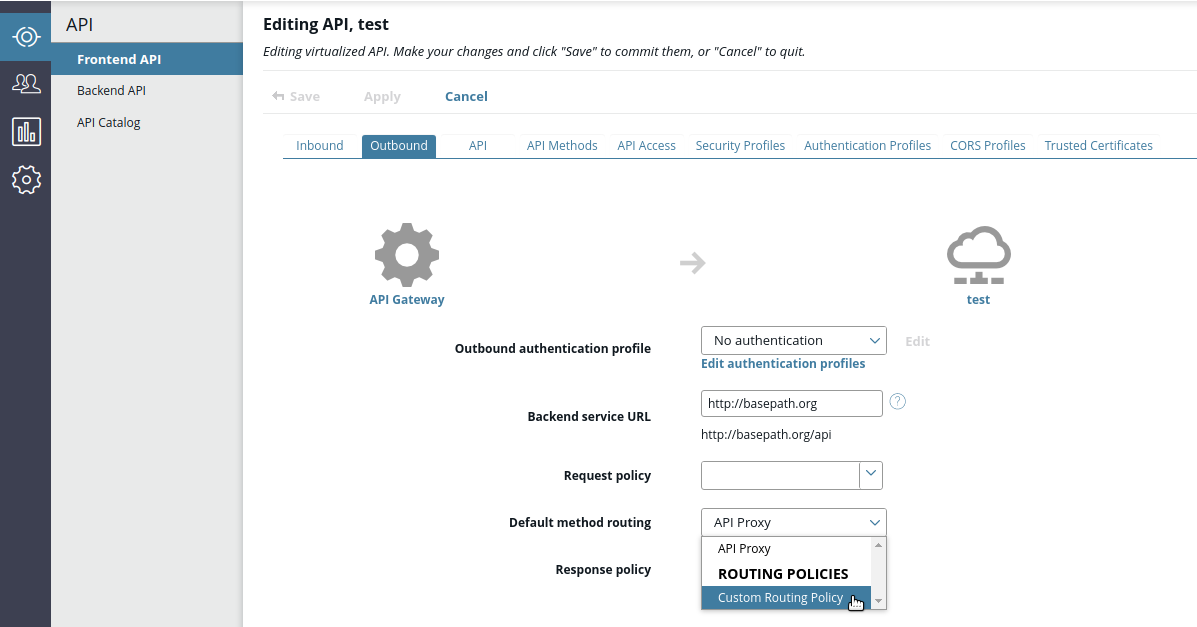
Invoke the registered API and view the API key in the request
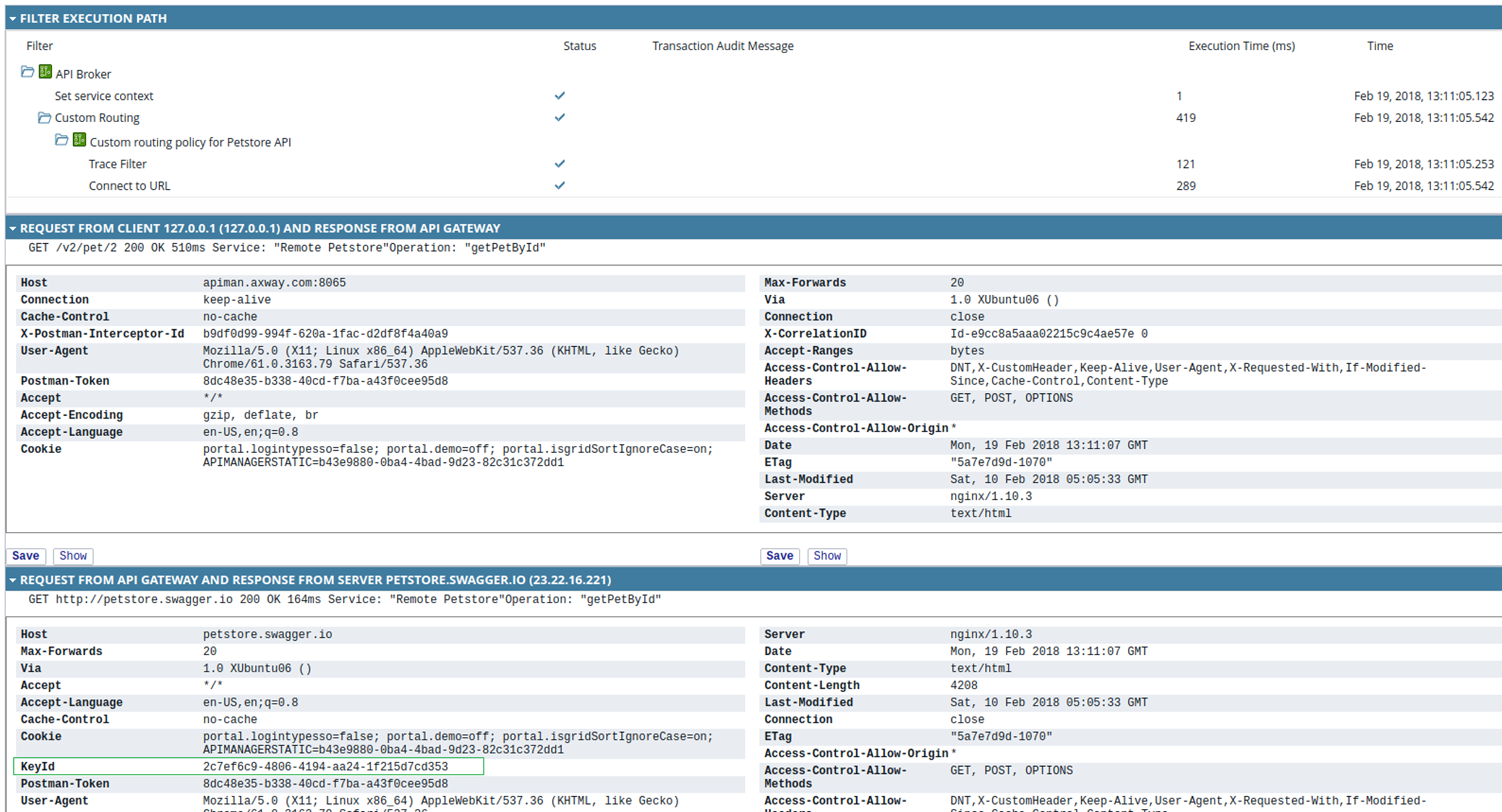
You can now invoke the API registered in API Manager and view that the API key header is specified in the outbound request and that a successful response is returned. The following example in the API Gateway Manager web console shows the KeyId in the request at the bottom left:
Add a custom routing policy with OAuth authentication
This section describes how to use API Manager to invoke an API with outbound OAuth authentication using a custom routing policy. In this scenario, one API Gateway instance acts as an OAuth client and the other API Gateway instance acts as an OAuth server. This section shows how to configure both API Gateway instances appropriately using the Client Credentials OAuth flow.
Note
This section assumes that you are familiar with the Client Credentials OAuth flow.Configure the remote API Gateway as OAuth server in API Manager
To configure a remote API Gateway instance to act as an OAuth server, perform the following steps in API Manager:
-
Click Clients > Applications > New application.
-
On the Authentication tab, under OAuth Credentials, click New client ID > Create, and use the default settings.
-
Click API > Backend > New API to import a back-end API.
-
Click API > Frontend > New API to create a front-end virtualized API from the back-end API.
-
Set the Inbound security to OAuth. This example uses the default setting to obtain the access token from the header:
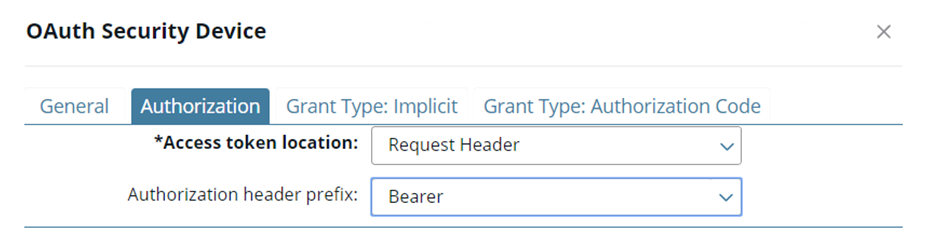
You must select an OAuth access token store on the General tab.
-
Click Clients > Applications > API Access > Add API to add the virtualized front-end API to the list of APIs that the application can access.
-
Click Settings > API Manager Settings >General settings, and ensure that Enable OAuth scopes per application is set.
-
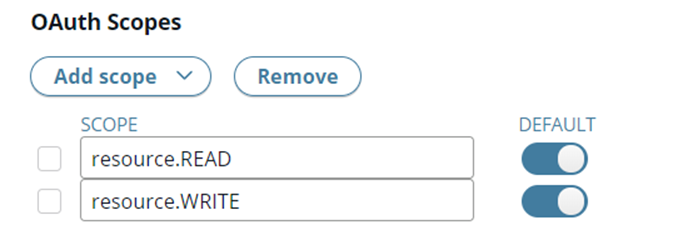
Click Clients > Applications > Authentication > OAuth Scopes > Add scopes, and select the resource.READ and resource.WRITE scopes (You might need to refresh your browser if OAuth Scopes are not displayed):
Configure the client credentials in Policy Studio
When using the Client Credentials OAuth flow for the client, you must first configure the client credentials correctly in Policy Studio. This ensures that the client can request an OAuth access token using only its client credentials and that the authorization is specified in the header as expected.
Perform the following steps:
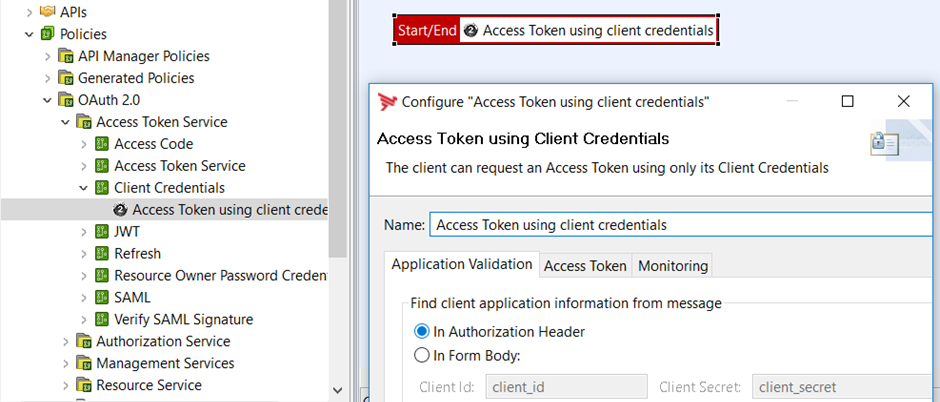
- In the Policy Studio tree, select Policies > OAuth 2.0 > Access Token Service > Client Credentials.
- Right-click the Access Token using client credentials filter, and select Edit.
- On the Application Validation tab, select the In Authorization Header option:
The following image shows how to configure client credentials:
Configure the local API Gateway as OAuth client in Policy Studio
To configure a local API Gateway instance to act as an OAuth client, perform the following steps:
-
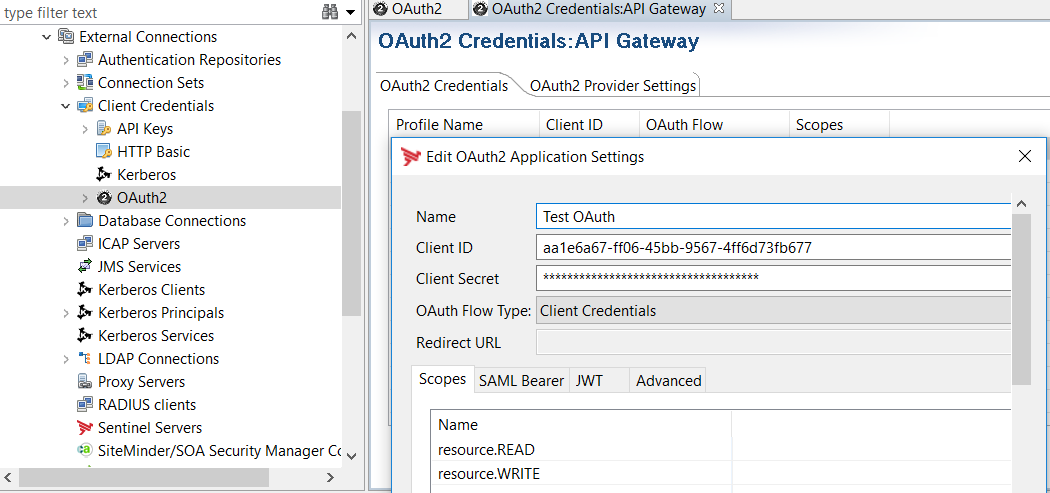
To create an OAuth2 credentials application using the Client Credentials flow, select Environment Configuration > External Connections > Client Credentials > OAuth2, right-click and select Add OAuth2 Client Credential.
-
Click Add OAuth2 Application Settings on the right, and ensure the following settings are configured:
- Enter the Client ID and Client Secret that were generated on the remote API Gateway instance.
- Select an OAuth Flow Type of Client Credentials.
- On the Scopes tab, click Add to add the resource.READ and resource.WRITE scopes.
-
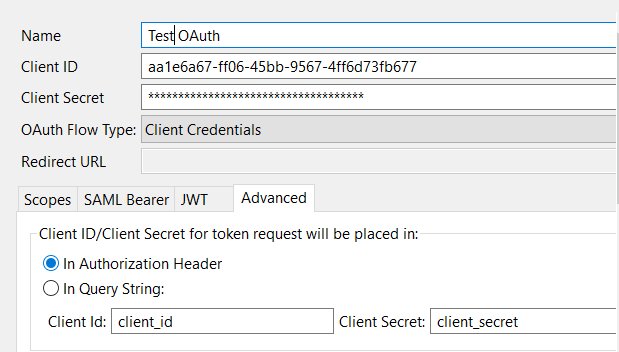
On the Advanced tab, you must also ensure that In Authorization Header is selected for the location of the client ID and client secret:
-
Click Save on the right to save the application.
-
On the OAuth2 Provider Settings tab, enter the IP address of the remote instance in the Authorization Endpoint and Token Endpoint:
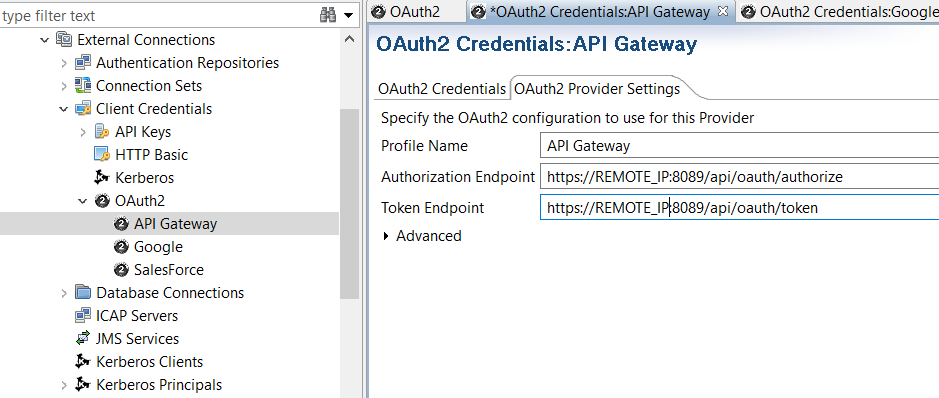
Create the custom OAuth routing policy in Policy Studio
To create a new policy to use as the custom OAuth routing policy in API Manager, perform the following steps in Policy Studio:
-
Right-click the Policies node in the tree, and select Add Policy.
-
Enter a meaningful Name for the new policy (for example, Custom routing policy with OAuth).
-
Click the new policy in the tree to start configuring the filters for this policy. You can do this by dragging the required filters from the filter palette on the right, and dropping them on to the policy canvas. This example includes Get OAuth Access Token and Connect to URL filters:
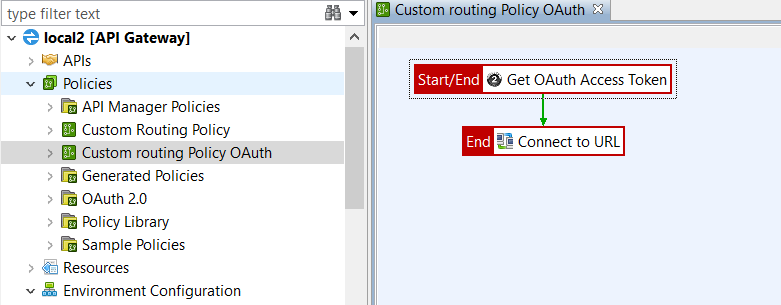
-
In the Get OAuth Access Token filter, the client credentials profile is obtained from the message whiteboard by default, so the token should now be available.
-
Open the Connect to URL filter, and in the URL field, enter
${destinationURL}. -
On the Authentication tab, the client credential is set to the
${params.authn}selector by default, but you can enter a different selector or select a credential profile if necessary:
The following image shows how to configure the Connect to URL filter:

Configure the list of API Manager routing policies and OAuth outbound credentials in Policy Studio
You must add the new custom routing policy and OAuth credentials to the lists of available routing policies and credentials that APIs registered in API Manager can use.
Perform the following steps:
- Select Server Settings in the tree, and select API Manager > Routing Policies.
- Click Add on the right, and select the custom routing policy that you created (for example, Custom routing policy with OAuth).
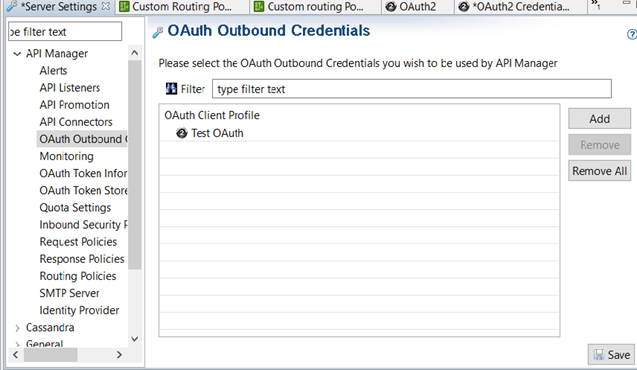
- Select API Manager > OAuth Outbound Credentials.
- Click Add on the right, and select the OAuth client credentials that you created (for example, Test OAuth).
- Click OK, and click Save at the bottom right.
The following image shows how to configure the OAuth Outbound Credentials.
Configure the custom OAuth routing policy in API Manager
When the custom routing policy and OAuth outbound credentials have been added in Policy Studio, perform the following steps in API Manager:
-
Click API > Backend > New API to import a back-end API, and ensure the Base path URL is set to the API on the remote server.
-
Click API > Frontend > New API to create a front-end virtualized API from the back-end API.
-
On the Inbound tab, set the Inbound security to Pass Through.
-
On the Outbound tab, set the Outbound authentication profile to OAuth, and configure the following:
- Provider profile: Enter the OAuth outbound credentials profile that you created in Policy Studio (for example, Test OAuth).
- Token Key (Owner ID): Use the default
${authentication.subject.id}selector setting to obtain this value.
-
Click Advanced at the top right, and set the Default method routing to use your custom routing policy.
Invoke the registered API with OAuth authorization header in request
You can now invoke the API registered in API Manager and view that the authorization header is specified in the outbound request and that a successful response is returned. The following example in the API Gateway Manager web console shows the OAuth custom routing policy in the execution path:

The following example shows the Authorization Bearer header correctly displayed in the request in the bottom panel in API Gateway Manager:

Add a custom routing policy with SSL authentication
This section explains how to configure mutual authentication using a custom API Manager routing policy with SSL as the outbound authentication type. It first shows how to configure the back-end SSL server for mutual authentication, and then shows how to create the custom policy in Policy Studio and how to configure this policy in API Manager.
Set up the back-end SSL server for mutual authentication
You must first configure the certificates for the SSL server and client, and then create an HTTPS interface:
Create a certificate for the SSL server
- Ensure that your SSL certificate has been created and imported into the API Gateway certificate store. In Policy Studio, select Environment Configuration > Certifcates and Keys > Certifcates > Create/Import.
- On the Configure Certificate and Private Key dialog, click Edit to configure the distinguished name. For example:
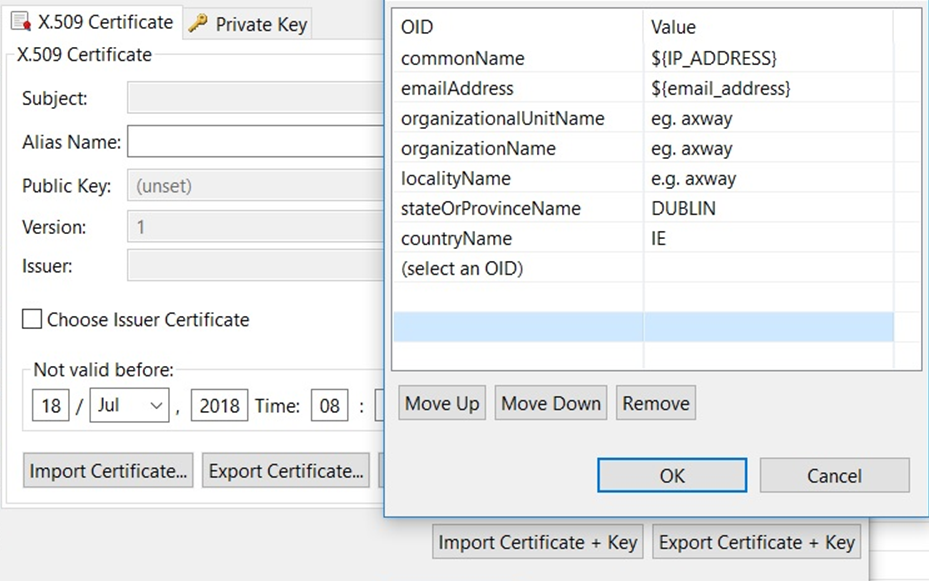
- Select the validity dates, and click Use Subject.
- Click Sign Certificate to create the certificate and keys.
Export the client certificate and key
- To select the client certificate that you wish to export, select Environment Configuration > Certifcates and Keys > Certificates, select the certificate, and click Edit.
- Click Export Certificate + Key to set a password and export your SSL client certificate (
.p12file). You will add this certificate to the list of certificates you trust when creating your HTTPS interface.
Create an HTTPS interface
-
Select Environment Configuration > API Gateway > Listeners > Default Services > Ports.
-
Click Add > HTTPS Interface on the right, and configure the tabs as follows:
- Network: Click X.509 Certificate and select the certificate that you created.
- Mutual Authentication: Select Requires client certificate, and select the Root Certificate Authorities trusted for mutual authentication.
- Traffic Monitor: Use the default settings.
- Advanced: Use the default settings.
- Advanced (SSL): You must deselect Check that the SLL certificate’s Subject CN resolves to network address. You can use the defaults for the other settings, for example:
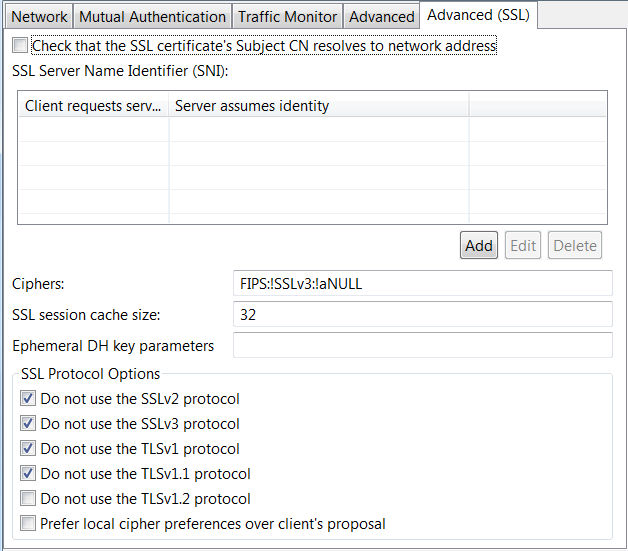
Create the custom SSL routing policy in Policy Studio
You must create a new policy in Policy Studio that will be used as the custom routing policy in API Manager.
Perform the following steps:
-
Right-click the Policies node in the tree, and select Add Policy.
-
Enter a meaningful Name for the new policy (for example, Custom SSL routing policy).
-
Click the new policy in the tree to start configuring its filters. You can do this by dragging the required filters from the filter palette on the right, and dropping them on to the policy canvas. You must include a Connect to URL filter for SSL:
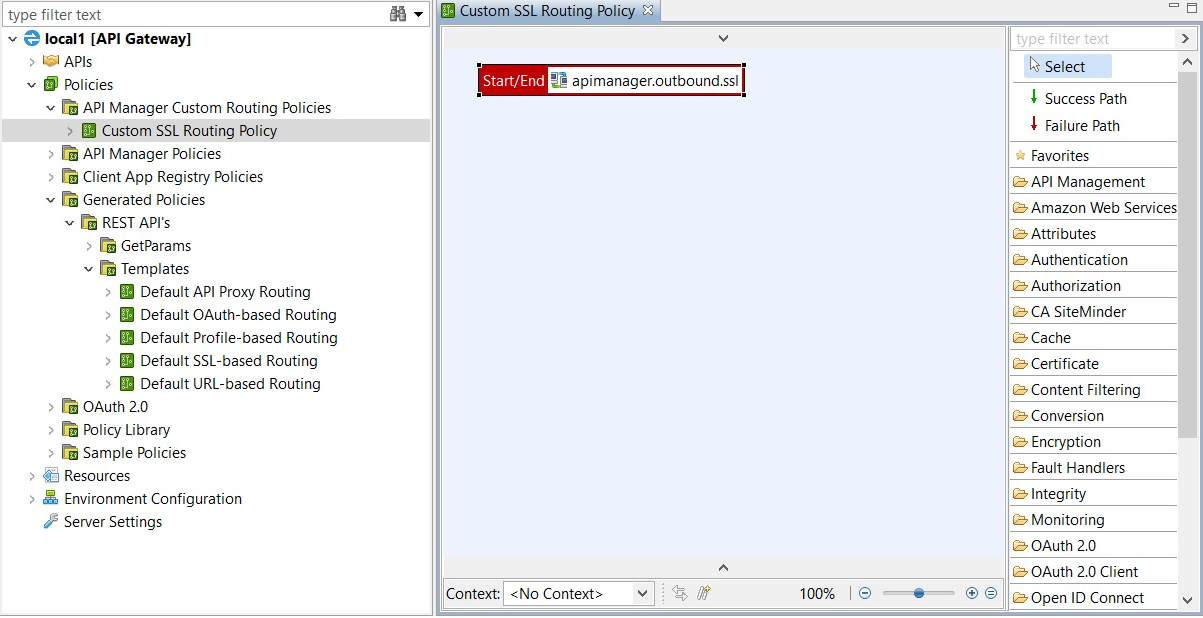
-
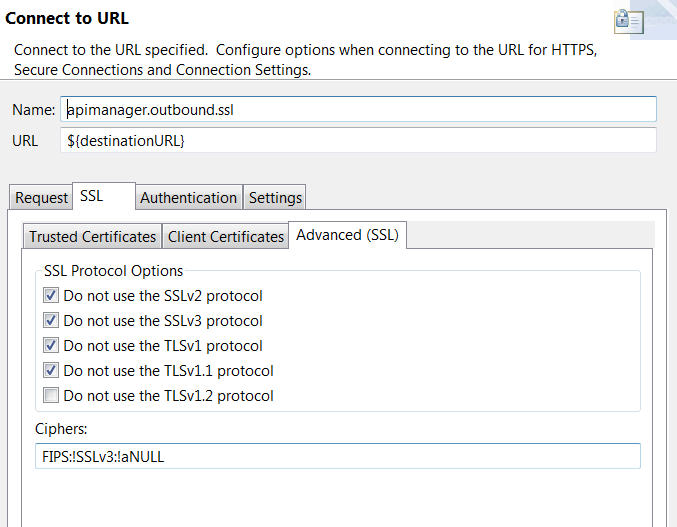
In the Connect to URL filter, you must enter a Name of
apimanager.outbound.ssl, which is only used for API Manager. -
In the URL field, enter
${destinationURL}. -
On the SSL > Advanced (SSL) tab specifies TLS version 1.2 with strong FIPS-compliant ciphers by default for SSL/TLS connections, but you can modify these settings to suit your requirements.
-
On the Authentication tab, the client credential is not set by default.
Add the custom SSL routing policy to Policy Studio
You must add the new custom SSL routing policy to the list of available routing policies that APIs registered in API Manager can use.
Perform the following steps:
-
Select Server Settings in the tree, and select API Manager > Routing Policies.
-
Click Add on the right, and select the custom routing policy that you created (for example, Custom SSL Routing Policy).
-
Click OK, and click Save at the bottom right.
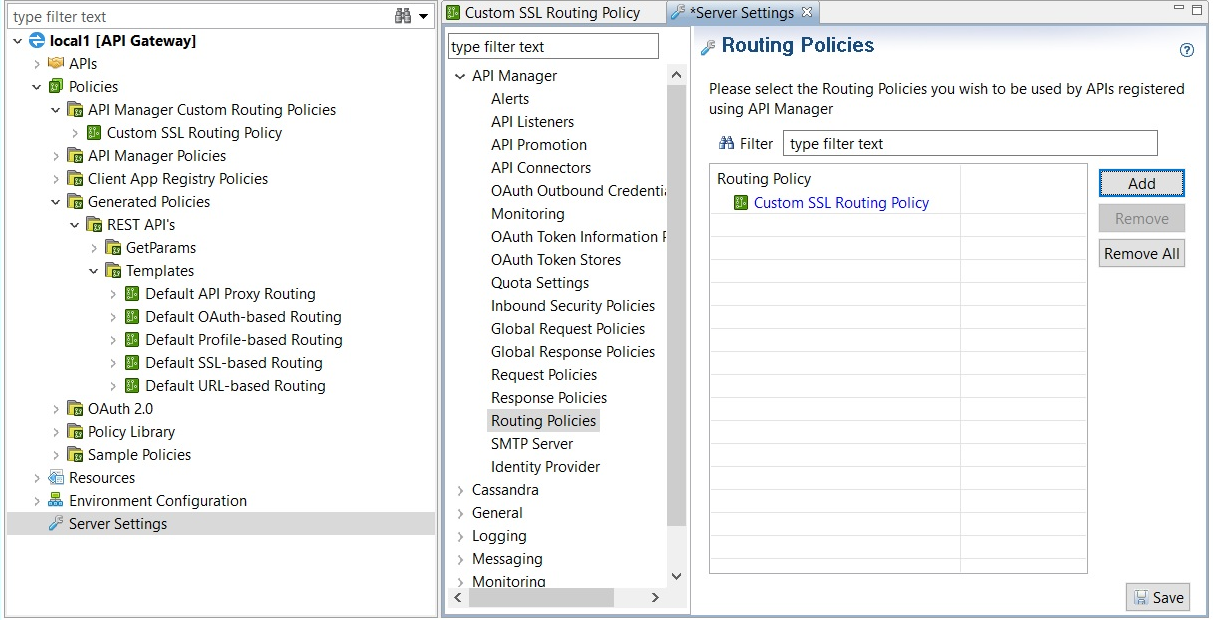
Configure the custom SSL routing policy in API Manager
When the custom routing policy has been added to the list of available routing policies in Policy Studio, perform the following steps in API Manager:
-
Click API > Backend > New API to import a back-end API, and ensure the Base path URL is set to the host and port of your SSL server..
-
On the API Methods tab, add a method for testing purposes (for example,
healthcheck). -
Click API > Frontend > New API to create a front-end virtualized API from the back-end API..
-
On the Inbound tab, set Inbound security to Pass Through.
-
On the Trusted Certificates tab, click the + sign and import the SSL server certificate.
-
On the Authentication Profiles tab, click the + sign, select SSL to specify the PFX/P12 file for the SSL client certificate and enter the password.
-
On the Outbound tab, set Outbound authentication profile to SSL, click Edit, and configure the following settings:
- PFX/P12 file: Select the SSL client certificate
- PFX/P12 password: Enter the password for the SSL client certificate.
- Trust all certificates in chain: Ensure this setting is selected.
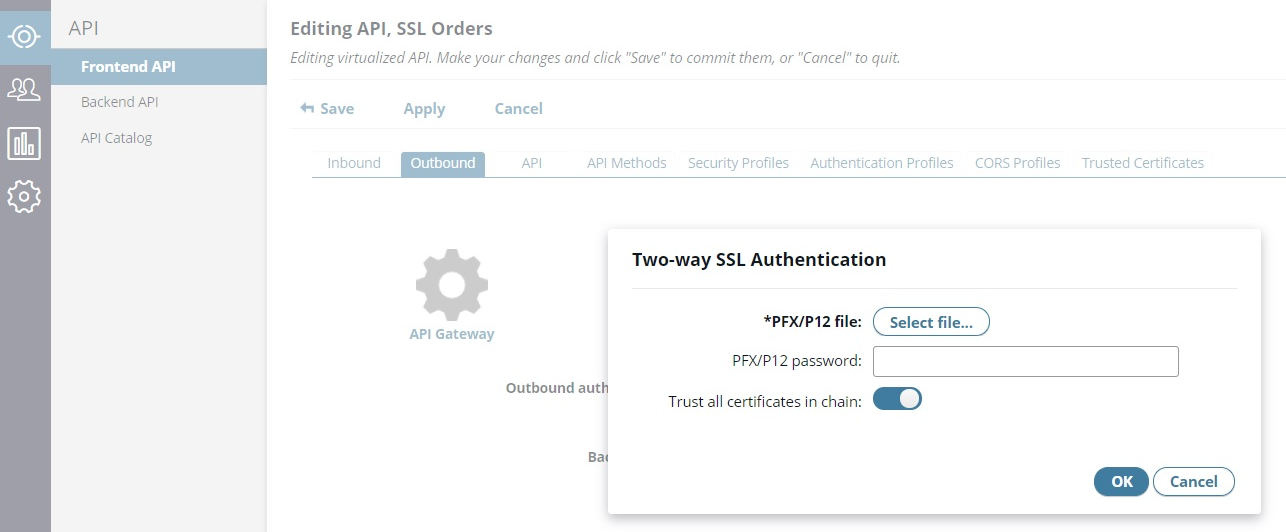
-
Click Advanced on the right, and set Default method routing to use your custom SSL routing policy.
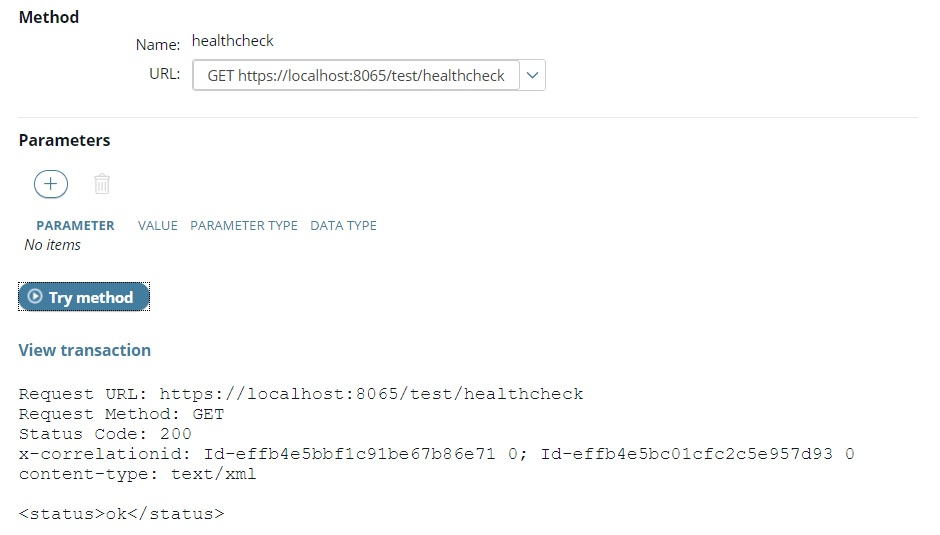
Invoke the registered API and test SSL authentication
You can now invoke the API registered in API Manager and view that the SSL Two-way authentication works correctly.
The following image shows how to use the Try Method feature on the API Methods tab to test with a healthcheck method:
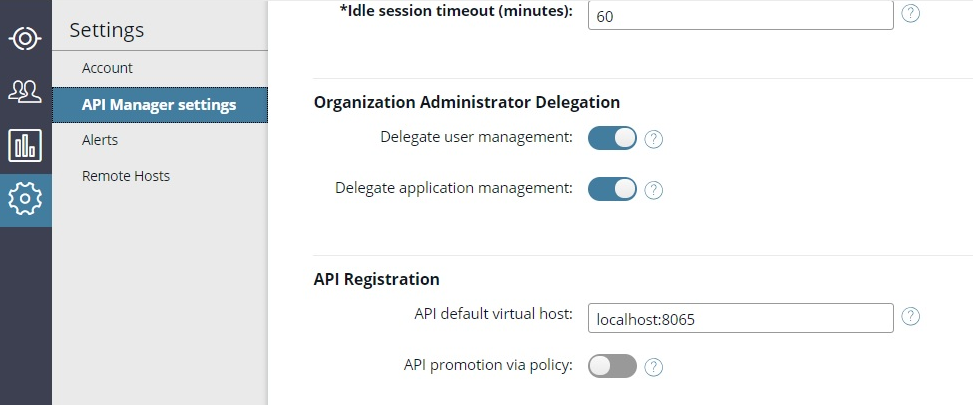
You might need to configure your localhost and port in API Manager settings > API Registration > API default virtual host. For example:
Enforce API Manager global policies
Use API Manager to apply mandatory security, compliance, or governance policies, which are executed as part of every API call across your entire API portfolio.
Global enforcement of policies enables API administrators to configure global request and response policies that are executed for every virtualized API method invocation. You can achieve this as follows:
- In Policy Studio, as a policy developer, you must first configure your chosen policies as API Manager global request and response policies, which are then displayed in API Manager on the API Manager settings page.
- In API Manager, as an API administrator, select a global request policy and a global response policy from the list of available global policies.
API Manager global request and global response policies are both optional features, and you can configure one without the other, or neither, depending on your requirements.
API Manager global policy flow
Configuring global policies in API Manager extends the policy execution path for front-end APIs as follows:
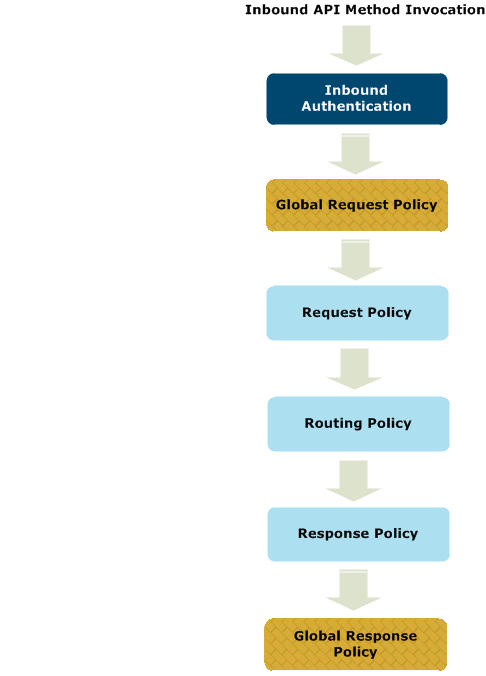
In this policy flow, all policies are optional, and the global policies are executed as follows:
- The global request policy is executed after inbound authentication but before any non-global request, routing, or response policies configured for the front-end API.
- The global response policy is executed last after any non-global response policy configured for the front-end API.
For details on configuring non-global request, routing, and response policies, see Configure API Manager settings in Policy Studio.
Configure API Manager global policies in Policy Studio
You must first configure API Manager global request and response policies in Policy Studio before you can apply them in API Manager.
Configure global request policies
To configure API Manager global request policies, perform the following steps:
- In the Policy Studio tree, select Server Settings > API Manager > Global Request Policies.
- Click Add, and select policies in the dialog. By default, no global request policies are configured.
- Click Save at the bottom right.
- Click the Deploy button at the right of the toolbar to deploy the configuration to the API Gateway.
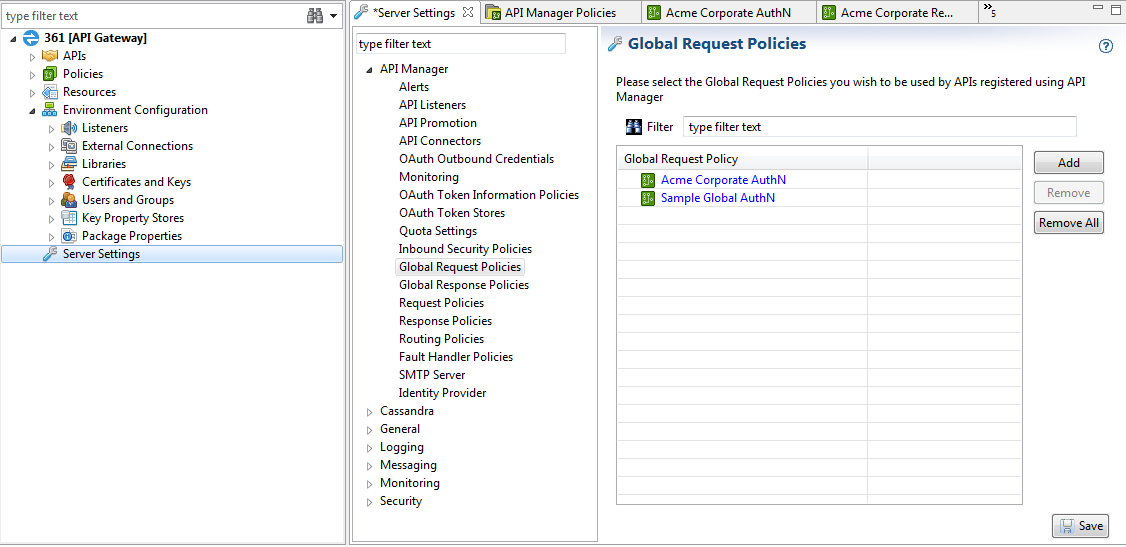
Configure global response policies
To configure API Manager global response policies, perform the following steps:
- In the Policy Studio tree, select Server Settings > API Manager > Global Response Policies.
- Click Add, and select policies in the dialog. By default, no global response policies are configured.
- Click Save at the bottom right.
The following image shows how to configure global response policies:
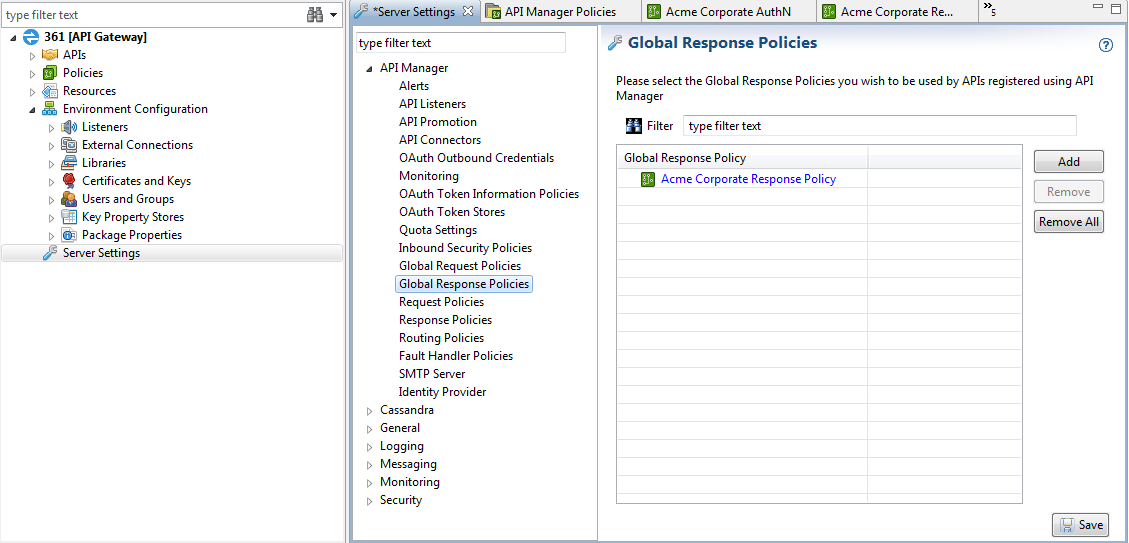
Select global policies in API Manager
When API Manager global request and response policies are configured in Policy Studio, the API administrator can select the available policies in API Manager on the Settings > API Manager settings page.
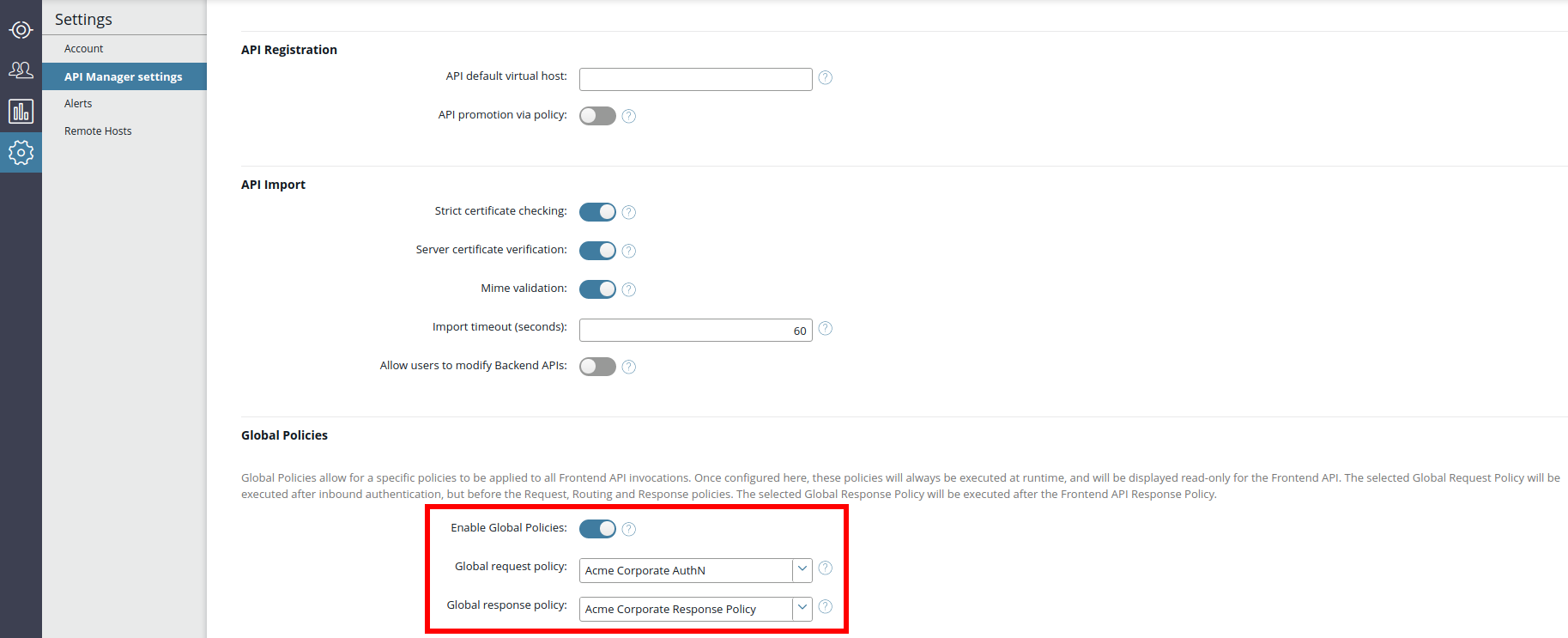
To apply API Manager global policies, perform the following steps:
- In API Manager, under Settings > API Manager settings > Global Policies, select Enable Global Policies. This setting is disabled by default.
- Select a global policy from the Global Request Policy list (for example, a corporate security policy).
- Select a global policy from the Global Response Policy list (for example, a corporate governance policy).
When global policies have been selected by the API administrator, they are then displayed as read-only for all APIs on the Frontend API > Outbound tab when you click Advanced. The following image shows the Outbound tab for a front-end API previously configured with global request and response policies:
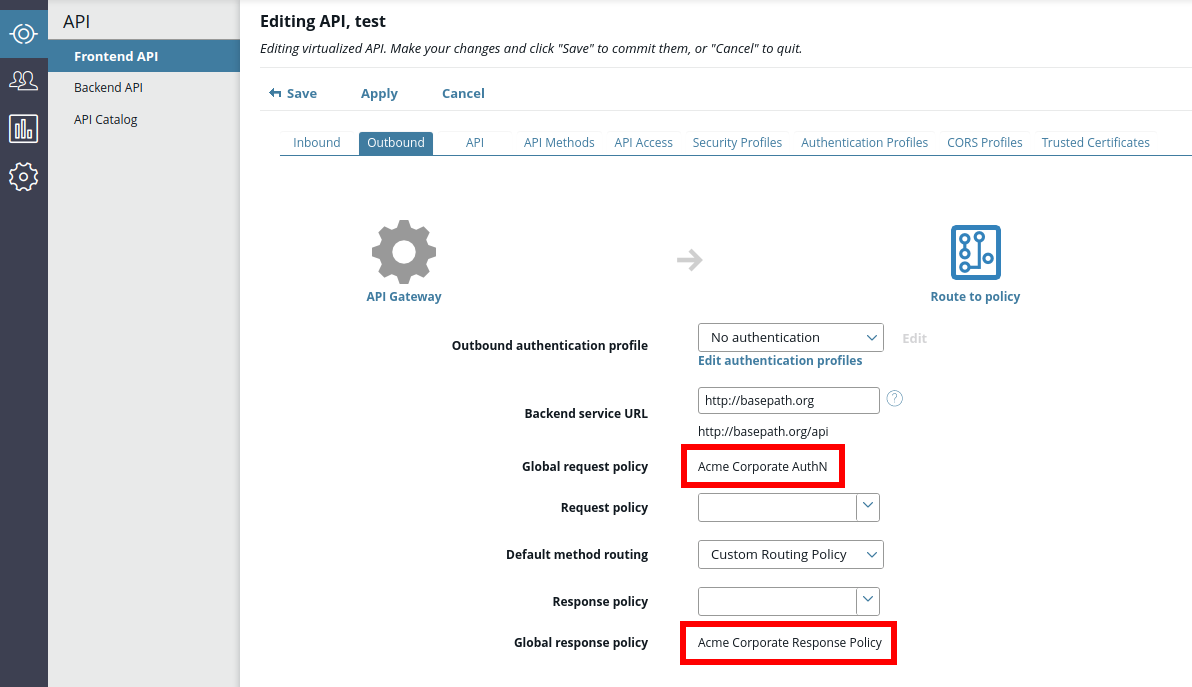
API transaction analysis in API Gateway Manager
When a global policy is selected in API Manager, it is also displayed for all API runtime invocations in the API Gateway Manager console in the Filter Execution Path on the Traffic page.
The following image shows the global request policy after an API call:
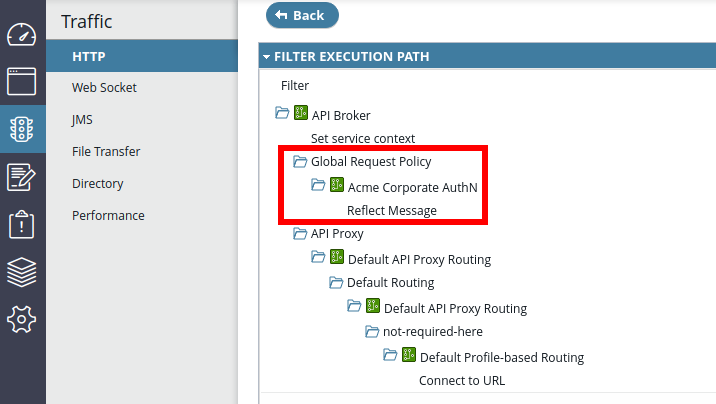
Export of API collections with global policies
Global policies configured in API Manager are not exported as part of the API collection. This is because global policies are part of the API Manager system settings only. When a global policy is selected, it is displayed as being executed on the Frontend API > Outbound > Advanced tab.
Note
When moving API collections to upstream environments (for example, from Test to Pre-production to Production), and global policies are configured in Policy Studio, the global policies must be enabled in API Manager and must be available in those upstream environments. These steps must be performed out-of-band of any export or import of API collections.Add API Manager fault handler policies
Use API Manager to add a fault handler policy at the global, API, and API method level. The configured fault handler is then executed when an error or exception occurs during the API Manager runtime API invocation.
You can enable fault handler policies in API Manager as follows:
- Policy developers can configure policies in Policy Studio as API Manager fault handler policies, which are then displayed in API Manager.
- API administrators can enable and configure a global API Manager fault handler policy that is executed when an error occurs for all virtualized API methods.
- API developers can configure specific fault handler policies at the front-end API and method levels, which override any other fault handler policies that are configured.
API Manager fault handler policies are optional features that you can configure depending on your requirements.
API Manager fault handler template
API Manager provides a fault handler template, which acts as the default fault handler for an API Manager instance. This simple fault handler policy consists of an API Gateway Generic Error filter:
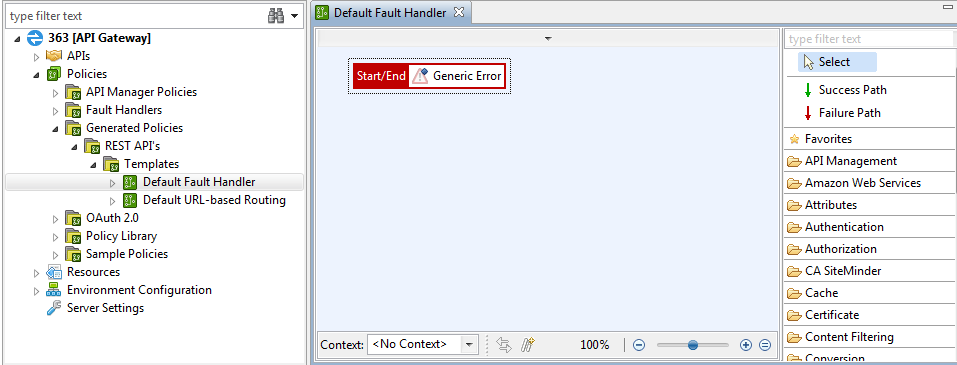
When API Manager fault handlers are executed
API Manager fault handlers are switched off in a vanilla API Manager installation. However, the API Manager default fault handler policy is configured and selected. This maintains existing functionality post-installation or upgrade, and also makes the transition to employing API Manager fault handlers a simple toggle of a button.
You can configure fault handlers at the following levels:
| Fault Handler | Description |
|---|---|
| Global | System global fault handler, configured using Policy Studio. This is existing functionality (pre-version 7.6.2) for all API Manager instances. |
| API Manager default | Configured for a specific API Manager instance by the API administrator. This fault handler acts as the default for all virtualized APIs, and overrides any fault handler configured at the global level. |
| API | Configured for a specific front-end API (in the Outbound > Advanced view). This fault handler overrides any fault handler configured at the API Manager default or global levels. |
| API method | Configured for a specific front-end API as a per-method override (in the Outbound > Advanced view). This fault handler overrides any fault handler configured at the API, API Manager instance, or global level. |
Configure API Manager fault handler policies in Policy Studio
You must first configure API Manager fault handler policies in Policy Studio before you can apply them in API Manager at the API Manager default, API, or API method levels.
Configure fault handler policies
To configure API Manager fault handler policies, perform the following steps:
- In the Policy Studio tree, select Server Settings > API Manager > Fault Handler Policies.
- Click Add, and select policies in the dialog. The API Manager Default Fault Handler policy is configured by default.
- Click Save at the bottom right.
- Click the Deploy button at the right of the toolbar to deploy the configuration to the API Gateway.
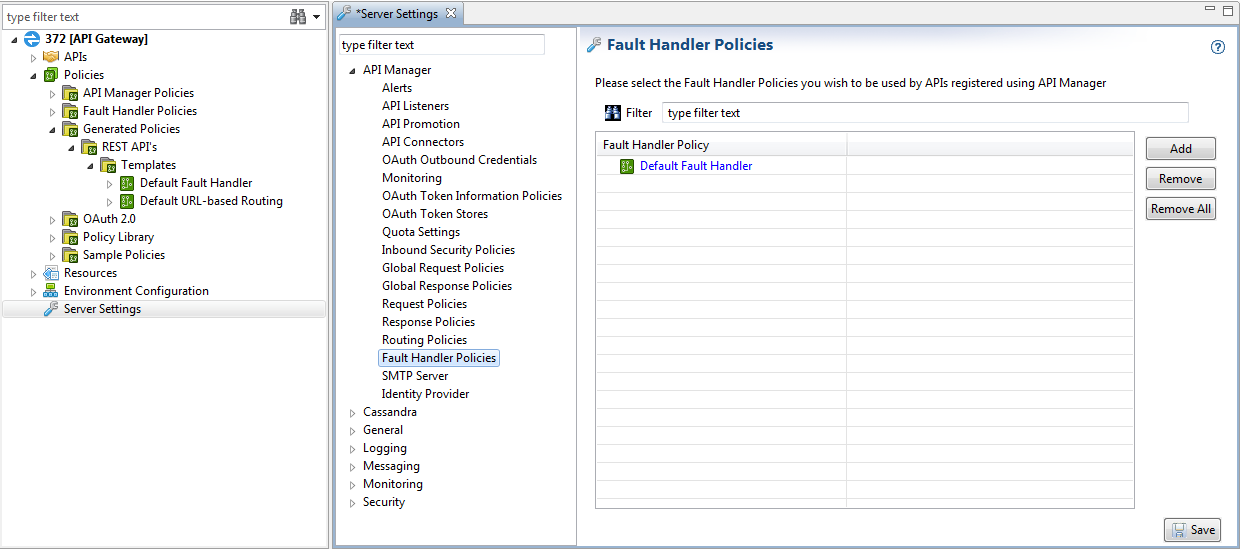
Enable fault handlers and select a global fault handler in API Manager
When API Manager fault handler policies are configured in Policy Studio, the API administrator can enable this feature and select a global fault handler from the available policies in on the Settings > API Manager settings page.
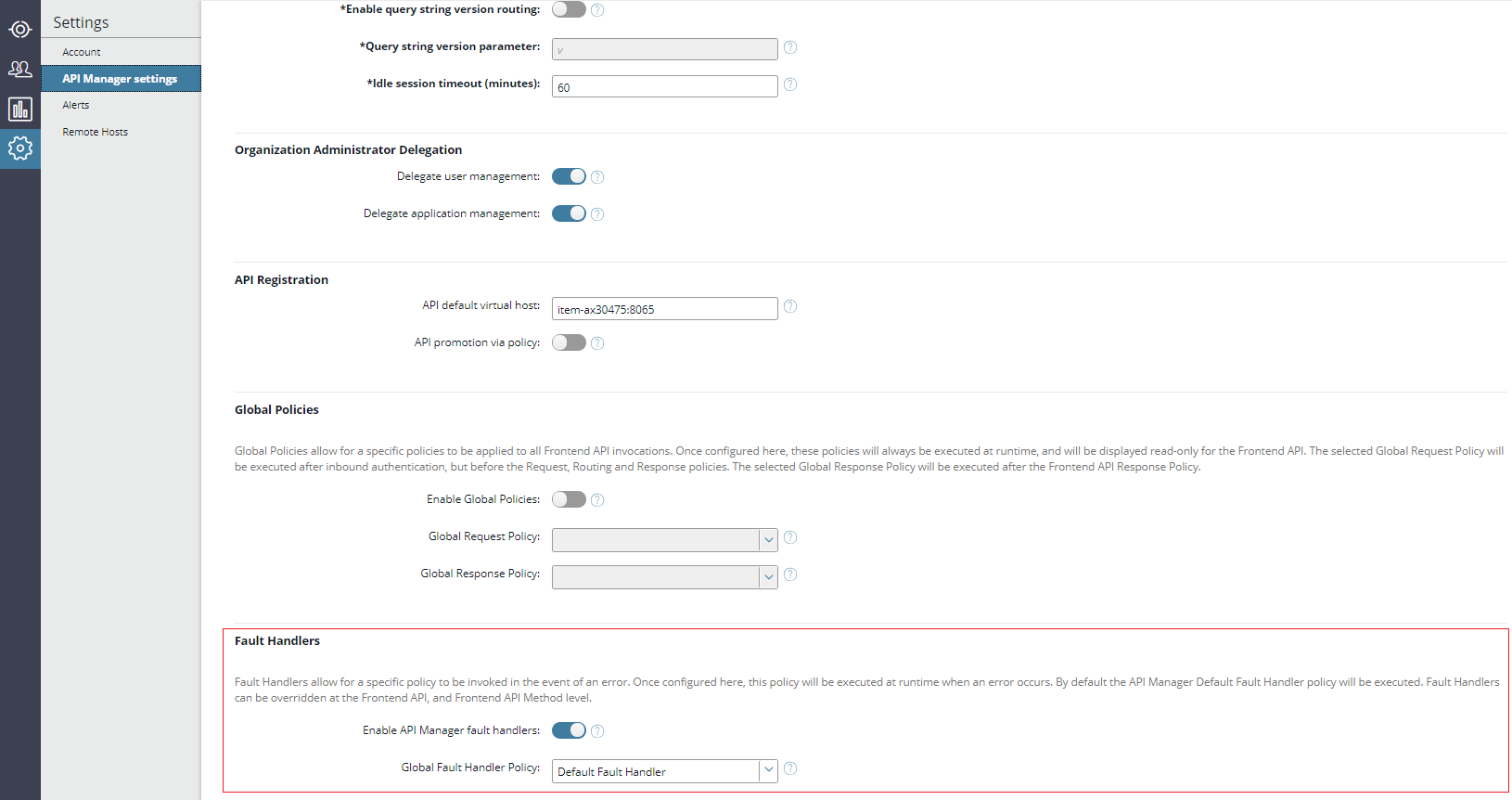
To enable fault handlers and select a global API Manager fault handler policy, perform the following steps:
- In API Manager, under Settings > API Manager settings > Fault Handlers, select Enable API Manager fault handlers. This setting is switched off by default.
- Select a policy from the Global Fault Handler Policy list. This setting defaults to the Default Fault Handler policy.
Select API and API method fault handler policies in API Manager
When API Manager fault handler policies have been enabled by the API administrator, you can then also select API and API method-level fault handler policies for a front-end API.
Select an API-level fault handler policy
To select a fault handler policy for a specific front-end API, perform the following steps:
- In API Manager, select Frontend API > Outbound, and click Advanced at the top right.
- Select a policy for this front-end API from the Fault Handler Policy list.
- Click Save at the top left.
Select an API method-level fault handler policy
To select a fault handler policy for a specific front-end API method, perform the following steps:
- In API Manager, select Frontend API > Outbound, and click Advanced at the top right.
- Under PER-METHOD OVERRIDE, click the plus sign (+) to add an API method.
- Select a policy for this front-end API method from the FAULT HANDLER POLICY list.
- Click Save at the top left.
Tips and tricks
-
When editing a front-end API, to enable fault handlers, perform the following steps:
- Remain in edit mode on the front-end API.
- Navigate to the Settings > API Manager settings page.
- Switch on the Enable API Manager fault handlers setting.
- Navigate back to the front-end API (notice that the Apply button at the top left is now enabled).
- Click Apply so that API Manager is updated to reflect the system configuration change.
- You should now be able to select a fault handler for your front-end API.
-
To output a complete list of attributes available to the fault handler, add a Trace filter to your fault handler policy. Not all attributes are available for every API invocation, depending whether authentication is performed, the error that occurs, where the error originates, and so on.
Order of precedence of fault handlers
-
When you have switched on the fault handler feature, because the Default Fault Handler policy is pre-selected in API Manager, there is no need to select the same fault handler at the API level. If an error occurs, the Default Fault Handler is invoked.
-
If a Global Fault Handler Policy is configured in API Manager, and the API Manager fault handler feature is switched off, this policy is executed when an error or exception occurs in the API Manager policy flow. This does not apply when a successful connection is made to the back-end, and the server responds with a non-
2xxresponse. In this case, no exception handler is invoked. -
If API Manager fault handlers are enabled and an API Gateway global fault handler policy is configured, and then an exception occurs in the API Manager fault handler (global, API, or method-level), both the API Manager fault handler and API Gateway global fault handler are executed. The API Manager fault handler is executed first, followed by the API Gateway global fault handler.
-
If a local fault handler is configured for any custom API Manager policies (global request, request, routing, response, or global response), and an exception occurs in any of these policies, the local fault handler is executed for the exception. The flow then continues as if the exception never occurred, which may not be the desired behavior.
A workaround is to define a policy that acts as the fault handler (using an API Gateway Policy Shortcut filter), and for that policy to return
false. This ensures that the API Manager fault handler (global, API, or method-level) also gets executed.
Export of API collections with fault handler policies
Fault handler policies configured in API Manager are not exported as part of the API collection in the same way that custom request, routing, or response policies are not exported. The exported API collection only contains references to any configured fault handler policies. The policies themselves remain in the API Manager configuration.
Note
When moving API collections to upstream environments (for example, from Test to Pre-production to Production), and fault handler policies are configured in Policy Studio, the fault handler policies must be deployed before the API collection is imported.Fault handler generated errors
The following tables describe the circumstances under which fault handlers configured in API Manager are executed.
API Manager generated errors
An api.error.reason message attribute is added to the message whiteboard prior to the fault handler policy being executed, so that users can make decisions on the reasons of the error being processed. This attribute is in java.lang.String format.
The following errors are generated by the API Manager default fault handler:
| Error | Description |
|---|---|
ApiShunt.noApiMatched |
The inbound request does not match any configured virtualized APIs. |
ApiShunt.noMethodMatched |
The inbound request does not match any configured virtualized API method. In this case, a match is found at the API level. |
ApiShunt.noMethodAllowed |
The inbound method does not match any configured virtualized API method. In this case, the API and method paths both match, but there is no match on the verb. |
ApiShunt.allAuthNDevicesFailed |
Inbound authentication has failed. |
ApiShunt.applicationNotAuthorized |
The client application does not have access to the API being invoked. Inbound security is set to something other than pass through. The application credentials are sent with the request. |
ApiShunt.invokableMethodParamFailure |
API method parameter validation has failed. |
ApiShunt.tooManyRequests |
The configured quota has been exceeded. |
ApiShunt.originNotAllowed |
The JavaScript Origin specified for the application credentials does not match the supplied Origin. |
ApiShunt.invokableMethodFailure |
Content-type mapping has failed. Content-type mapping is disabled for APIs registered in API Manager. |
ApiShunt.noAuthNDevicesConfigured |
No inbound authentication has been configured for the API. |
ApiShunt.unexpectedAPI |
The configured resourcePath does not match the resource path presented in the request. |
Policy generated errors
The following errors are generated by any custom policies configure in API Manager:
| Error | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom request policy fails | Custom request policy returns false. |
| Custom request policy aborts | Custom request policy throws an exception. |
| Custom routing policy fails | Custom routing policy returns false. |
| Custom routing policy aborts | Custom routing policy throws an exception. |
| Custom response policy fails | Custom response policy returns false. The response code and message may need to be updated because the back-end may have returned 200 OK, depending on your requirements. |
| Custom response policy aborts | Custom response policy throws an exception. The response code and message may need to be updated because the back-end may have returned 200 OK, depending on your requirements. |
| Global request policy fails | Global request policy returns false. |
| Global request policy aborts | Global request policy throws an exception. |
| Global response policy fails | Global response policy returns False. The response code and message may need to be updated because the back-end may have returned 200 OK, depending on requirements. |
| Global response policy aborts | Global response policy throws an exception. The response code and message may need to be updated because the back-end may have returned 200 OK, depending on your requirements. |
Back-end generated errors
The following errors are generated by the back-end API service.
| Error | Description |
|---|---|
3xx |
Back-end service has responded with a redirect. Technically, redirects are not errors, but some users may wish to perform additional processing of the response in the fault handler policy. If you have enabled the fault handler feature, but do not consider 3xx responses as errors, you must add specific logic to your fault handler policies. |
4xx |
Back-end service has responded with a client error. |
5xx |
Back-end service has responded with a server error. |
Fault handler message attributes
An api.error.source message attribute is added to the message whiteboard prior to the fault handler policy being executed, so that users can make decisions on the source of the error being processed. This attribute is in java.lang.String format.
The possible values for this attribute are:
| Error | Description |
|---|---|
apiManager |
The error was generated by the API Manager runtime. |
backend |
The error was generated by the back-end service by returning a status code other than 2xx. |